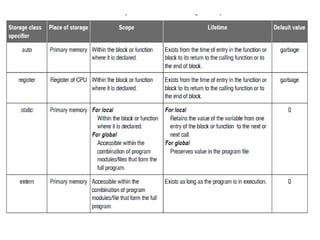
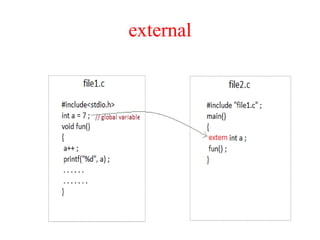
The document explains various storage classes in C programming, including automatic, register, static, and external storage classes. It provides definitions, examples, and behavior of variables associated with each storage class, highlighting their scope and lifetime. Additionally, it includes questions to assess understanding of the material presented.