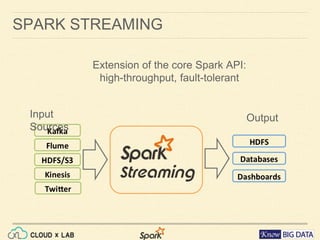
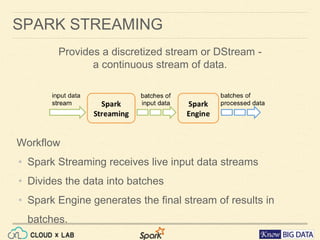
This document provides an agenda for a session on Apache Spark Streaming and Kafka integration. It includes an introduction to Spark Streaming, working with DStreams and RDDs, an example of word count streaming, and steps for integrating Spark Streaming with Kafka including creating topics and producers. The session will also include a hands-on demo of streaming word count from Kafka using CloudxLab.






![SPARK STREAMING - EXAMPLE
Problem: do the word count every second.
Step 1:
Create a connection to the service
from pyspark import SparkContext
from pyspark.streaming import StreamingContext
# Create a local StreamingContext with two working thread and
# batch interval of 1 second
sc = SparkContext("local[2]", "NetworkWordCount")
ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 1)
# Create a DStream that will connect to hostname:port,
# like localhost:9999
lines = ssc.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processingkafkastreamwithapachespark-160616055220/85/Stream-Processing-using-Apache-Spark-and-Apache-Kafka-10-320.jpg)









![Spark Streaming + Kafka Integration
Step 2:
Create the streaming objects
Problem: do the word count every second from kafka
sc = SparkContext(appName="KafkaWordCount")
ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 1)
#Read name of zk from arguments
zkQuorum, topic = sys.argv[1:]
#Listen to the topic
kvs = KafkaUtils.createStream(ssc, zkQuorum, "spark-
streaming-consumer", {topic: 1})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processingkafkastreamwithapachespark-160616055220/85/Stream-Processing-using-Apache-Spark-and-Apache-Kafka-20-320.jpg)
![Spark Streaming + Kafka Integration
Step 3:
Create the RDDs by Transformations & Actions
Problem: do the word count every second from kafka
#read lines from stream
lines = kvs.map(lambda x: x[1])
# Split lines into words, words to tuples, reduce
counts = lines.flatMap(lambda line: line.split(" "))
.map(lambda word: (word, 1))
.reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a+b)
#Do the print
counts.pprint()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processingkafkastreamwithapachespark-160616055220/85/Stream-Processing-using-Apache-Spark-and-Apache-Kafka-21-320.jpg)







