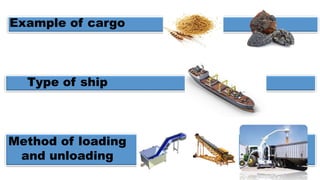
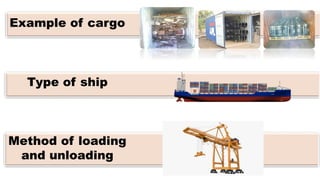
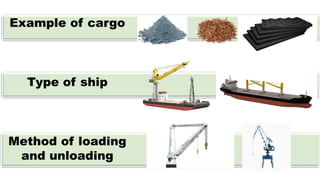
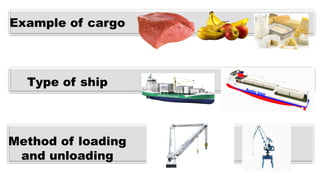
This document discusses the different types of cargo carried by ships, including examples of each cargo and the methods for loading and unloading. It describes four main types of cargo: liquid bulk, which is loaded via pipes and pumps; dry bulk, loaded by conveyor belts or tubes; containerized cargo, loaded by cranes; and non-containerized cargo, also loaded by cranes. It provides details on the ships used to transport each type of cargo and the loading and unloading processes.