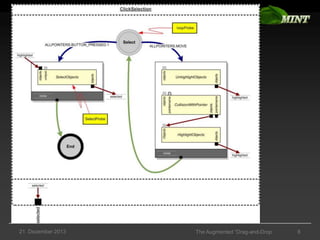
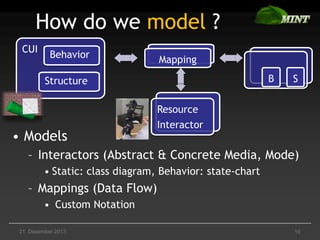
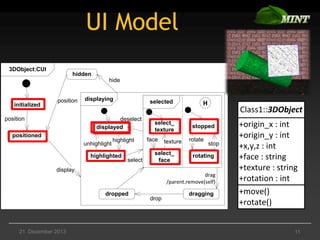
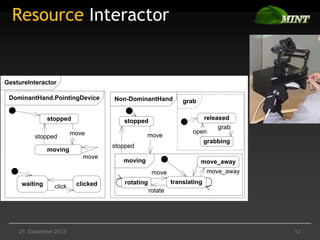
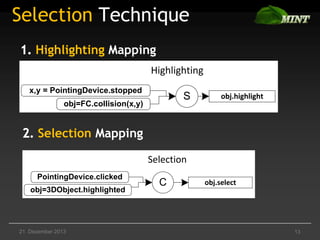
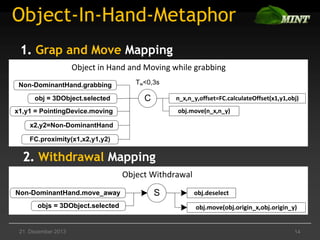
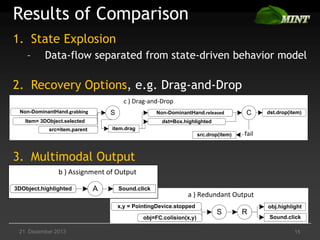
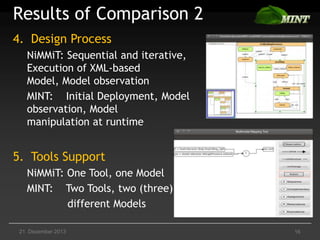
The document discusses the comparison of multimodal interaction techniques in the Mint and Nimmit systems, highlighting their design, modeling, and application in non-traditional user interfaces. It outlines issues like state explosion and recovery options, as well as differences in their design processes and the tools supporting each system. The exploration focuses on enhancing the modeling of multimodal interactions to improve usability in 3D environments.






![What is State of the Art ?
State-driven
Object Graphs [Carr97]
ICOs [Navarre05]
Dataflow-driven:
InTml [Figueroa02]
Icon [Dragicevic04]
NiMMiT [Boeck06]
State + Data + Event +
Hierarchy
21. Dezember 2013
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inttecdesignv6slideshare-131221101358-phpapp01/85/Comparing-the-Multimodal-Interaction-Technique-Design-of-MINT-with-NiMMiT-7-320.jpg)