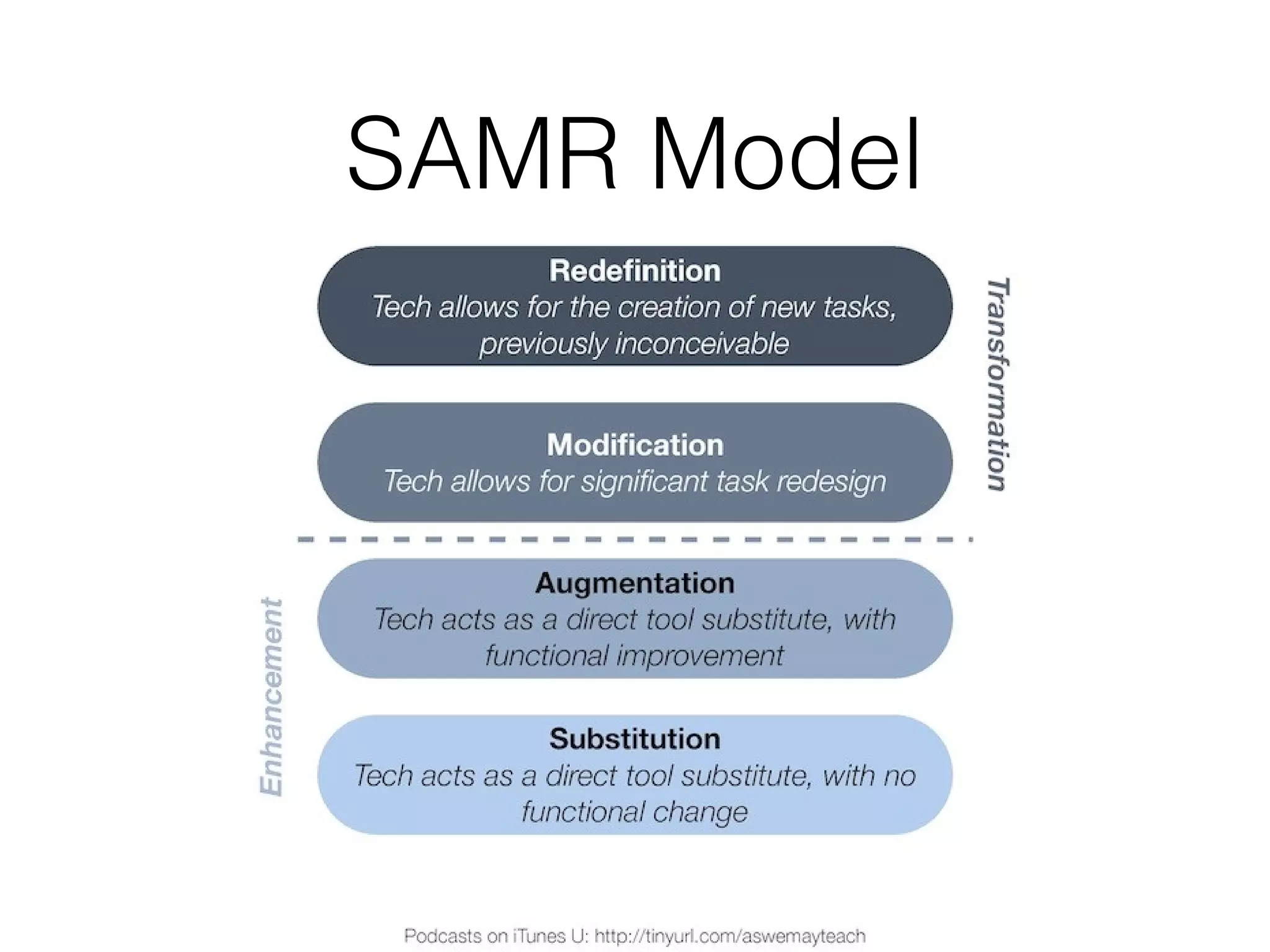
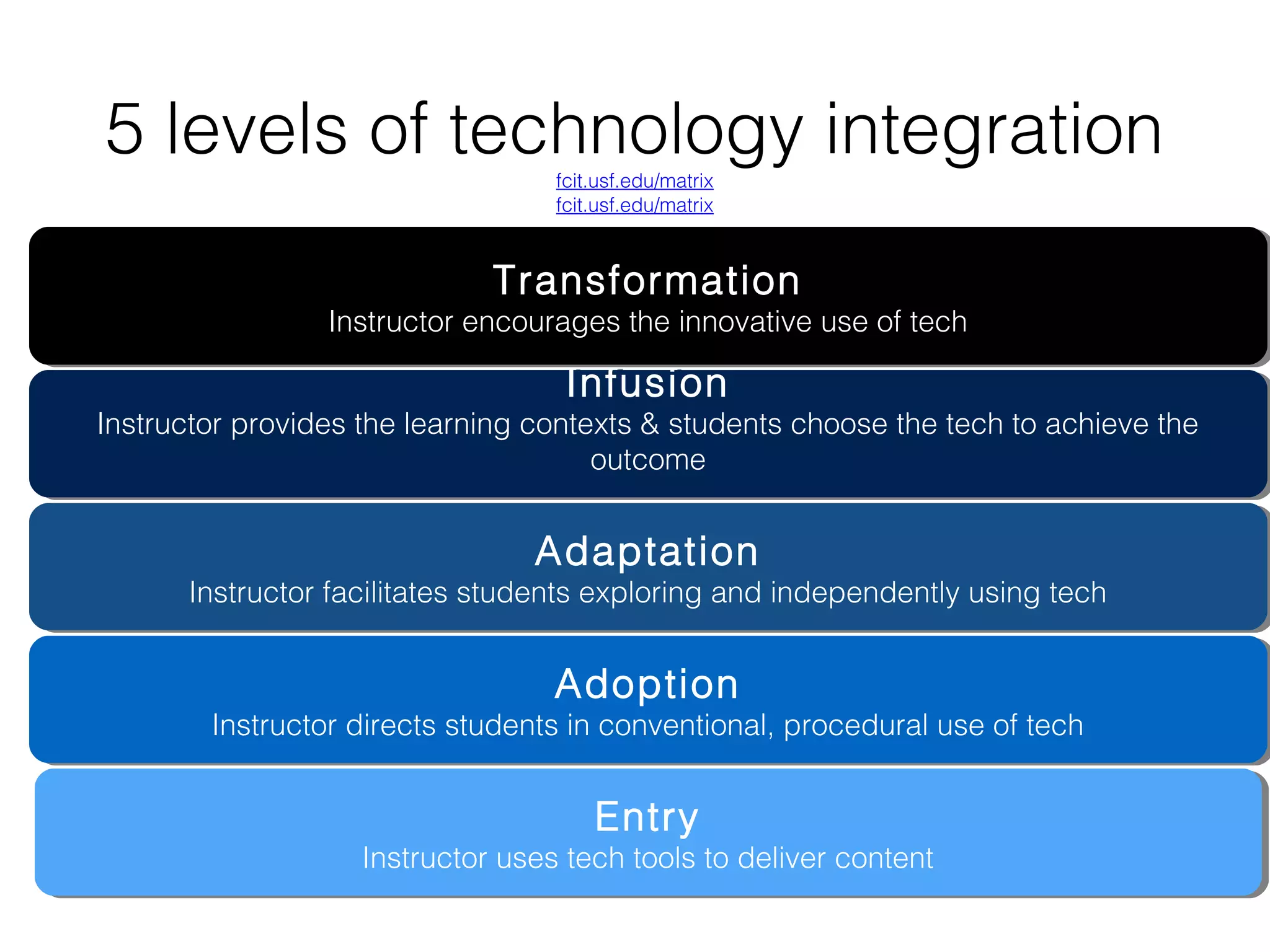
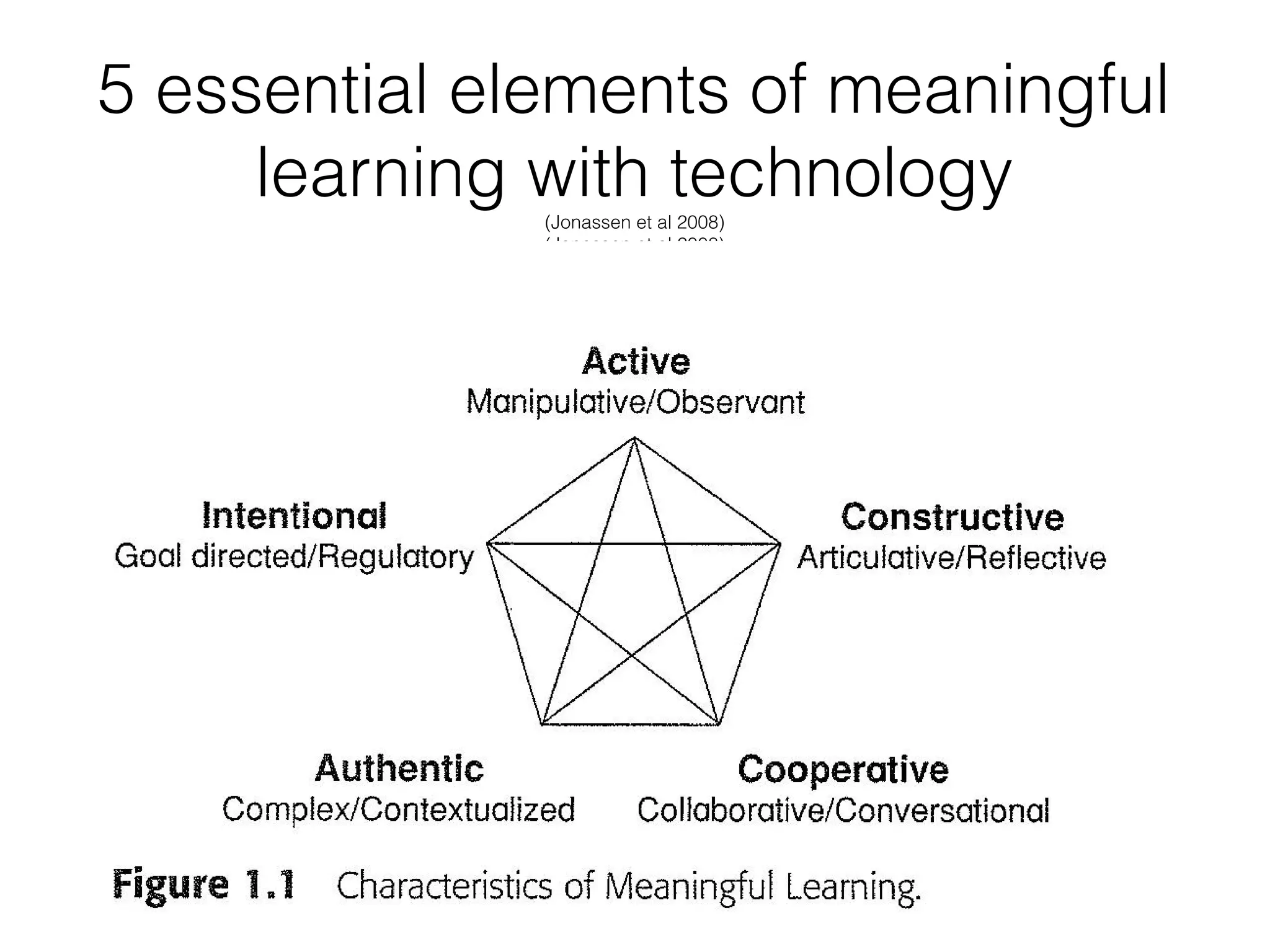
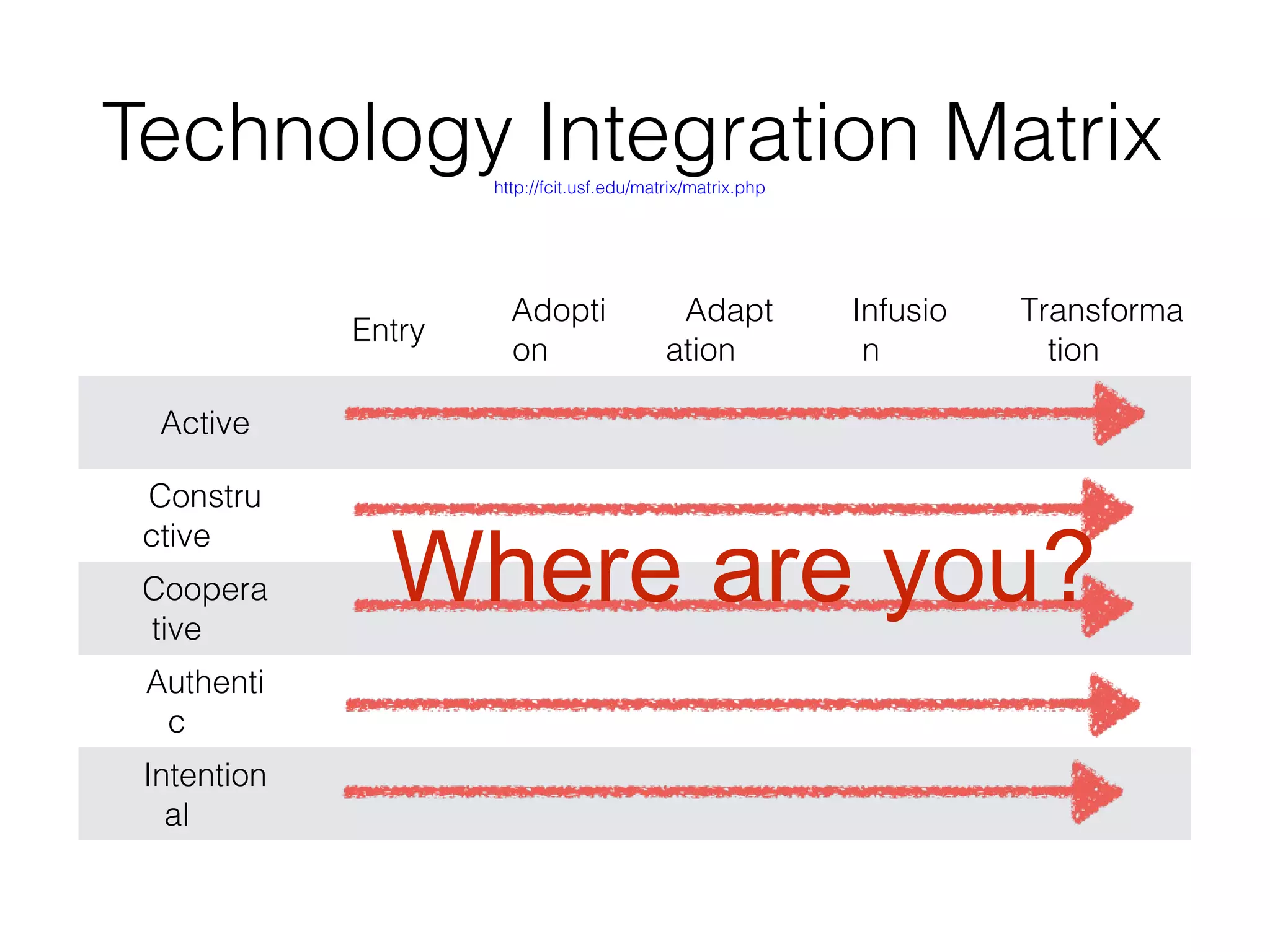
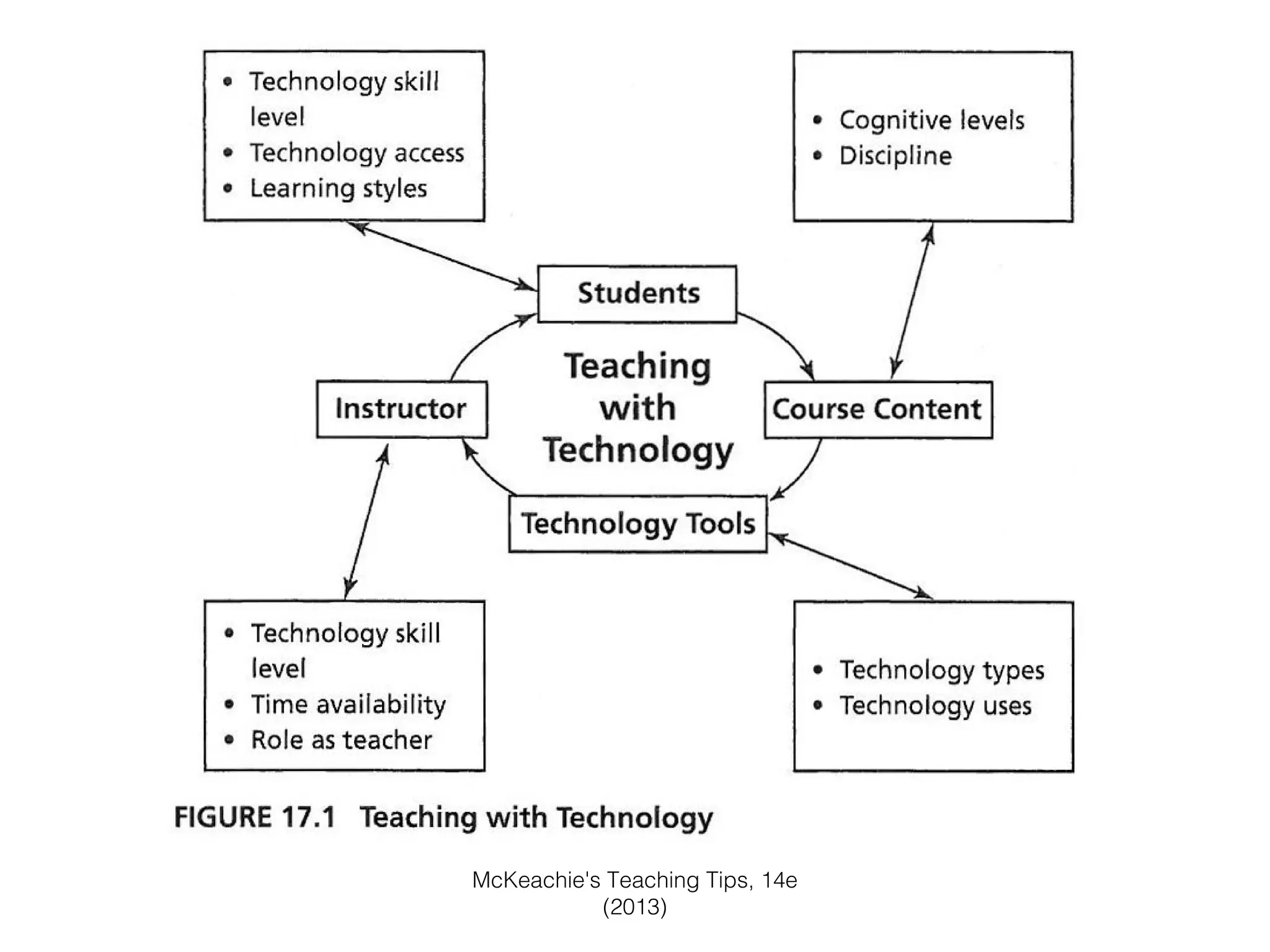
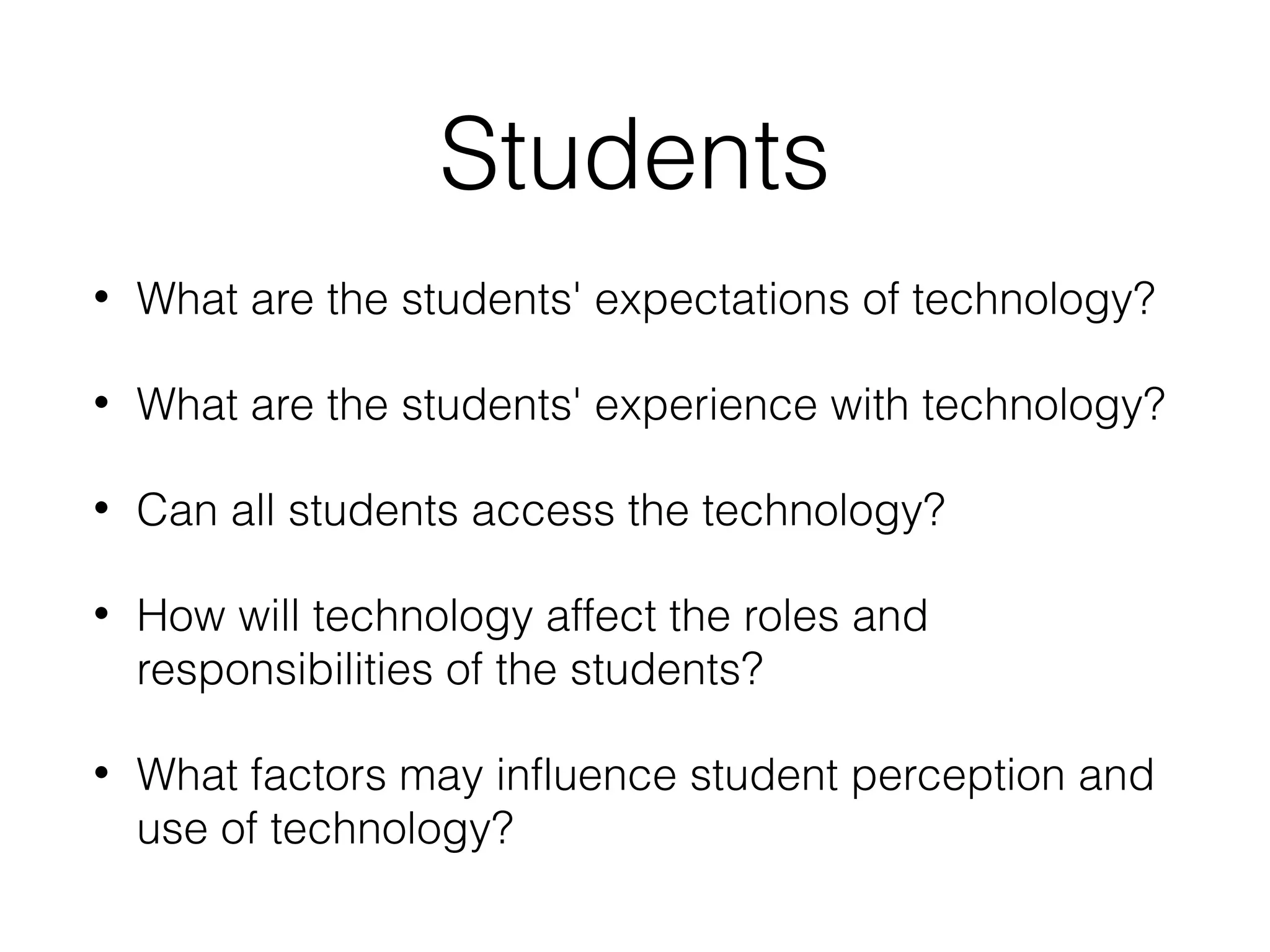
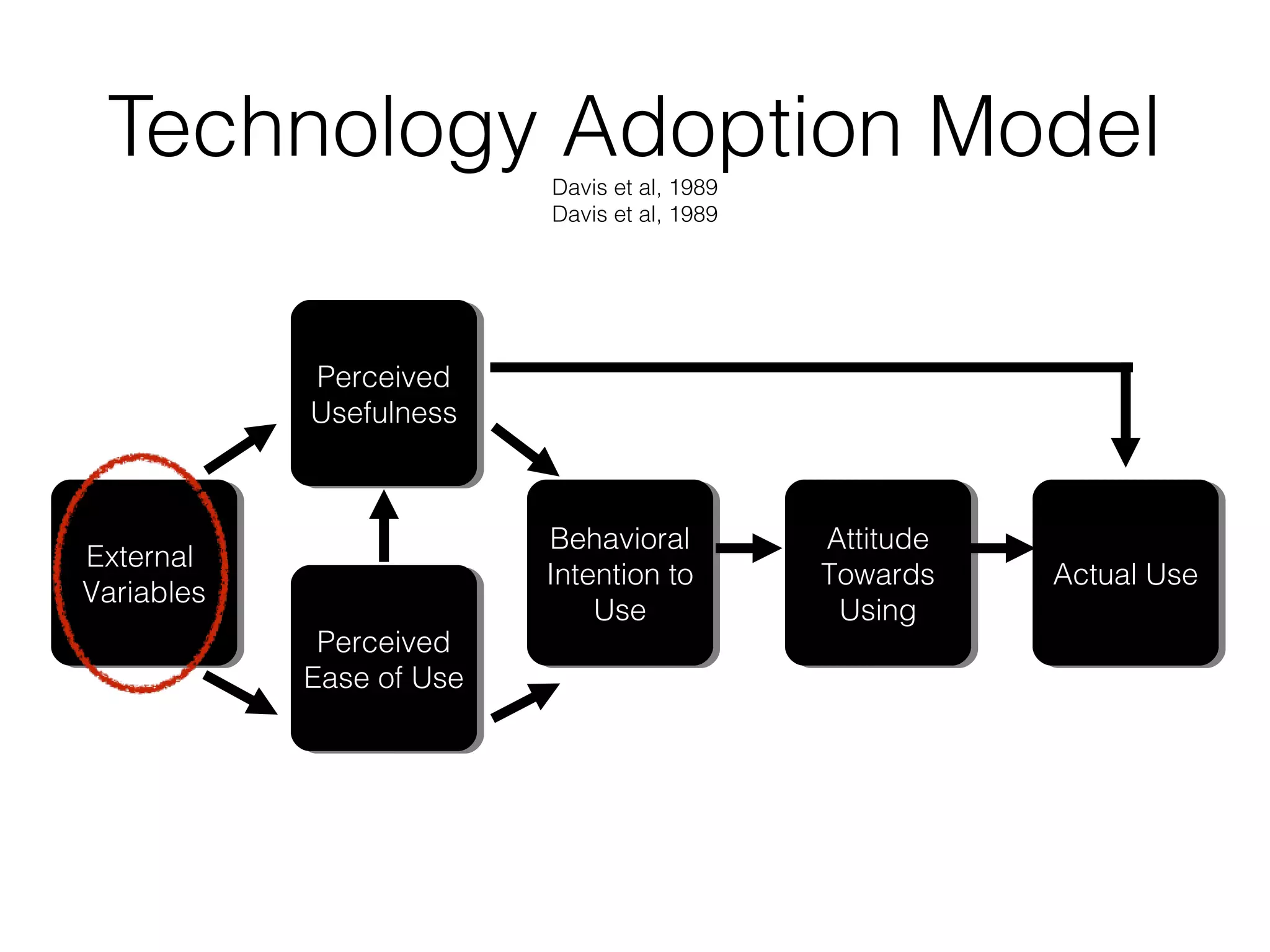
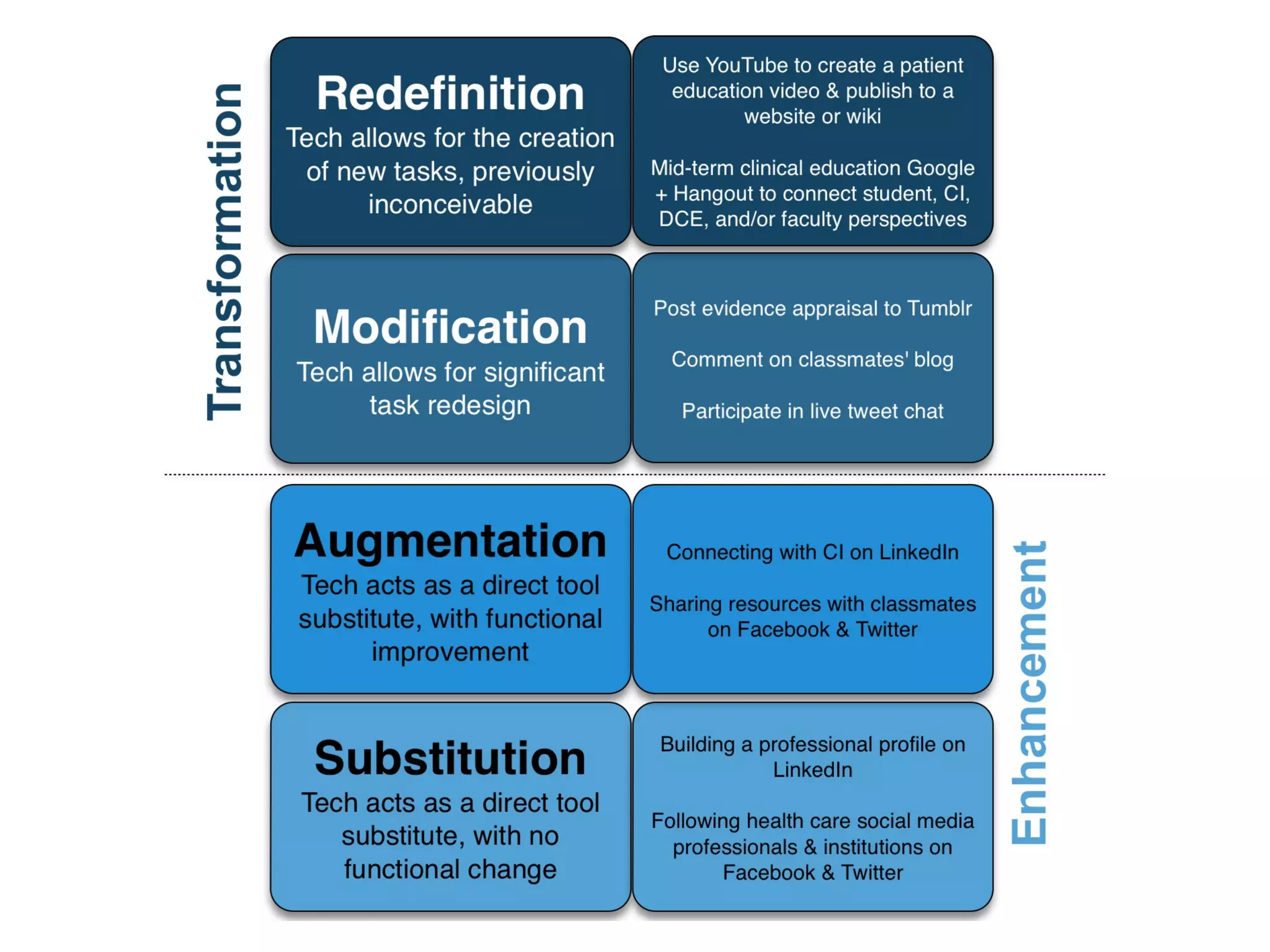
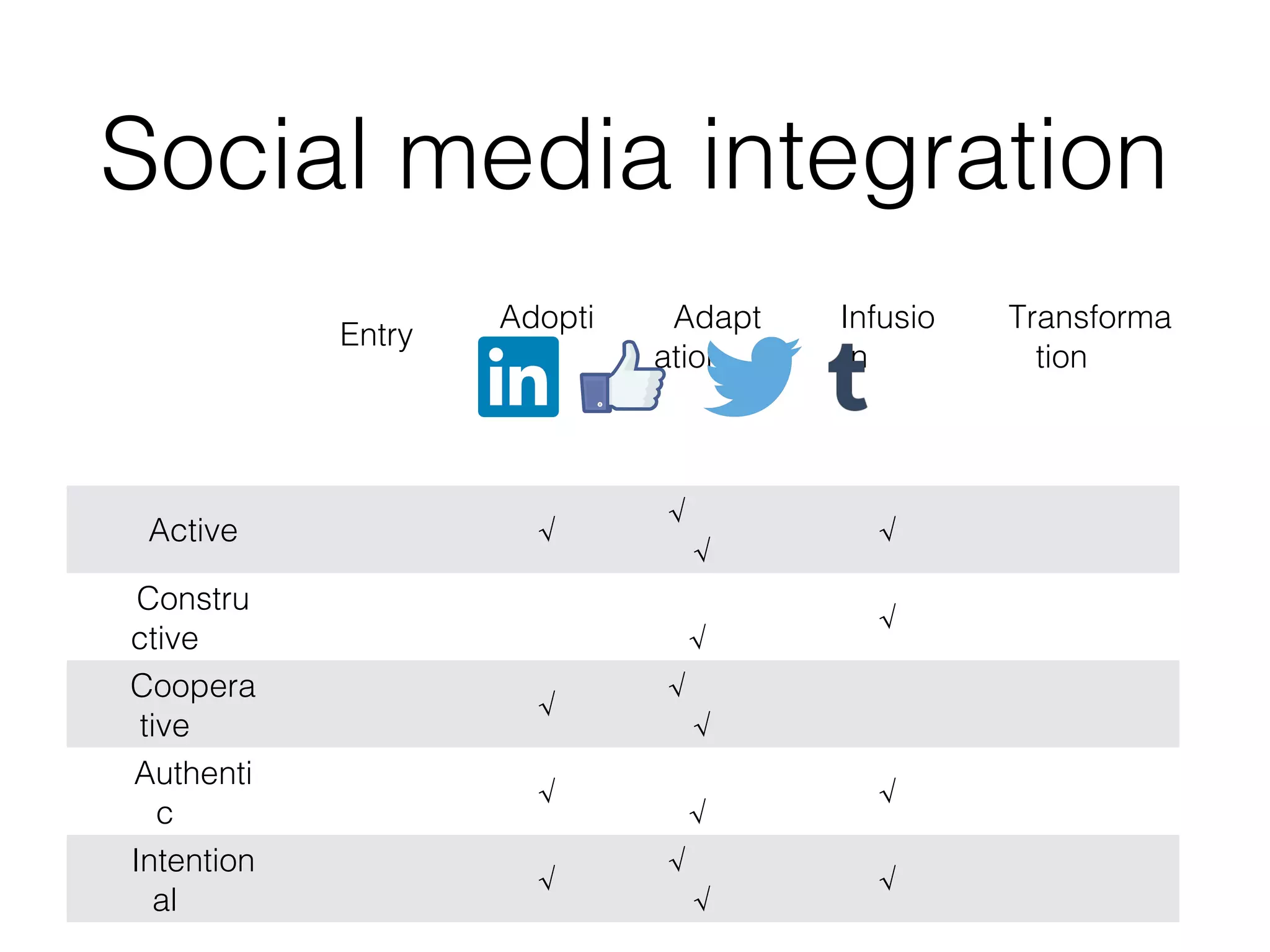
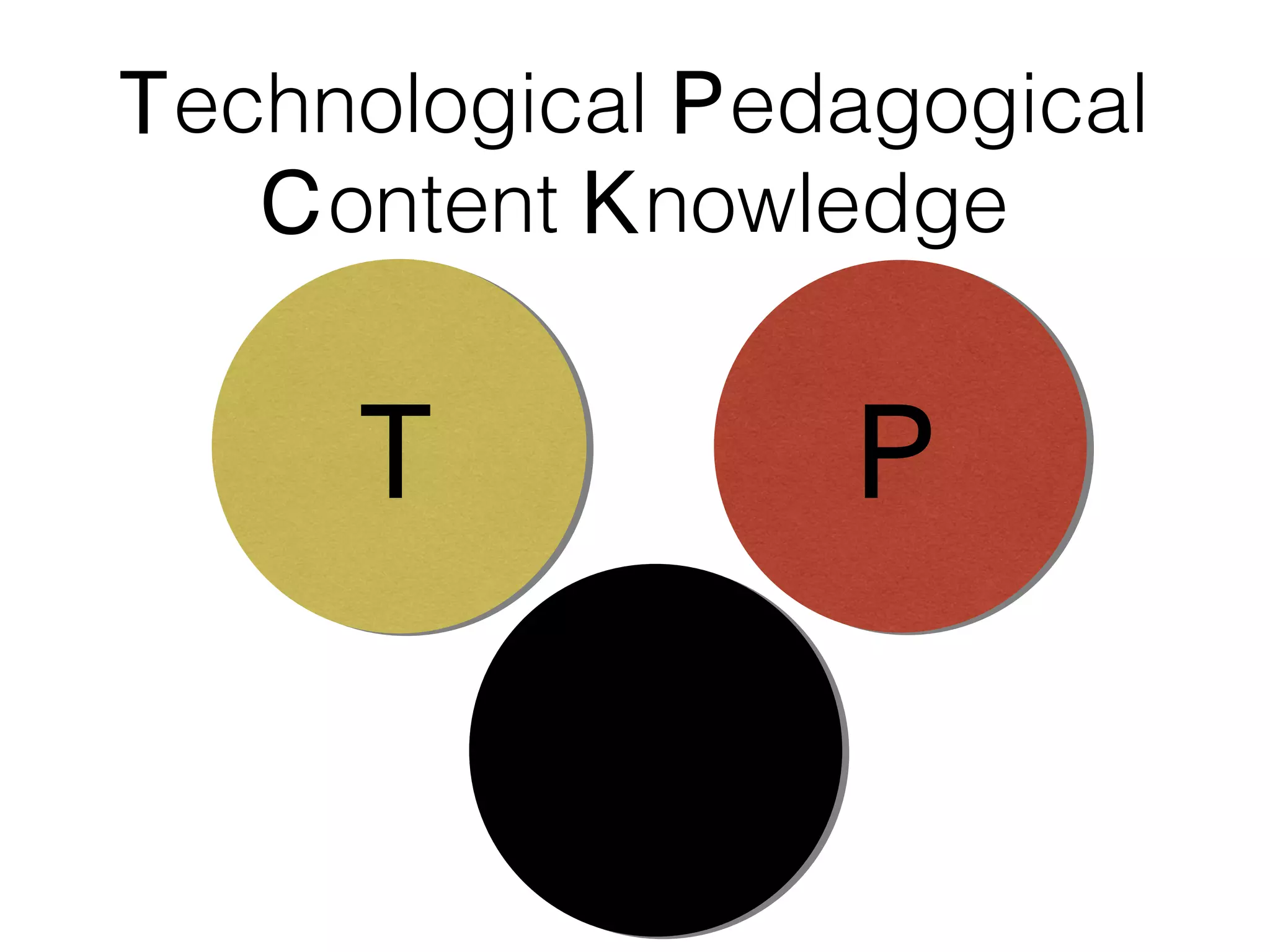
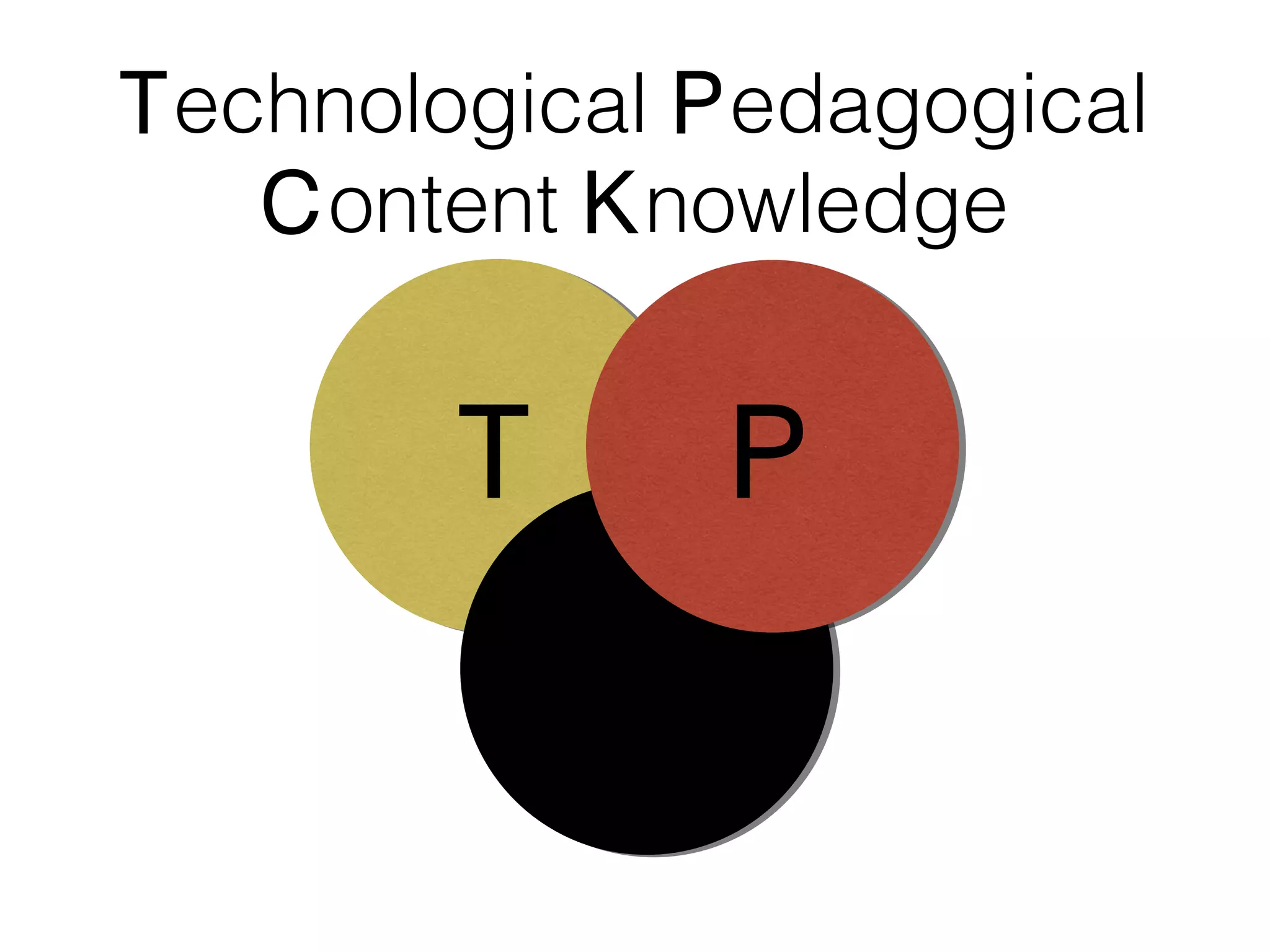
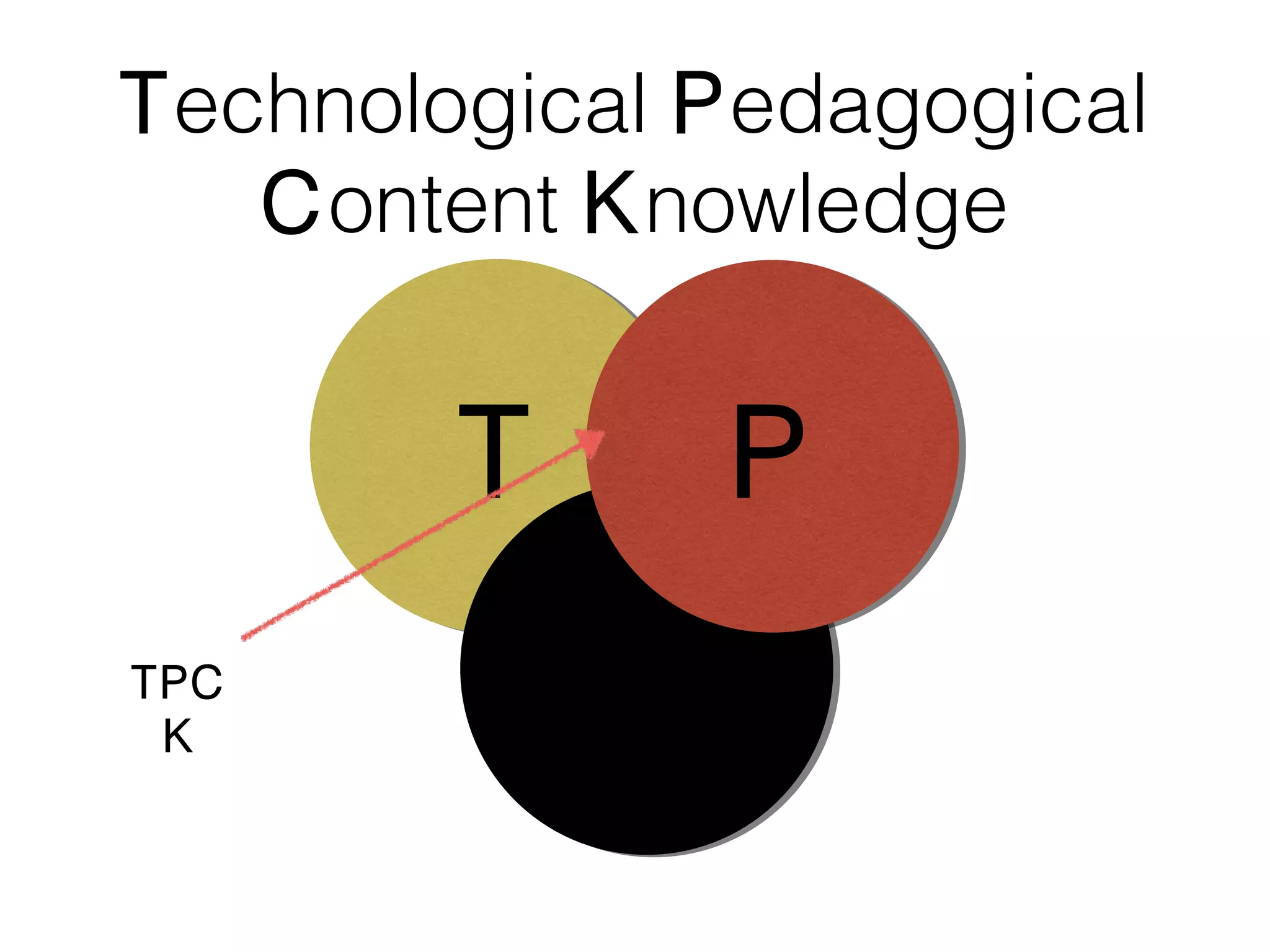
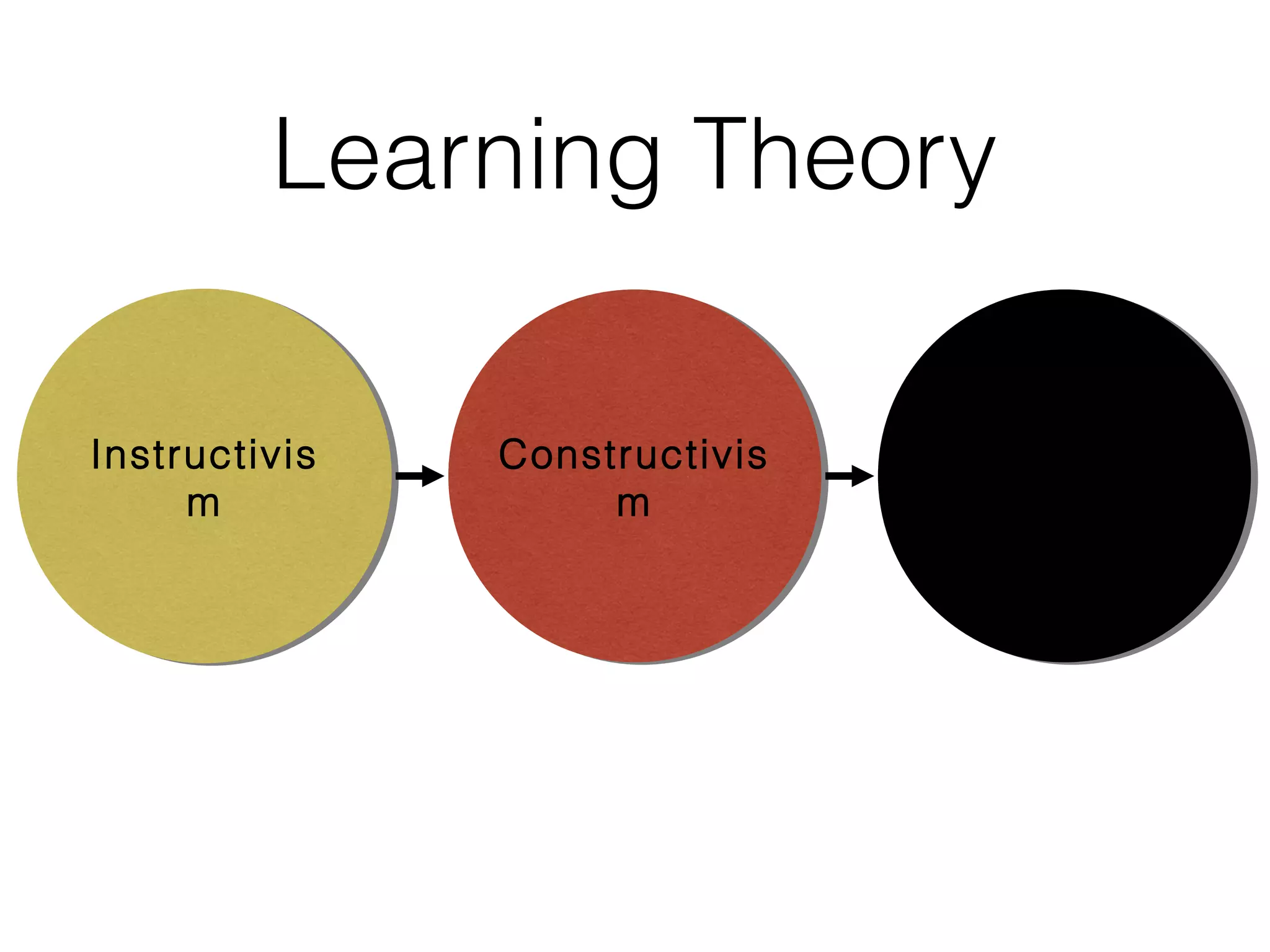
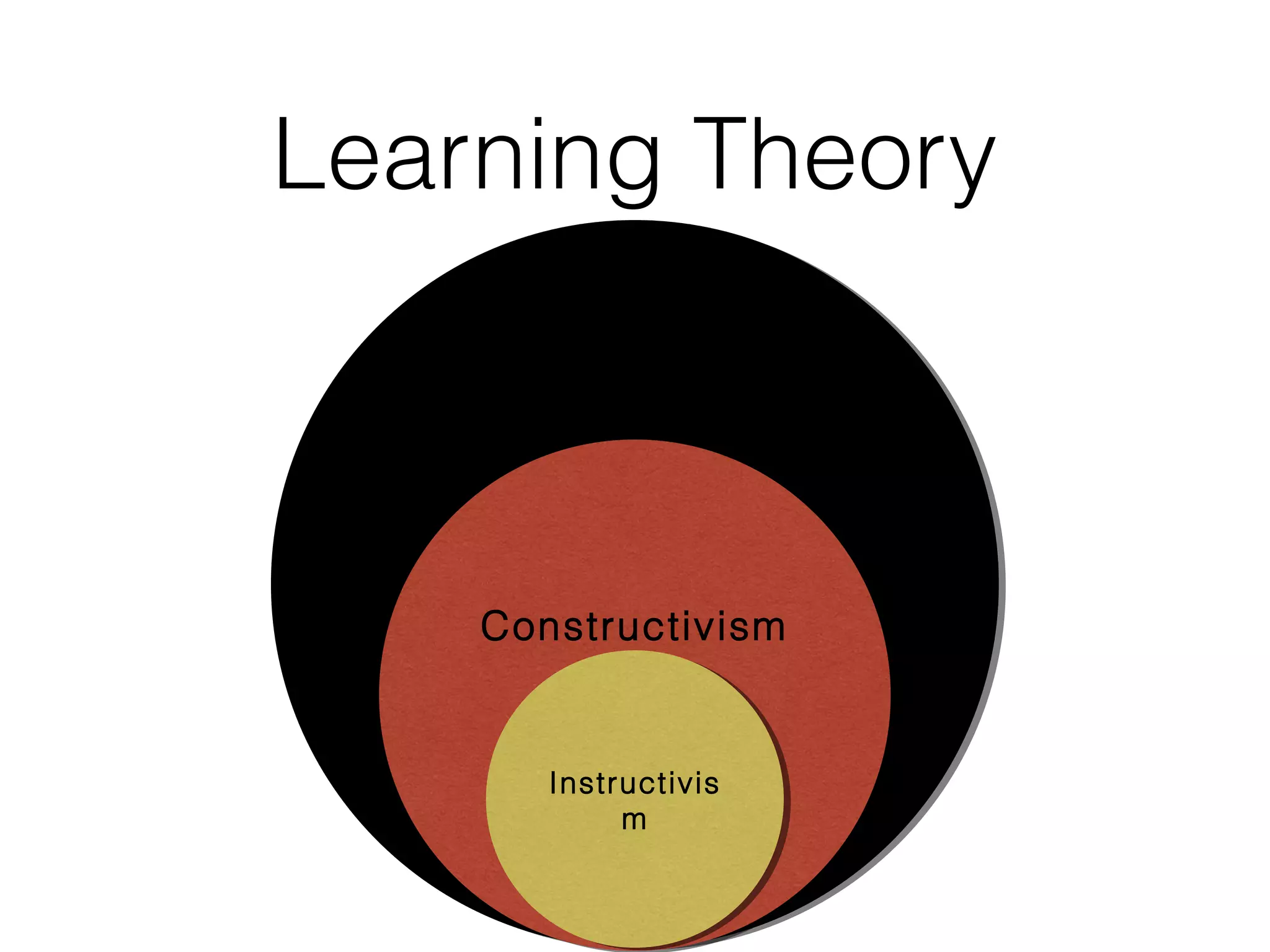
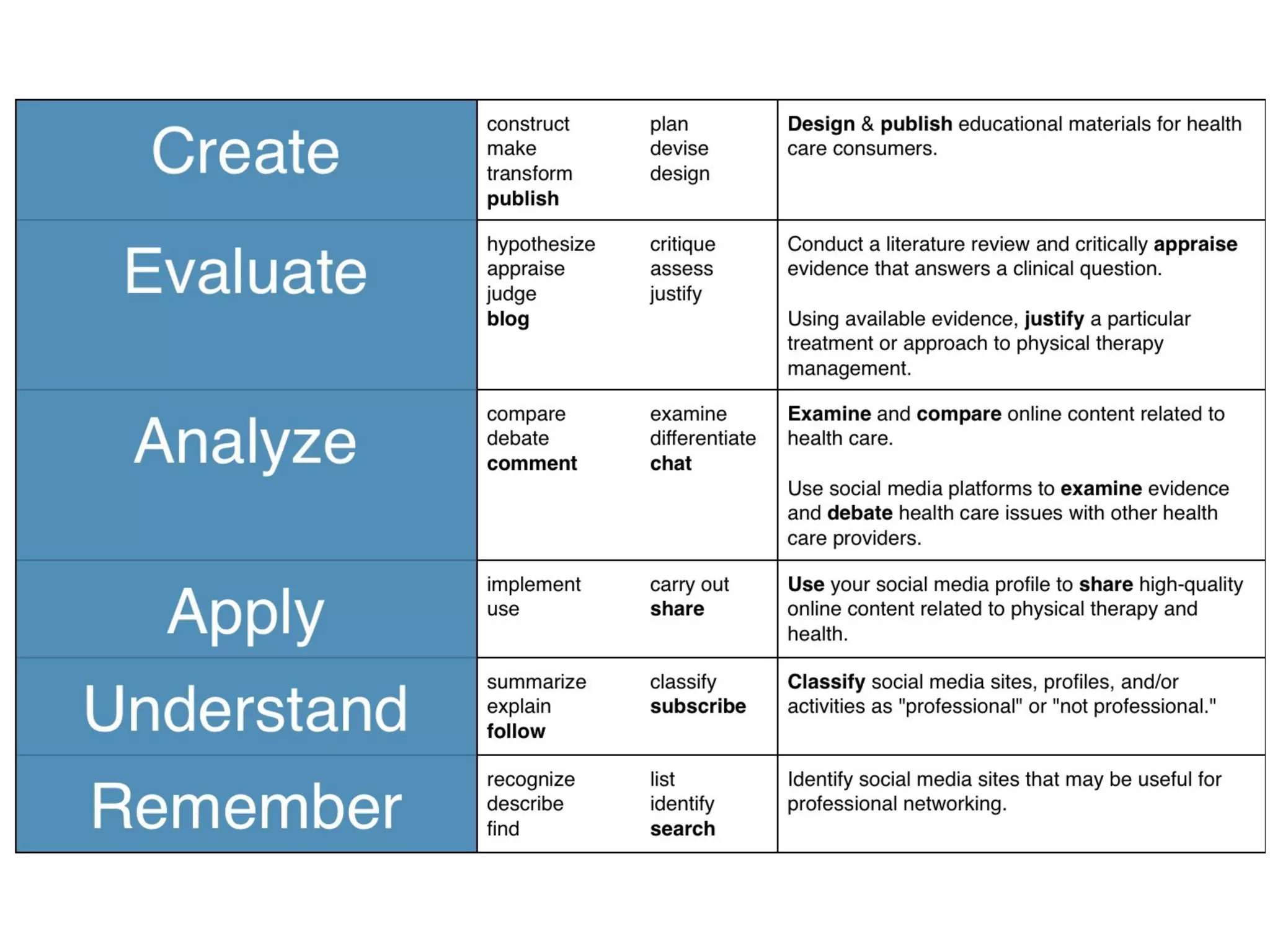
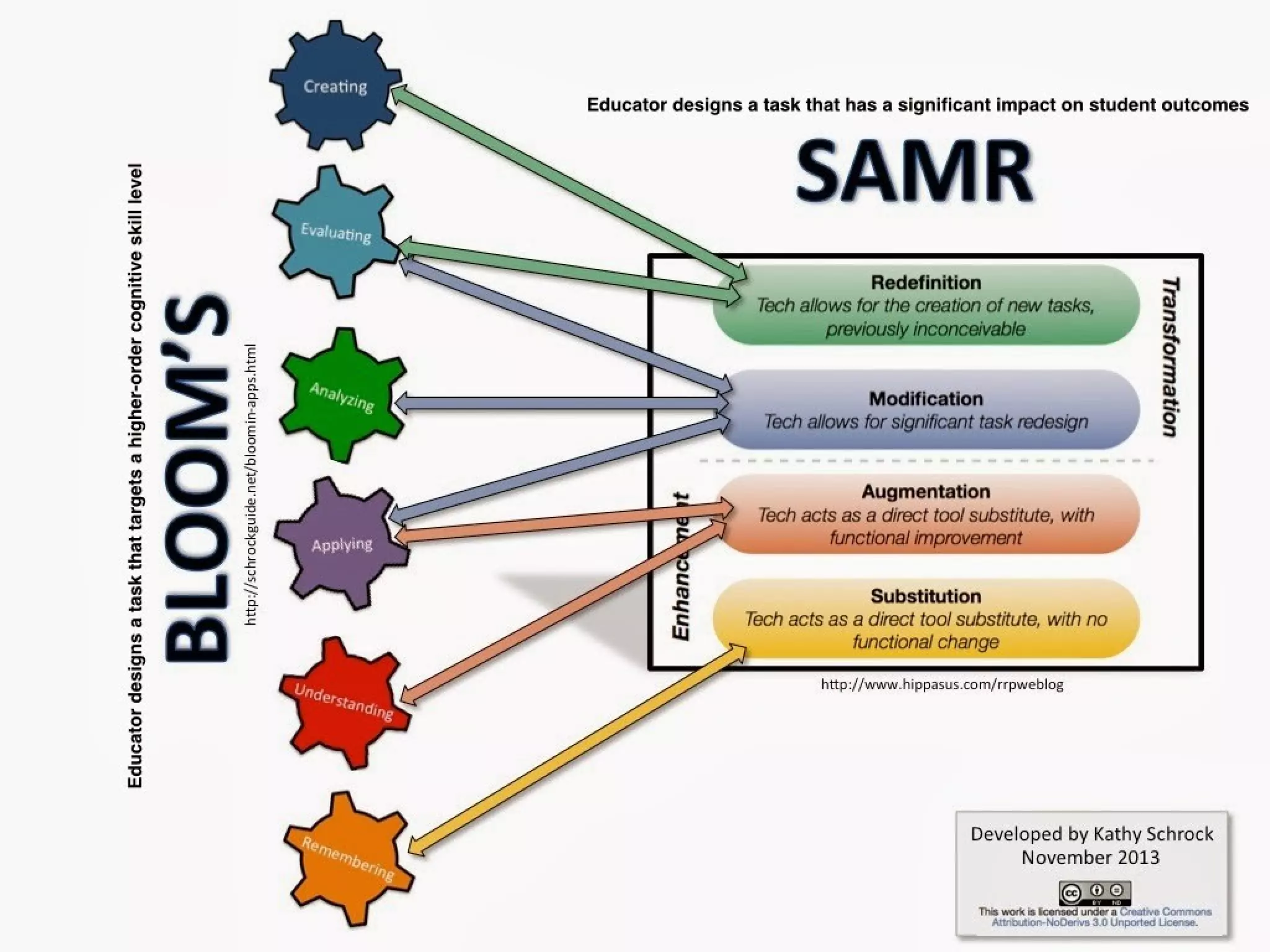
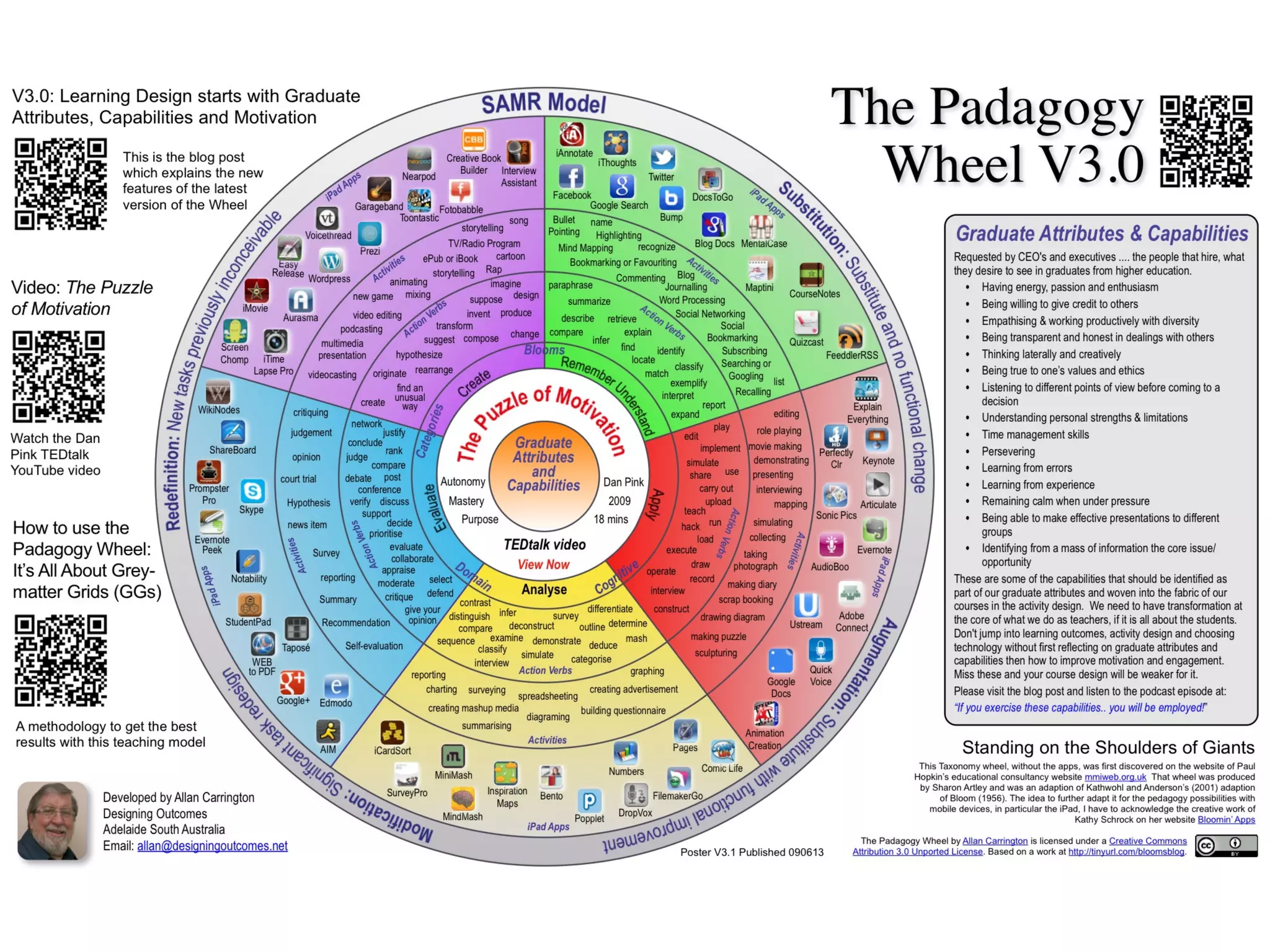
This document discusses various strategies for integrating instructional technology. It begins by distinguishing between using technology versus integrating it. Technology integration is planned and purposeful, supports learning objectives, and facilitates collaboration. The document then covers several models for conceptualizing levels of technology integration, including the SAMR model and the TPACK framework. It provides considerations for integrating technology based on content, students, instructors, institutions, and specific technologies. Overall, the document provides an overview of key strategies and frameworks for meaningfully integrating technology to support learning objectives.