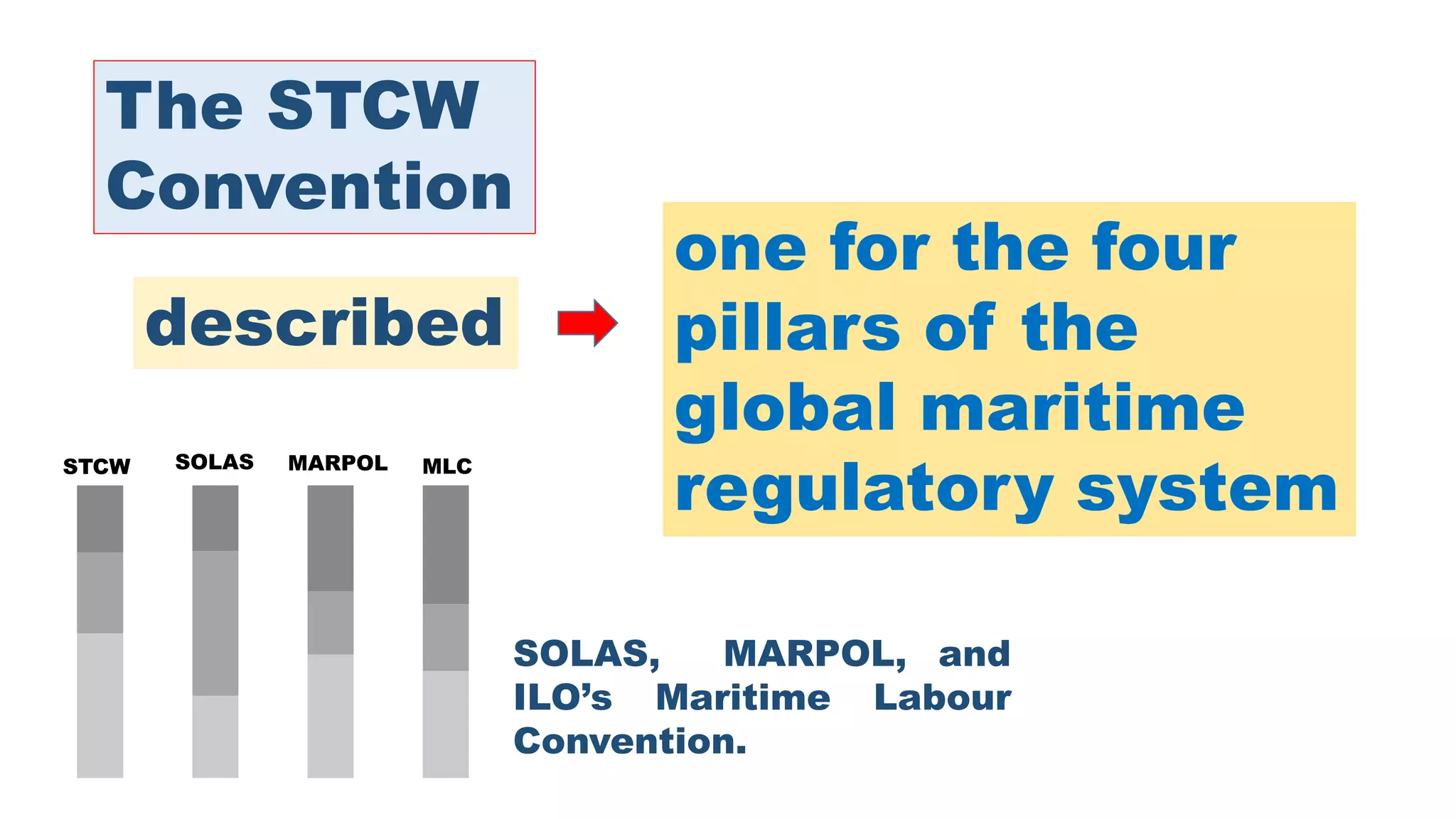
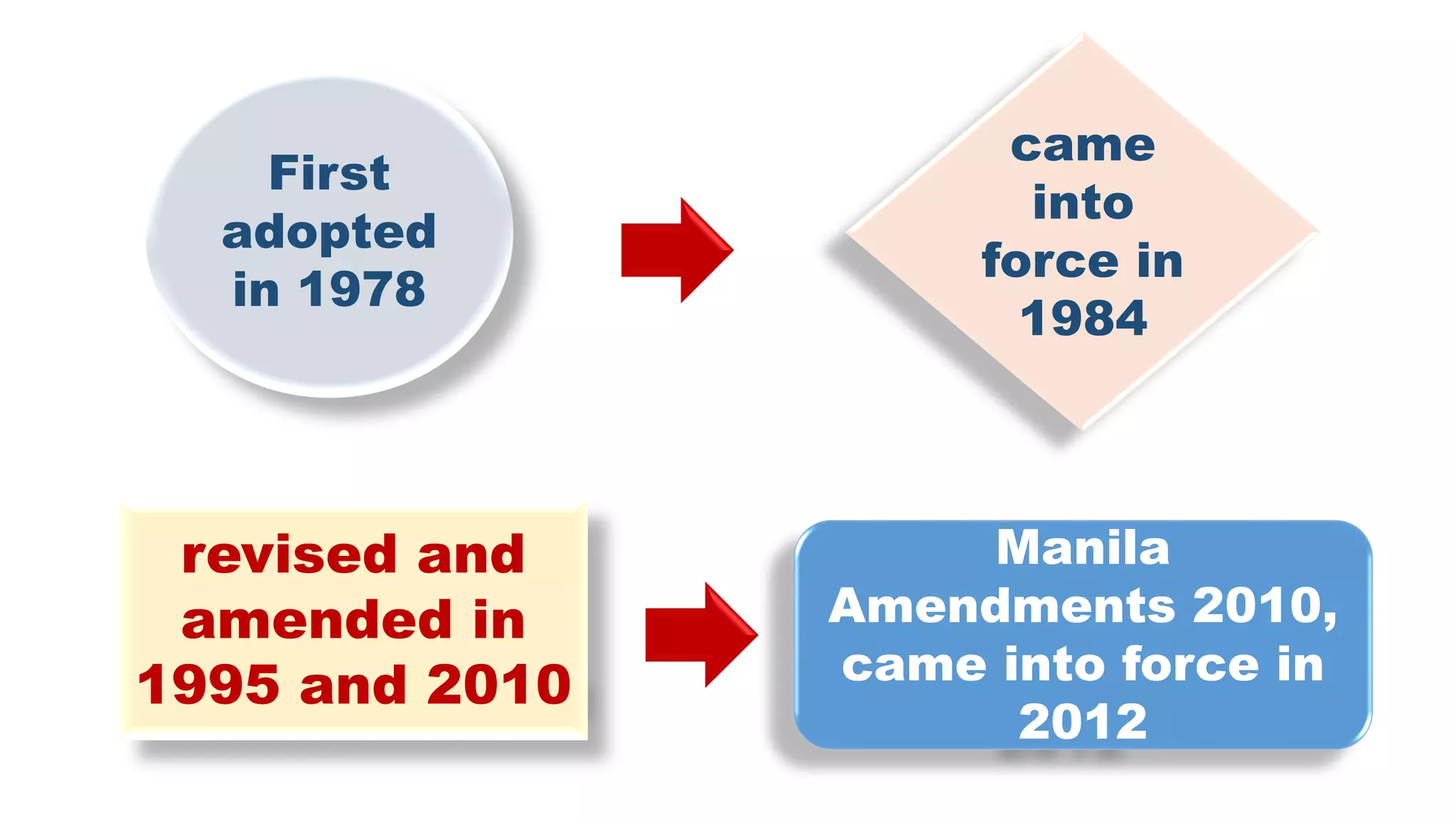
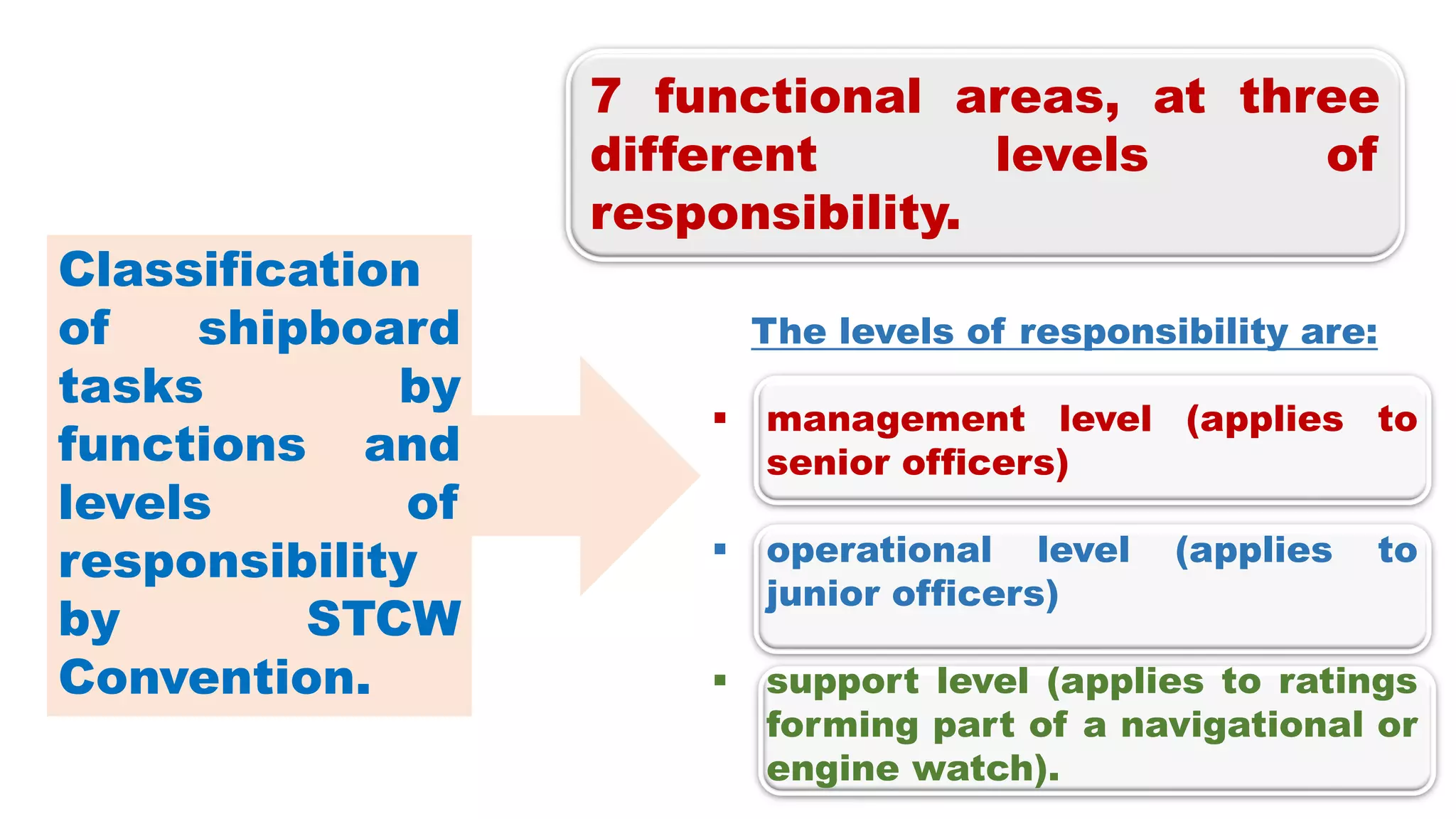
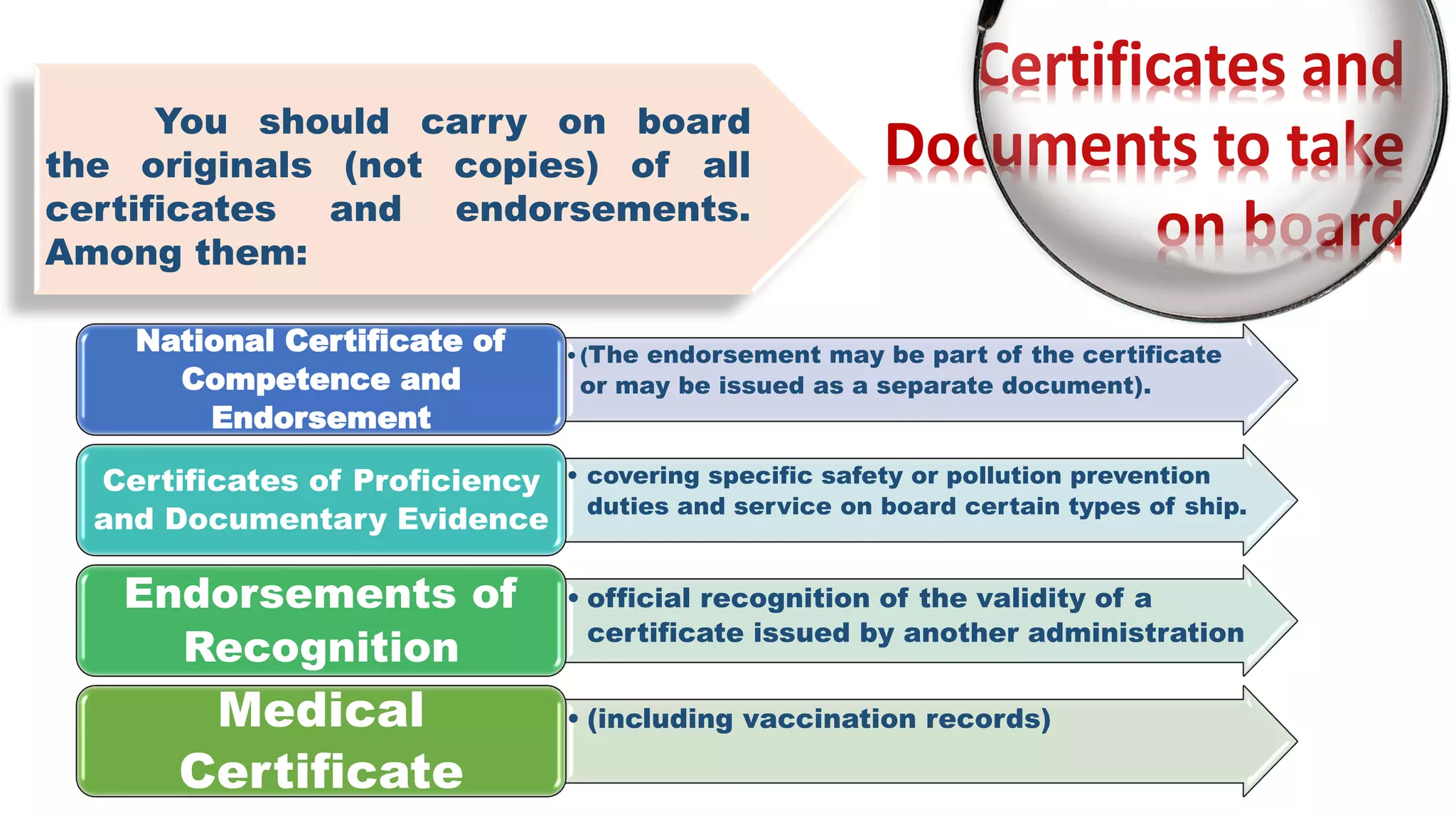
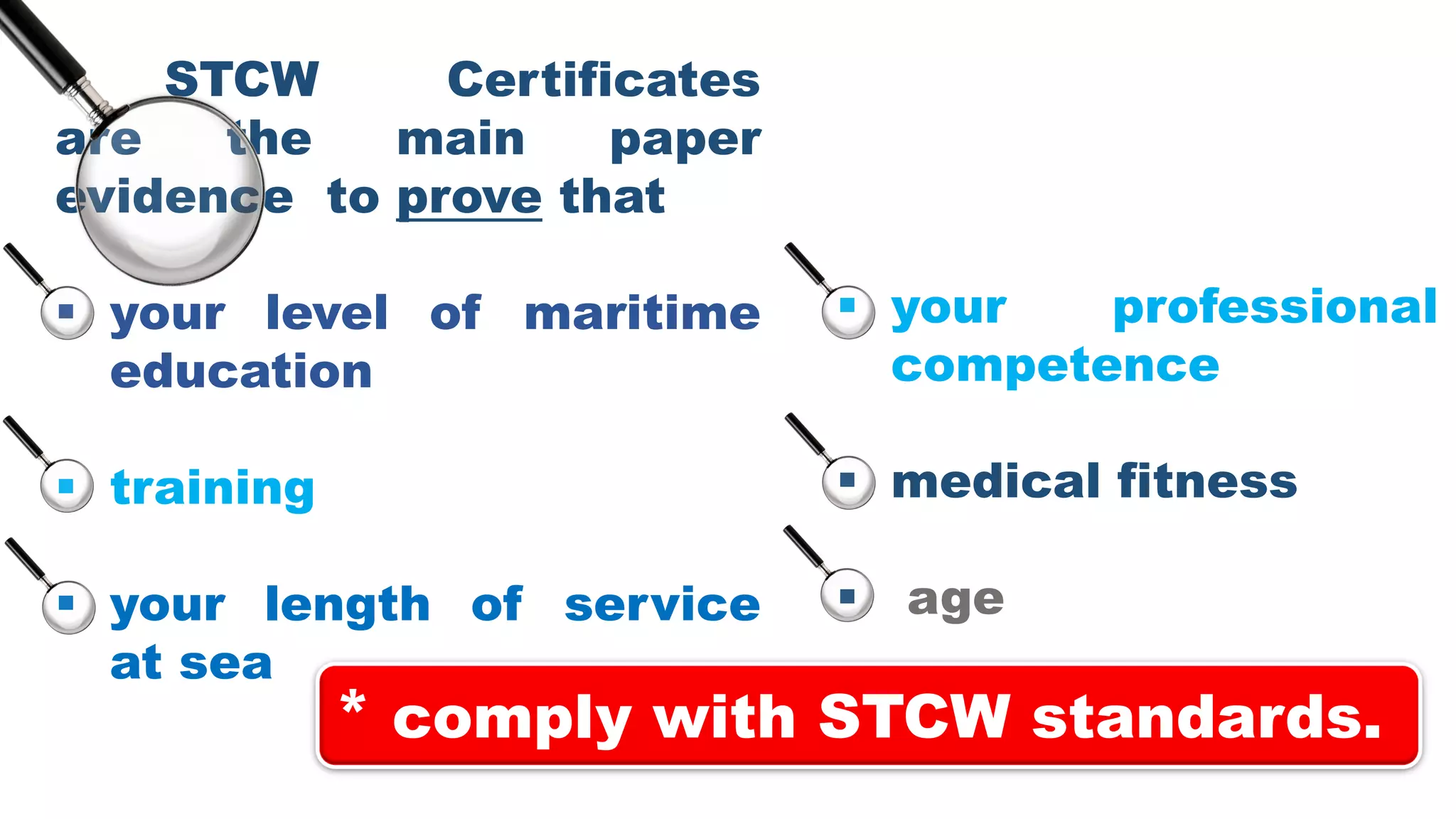
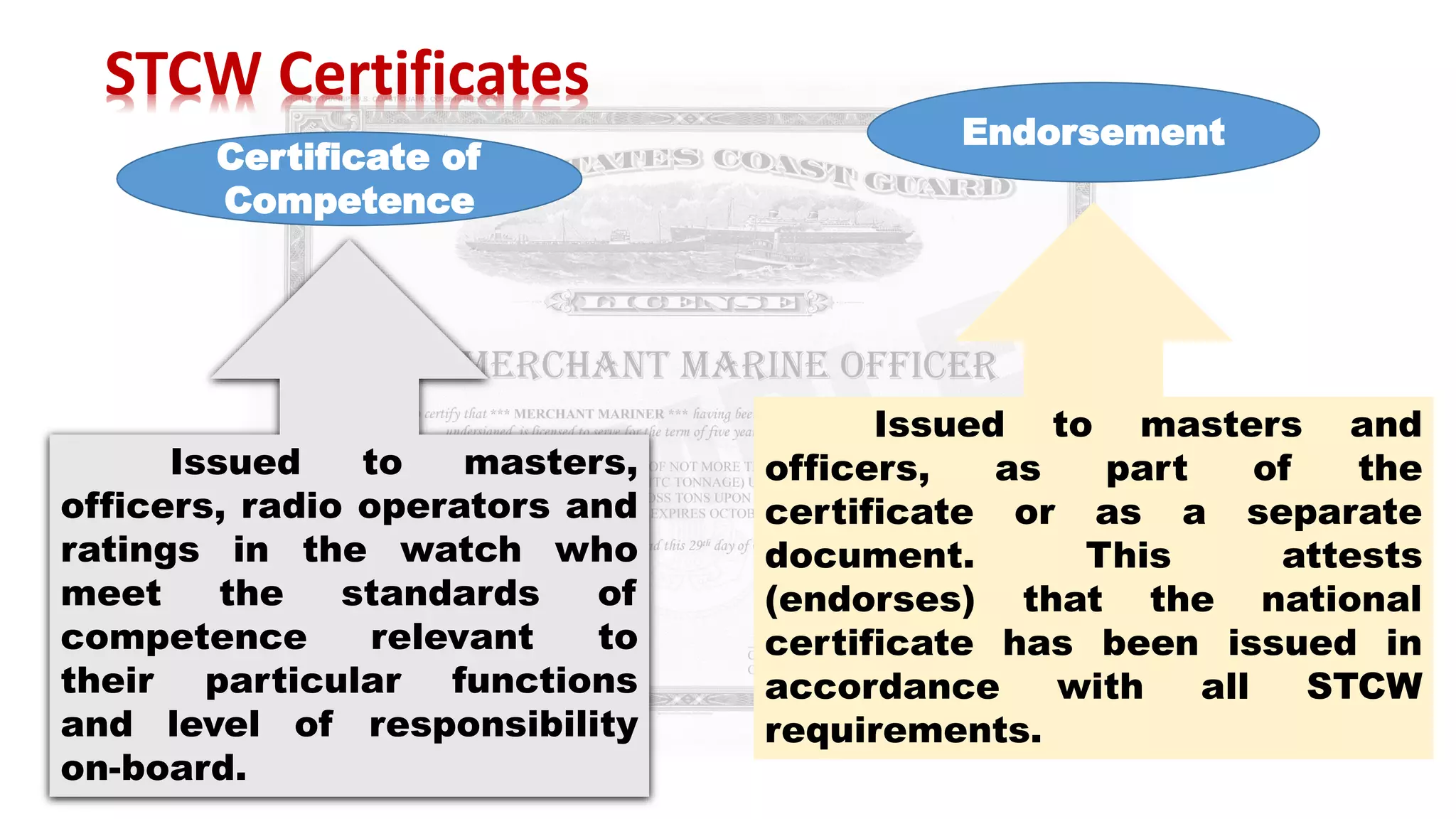
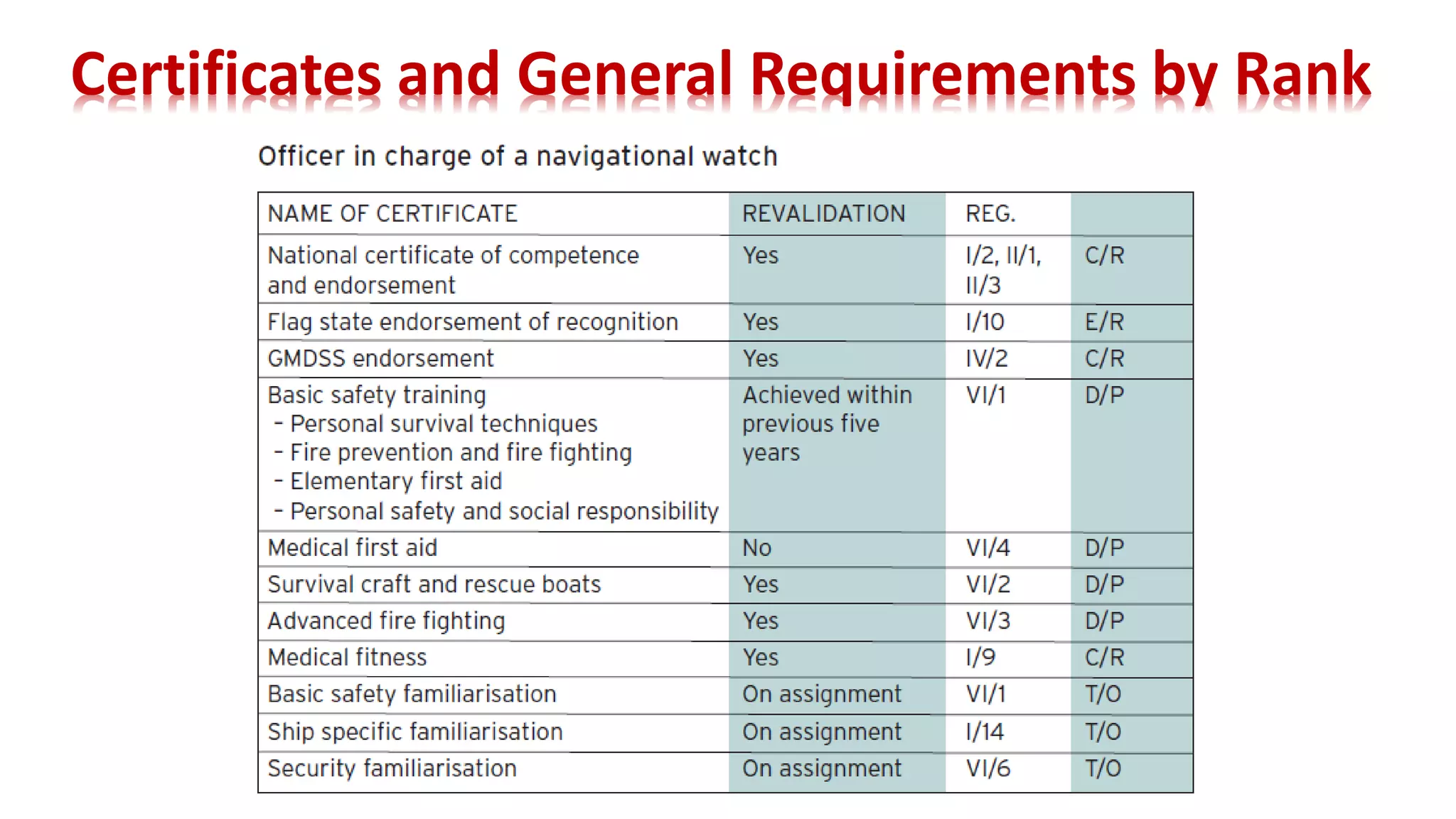
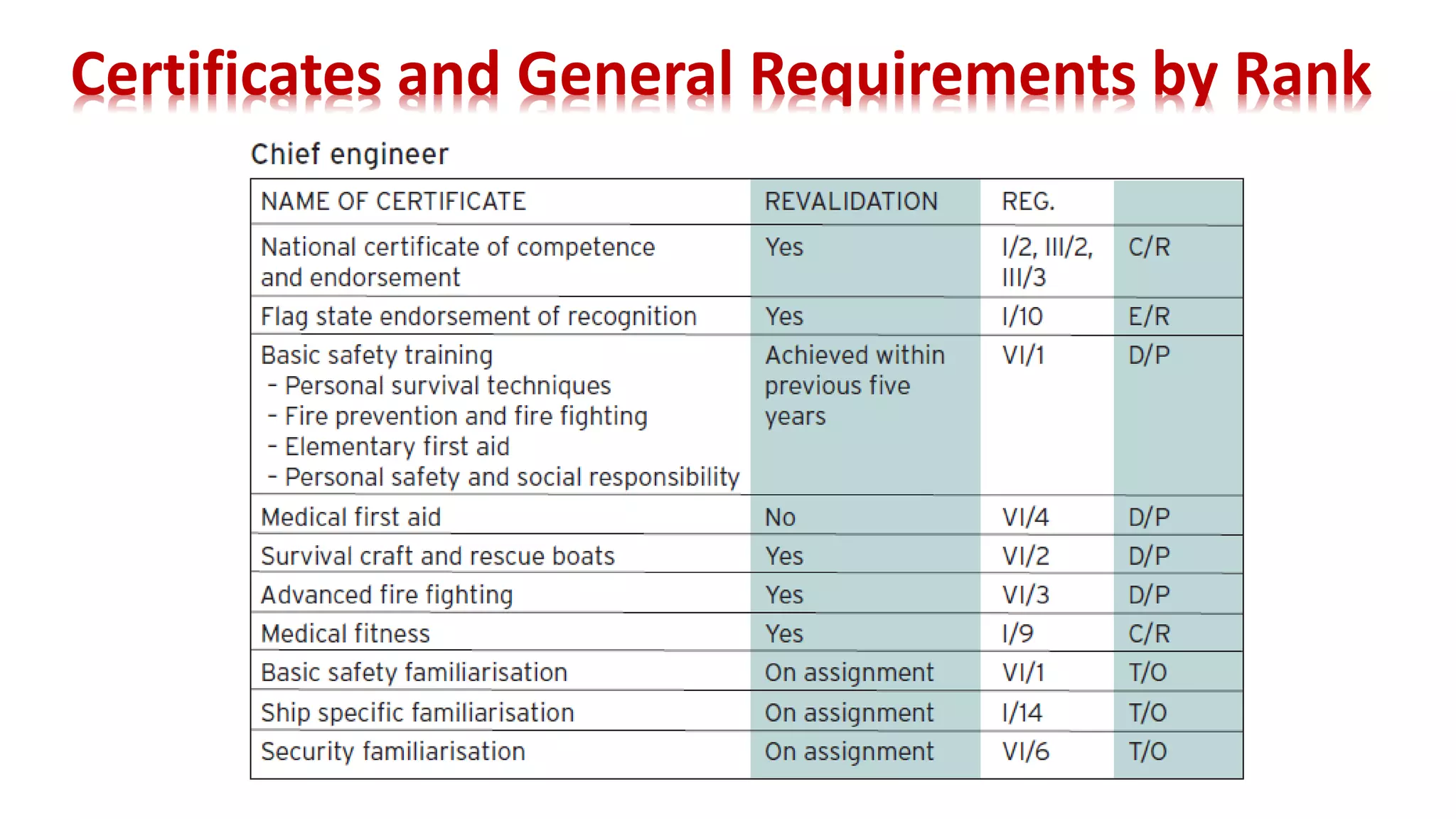
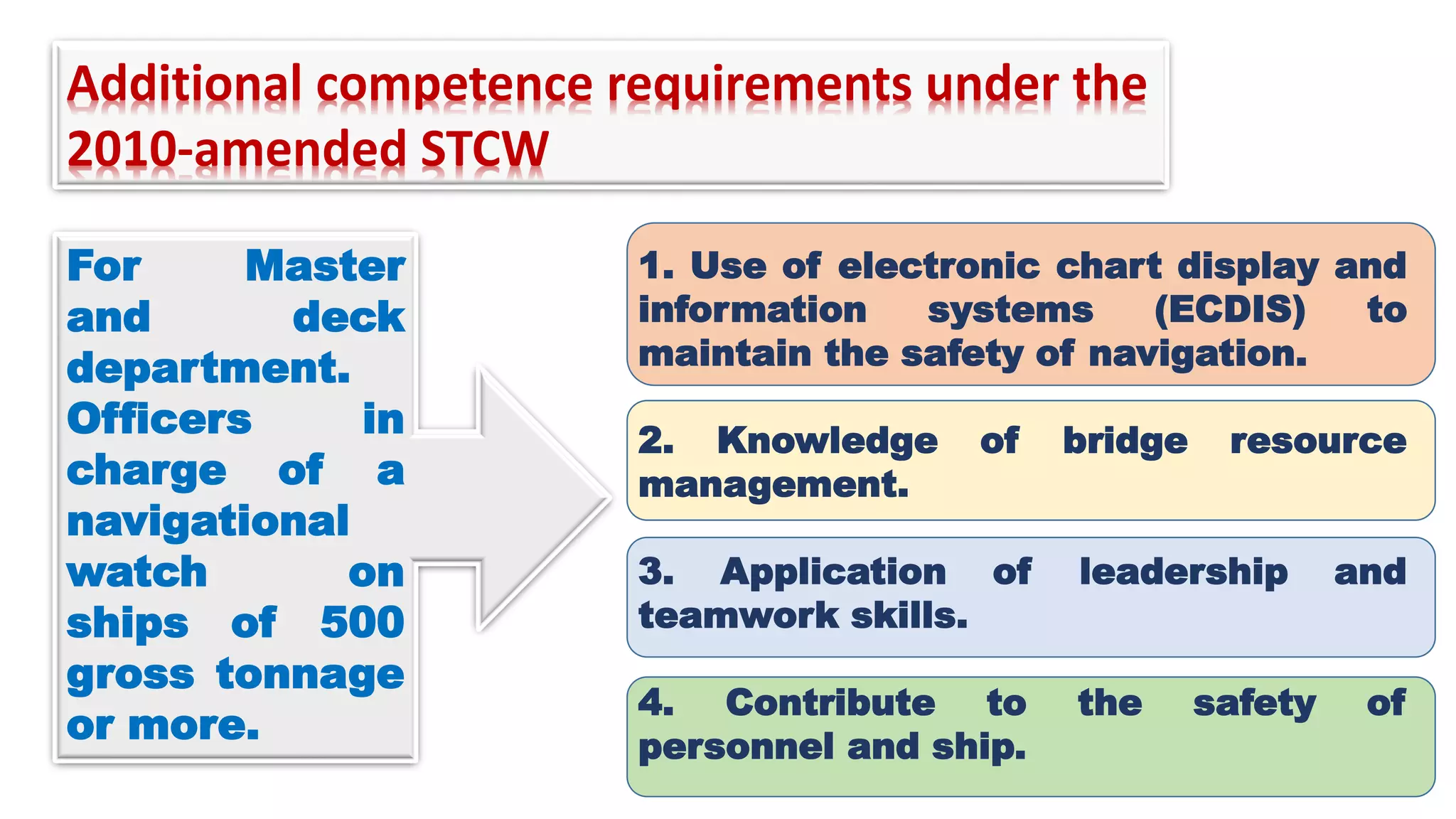
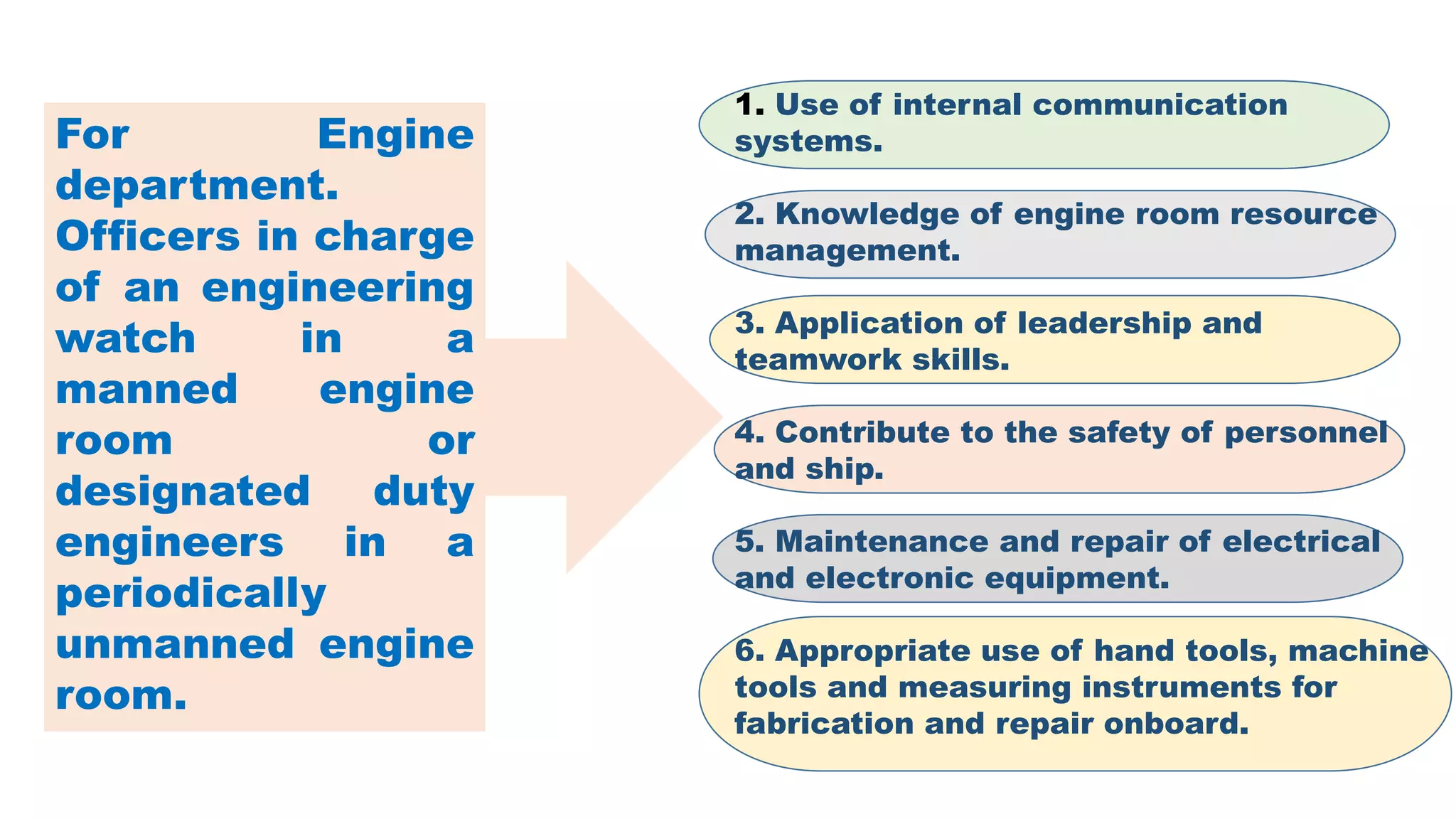
The STCW Convention is one of the four pillars of the global maritime regulatory system along with SOLAS, MARPOL, and the Maritime Labour Convention. It was first adopted in 1978 and aims to provide international standards for maritime training. It sets standards, governs certification, and controls watchkeeping arrangements. The STCW Convention includes provisions for seafarers, shipowners, training establishments, and administrations. It is composed of articles, an annex, and a code that specifies legal responsibilities and technical details. The code classifies shipboard tasks into seven functional areas at three levels of responsibility. The STCW Convention requires certificates and endorsements to prove a seafarer's qualifications and compliance with standards.