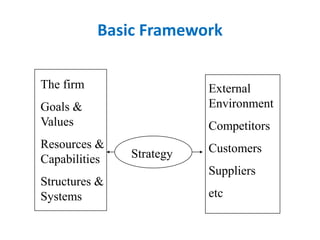
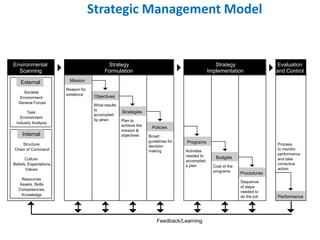
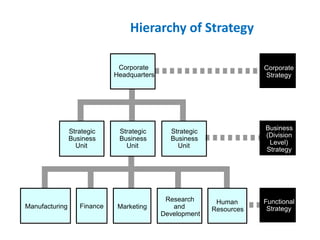
The document provides an overview of strategic management, including defining key terms like strategy, tactics, and the strategic management model. It discusses the importance of strategic management in providing strategic vision and understanding a changing environment. The strategic management model involves environmental scanning, strategy formulation through developing a mission, objectives and strategies, strategy implementation through programs and budgets, and evaluation and control by monitoring performance.