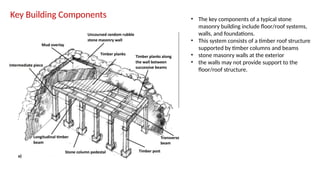
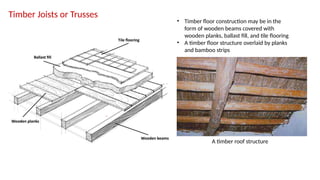
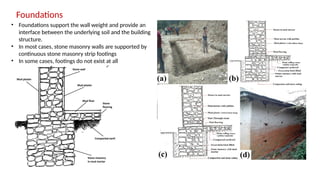
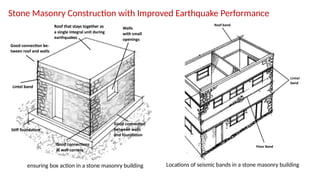
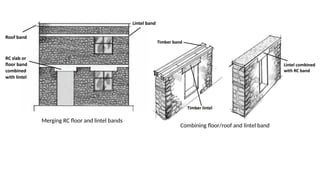
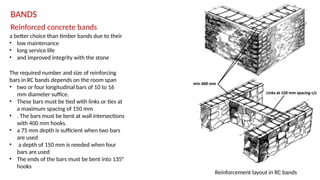
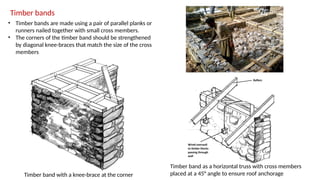
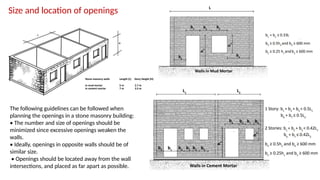
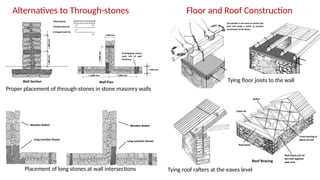
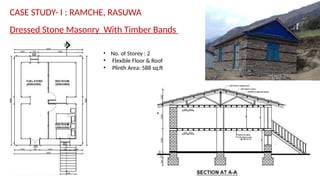
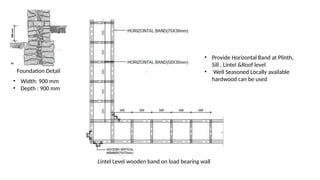
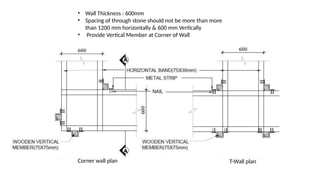
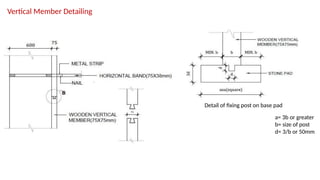
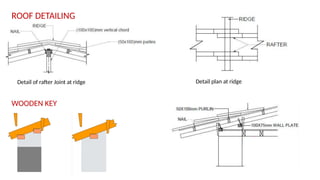
STONE IS A PRELIMINARY CONSTRUCTION MATERIAL IN MOUNTAIN ARCHITECTURE. HERE IS A BRIEF EXPLAINATION OF STONE MASONRY IN MOUNTAIN ARCHITECTURE OF NEPAL.STONE IS WIDELY USED IN NEPAL. Stone masonry is a construction technique in which stones are used as the primary building material to create structures like walls, buildings, temples, retaining walls, and bridges. It is one of the oldest forms of construction, especially common in places with abundant local stone. It provides durability, strength, and natural aesthetics. Stone masonry can broadly be categorized into two types:
1. Rubble Masonry
Made from undressed or roughly dressed stones. It is less uniform and commonly used in traditional or rural structures.
Uncoursed Rubble Masonry: Stones are laid without regular courses or alignment.
Coursed Rubble Masonry: Stones are laid in leveled courses, but the sizes and shapes may still vary.
Random Rubble Masonry: A more irregular type, stones are placed in a non-uniform way.
Dry Rubble Masonry: No mortar is used; relies on interlocking of stones.
2. Ashlar Masonry
Made from dressed (cut) stones, offering a clean and refined finish. Common in monumental and urban architecture.
Ashlar Fine Masonry: Stones are finely dressed and joints are very thin.
Ashlar Rough Tooled Masonry: Faces of stones are rough but the sides are smooth for proper fitting.
Ashlar Rock-faced Masonry: Outer surface is left rough; sides and beds are smooth.
🔹 Materials Used
Stones: Granite, sandstone, limestone, marble, etc.
Mortar: Cement mortar or lime mortar is used to bind stones (except in dry rubble).
Tools: Chisel, hammer, plumb bob, trowel, etc.
🔹 Construction Process
Selection of stones based on hardness, durability, and local availability.
Dressing of stones to the desired shape and size.
Laying the stones with or without mortar in layers (courses).
Filling the joints and curing the structure properly.
🔹 Advantages
Long-lasting and durable.
Aesthetic, natural look.
Fire and weather-resistant.
Low maintenance.
🔹 Disadvantages
Heavy and labor-intensive.
Time-consuming construction.
Costly compared to brickwork.
Needs skilled labor. Stone masonry offers several advantages such as strength, fire resistance, low maintenance, and natural aesthetics. However, it is heavy, labor-intensive, and requires skilled craftsmanship. In Nepal, stone masonry is widely used in hilly and rural areas due to the easy availability of local stones and its suitability for sloped terrain. Traditional structures in Kirtipur, Gorkha, and Mustang are good examples of rubble and dry masonry. Despite modern construction techniques, stone masonry continues to be relevant today in landscaping, boundary walls, and eco-resorts, especially when combined with sustainable and earthquake-resistant methods.
🔹 Applications
Heritage and religious structures (temples, monasteries).
Retaining walls and embankments.