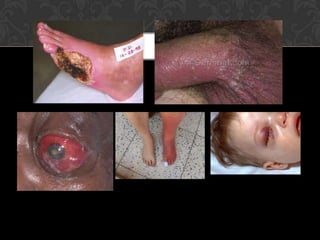
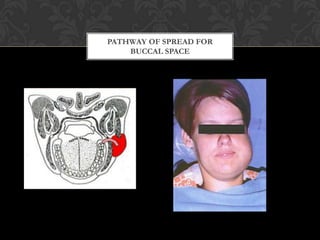
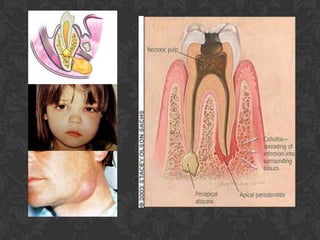
Streptococcus bacteria can cause various infections in humans including skin infections, strep throat, sinus infections, and pneumonia. They appear in chains and are found on the skin, in the oral cavity, and respiratory tract. Cellulitis is a localized skin infection caused by streptococcus bacteria invading through a cut or scrape, causing redness, swelling, and pain in the deepest skin layers, especially on the face or legs. Signs include fever, chills, and general illness. While antibiotics are usually effective, abscesses also require drainage to resolve regardless of the specific bacteria.