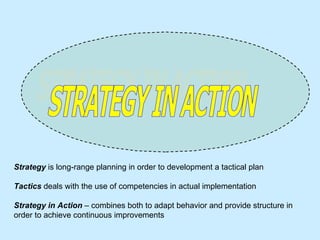
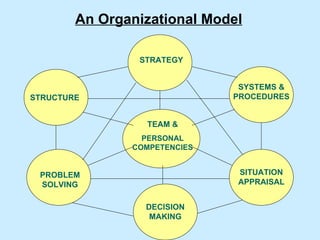
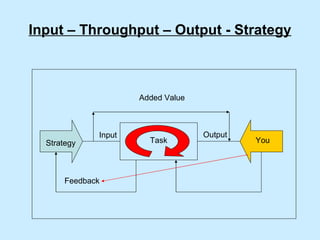
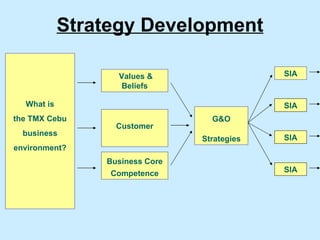
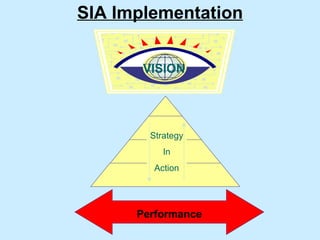
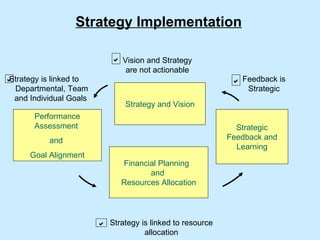
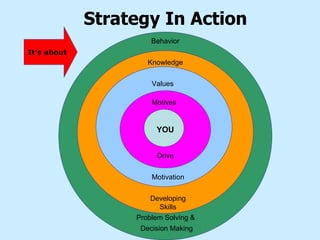
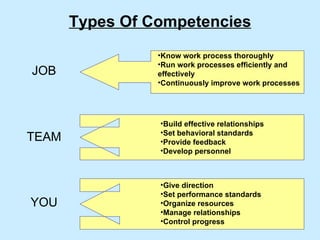
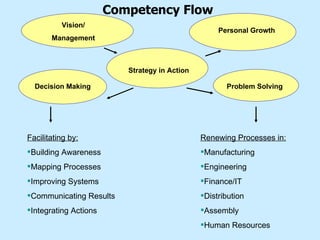
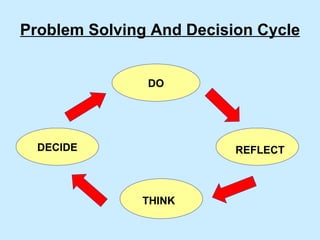
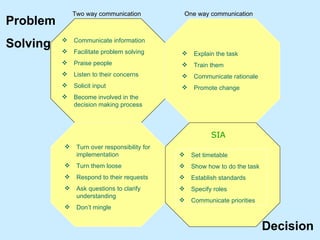
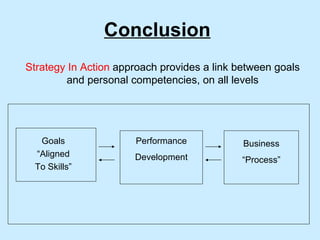
The document summarizes a two-day strategy session for middle managers and supervisors. The session aims to improve professional and personal development skills through interactive exercises and discussions around topics like leadership, problem-solving, decision-making, and aligning individual and team goals with organizational strategy. Facilitators will use lectures, group activities, videos, and feedback to help participants gain clarity on performance expectations and better coordinate efforts to achieve shared objectives.