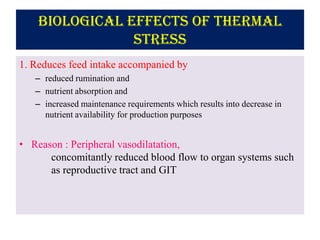
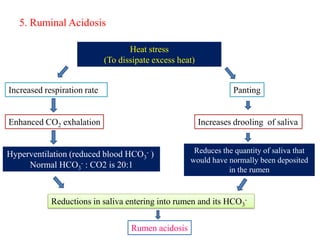
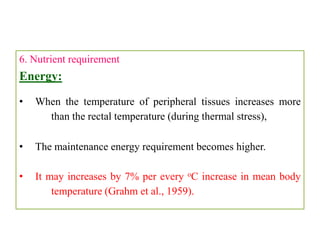
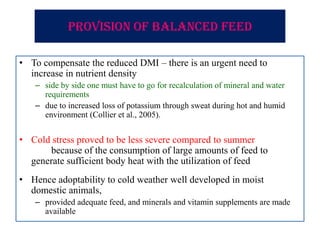
Thermal stress from extreme hot or cold temperatures can negatively impact livestock. This document discusses the biological effects of thermal stress and some nutritional strategies to help ameliorate it. Thermal stress can reduce feed intake, nutrient absorption, growth rate and alter hormone levels. It also increases maintenance energy requirements. Some nutritional strategies recommended include providing balanced diets with increased nutrient density; managing feeding times and intervals; ensuring access to clean water; optimizing protein and fat levels; and supplementing key minerals like sodium and potassium above standard recommendations.