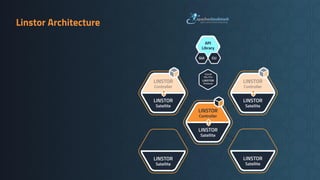
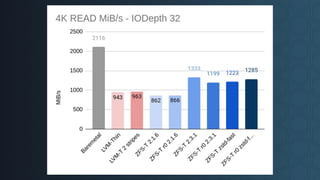
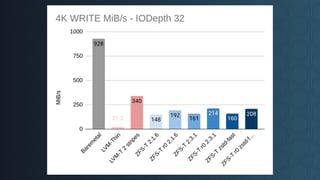
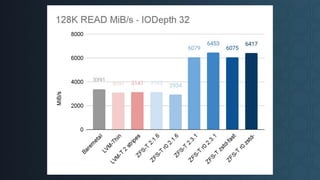
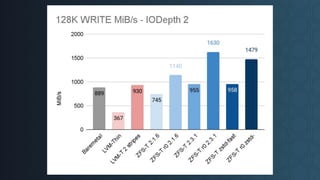
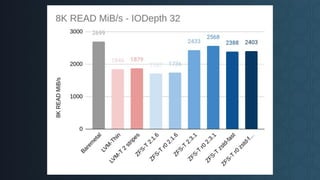
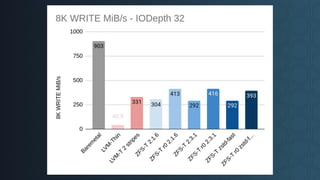
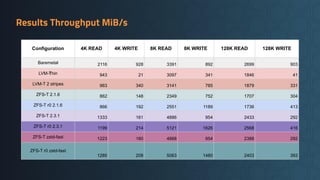
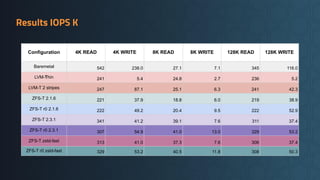
Deciding on a good storage layout is crucial for good performance and reliability on later operations of your LINSTOR/CloudStack installation. This session gave the attendees an overview on different storage setups (LVM-Thin, striping, ZFS) and explaining differences in failure domains and performance implications and how to use them in LINSTOR.
--
The CloudStack European User Group 2025 took place on May 8th in Vienna, Austria. The event once again brought together open-source cloud professionals, contributors, developers, and users for a day of deep technical insights, knowledge sharing, and community connection.