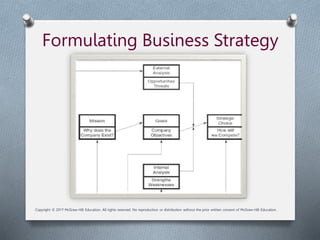
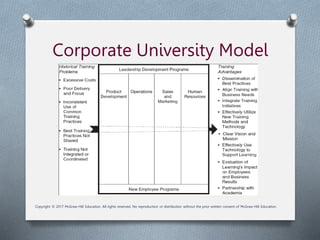
Chapter two discusses the strategic training objectives influenced by business strategy, emphasizing the alignment of training with company goals and staffing plans. It outlines a four-step strategic training process, including identifying business strategy, determining initiatives, translating them into activities, and evaluating success through metrics. Additionally, it covers the importance of top management support, cross-training, and the evolving nature of training in a learning organization.