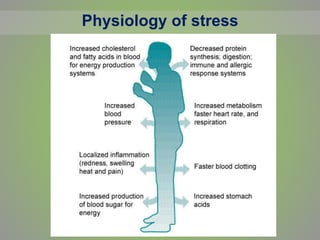
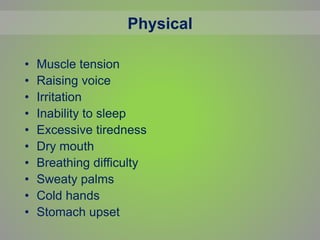
This document discusses stress, its causes and symptoms, and how yoga can be used for stress management. It defines stress as the physical and emotional strain caused by pressure from external demands. Stress can be positive or negative and has physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms. The document outlines the physiology of stress and how it impacts the body. It then explains how various yoga practices like asanas, pranayama, and meditation can help reduce stress by stimulating the vagus nerve and parasympathetic nervous system to lower heart rate, blood pressure, and stress hormones. Practicing yoga can provide physical, mental and biochemical benefits to manage stress.