The document provides an overview of key concepts in strategic management including:
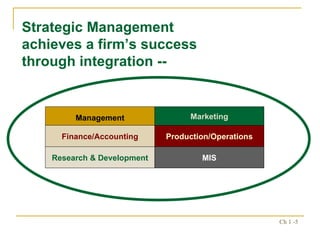
1. Strategic management involves formulating, implementing, and evaluating cross-functional decisions to achieve organizational objectives.
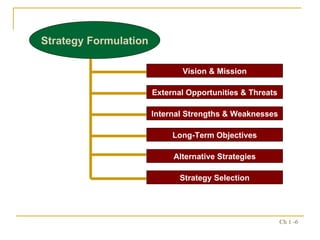
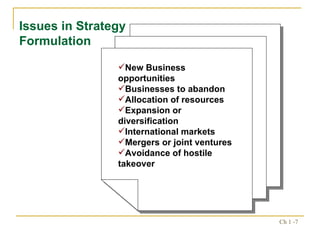
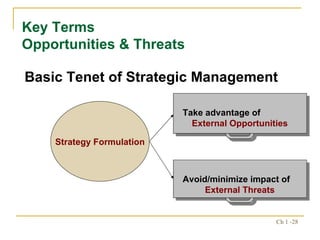
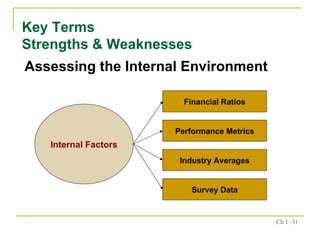
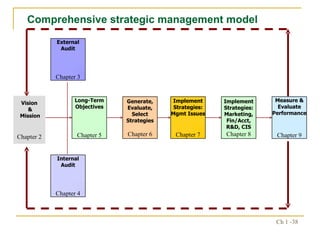
2. The strategic management process includes assessing external opportunities/threats and internal strengths/weaknesses to develop long-term objectives and strategies.
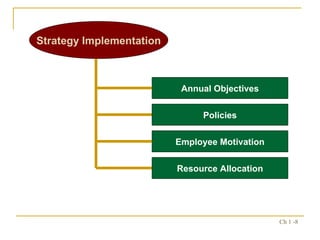
3. Implementing, evaluating, and updating strategies is critical for organizations to adapt to changing conditions and gain sustained competitive advantages.