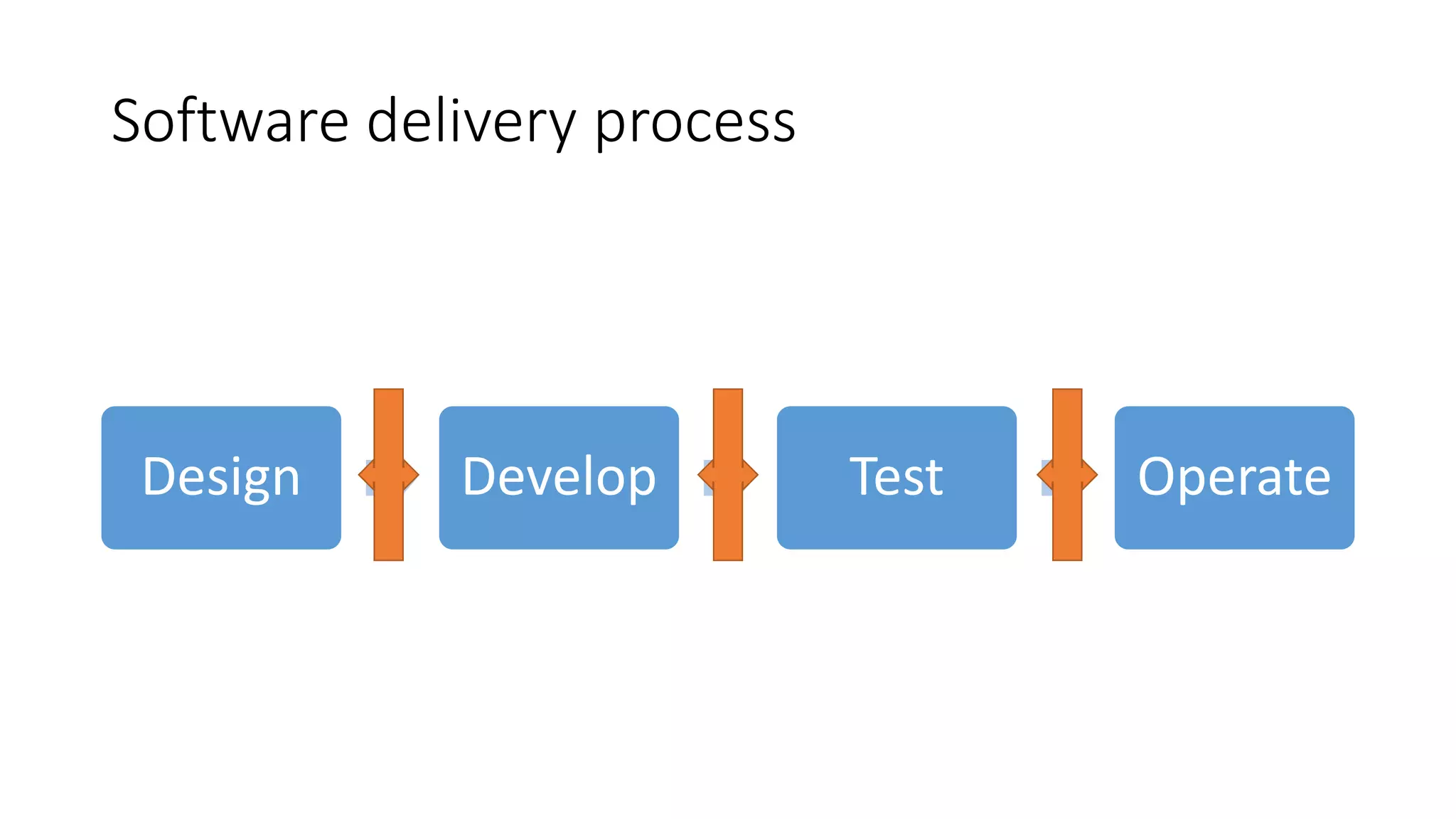
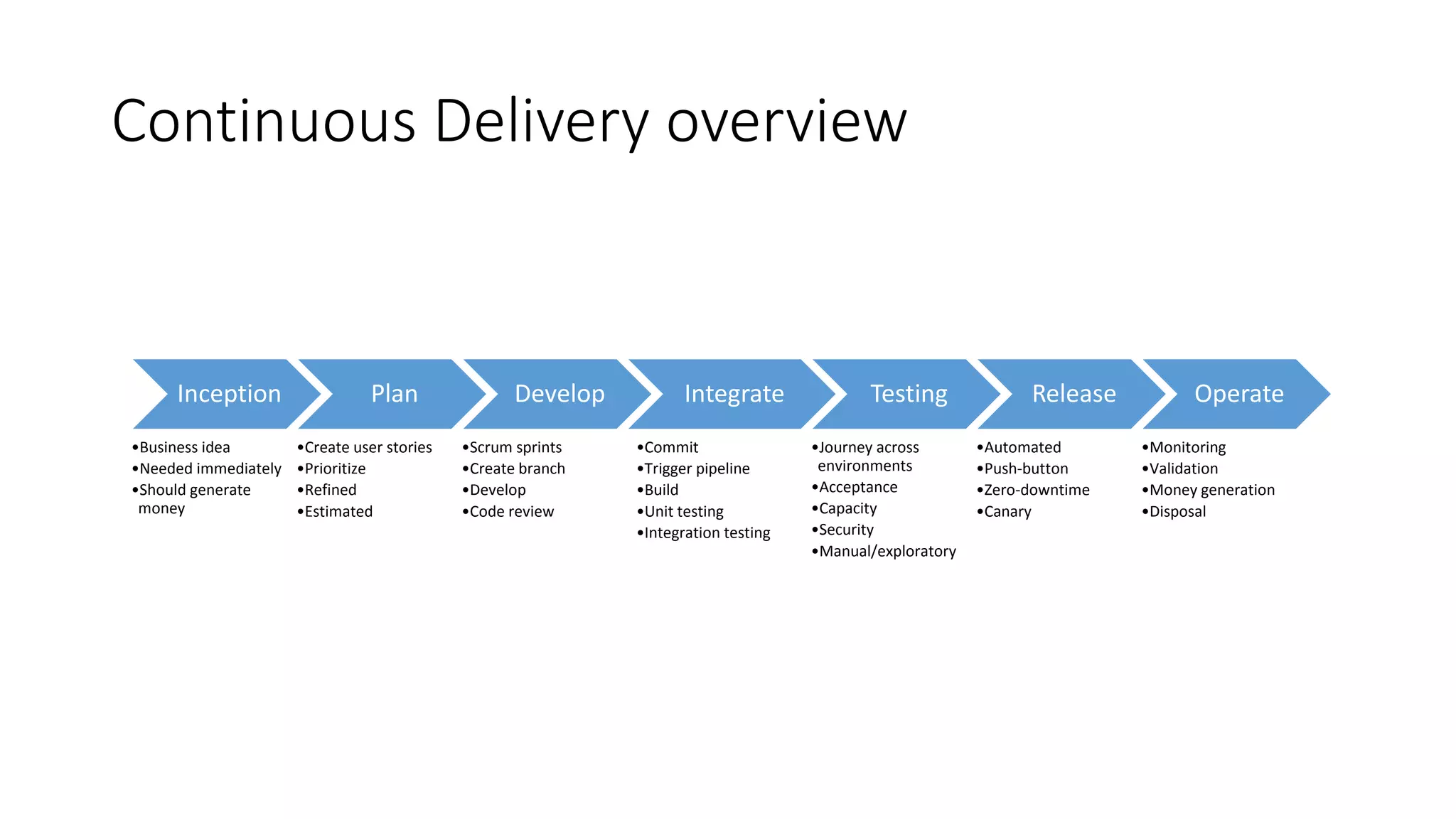
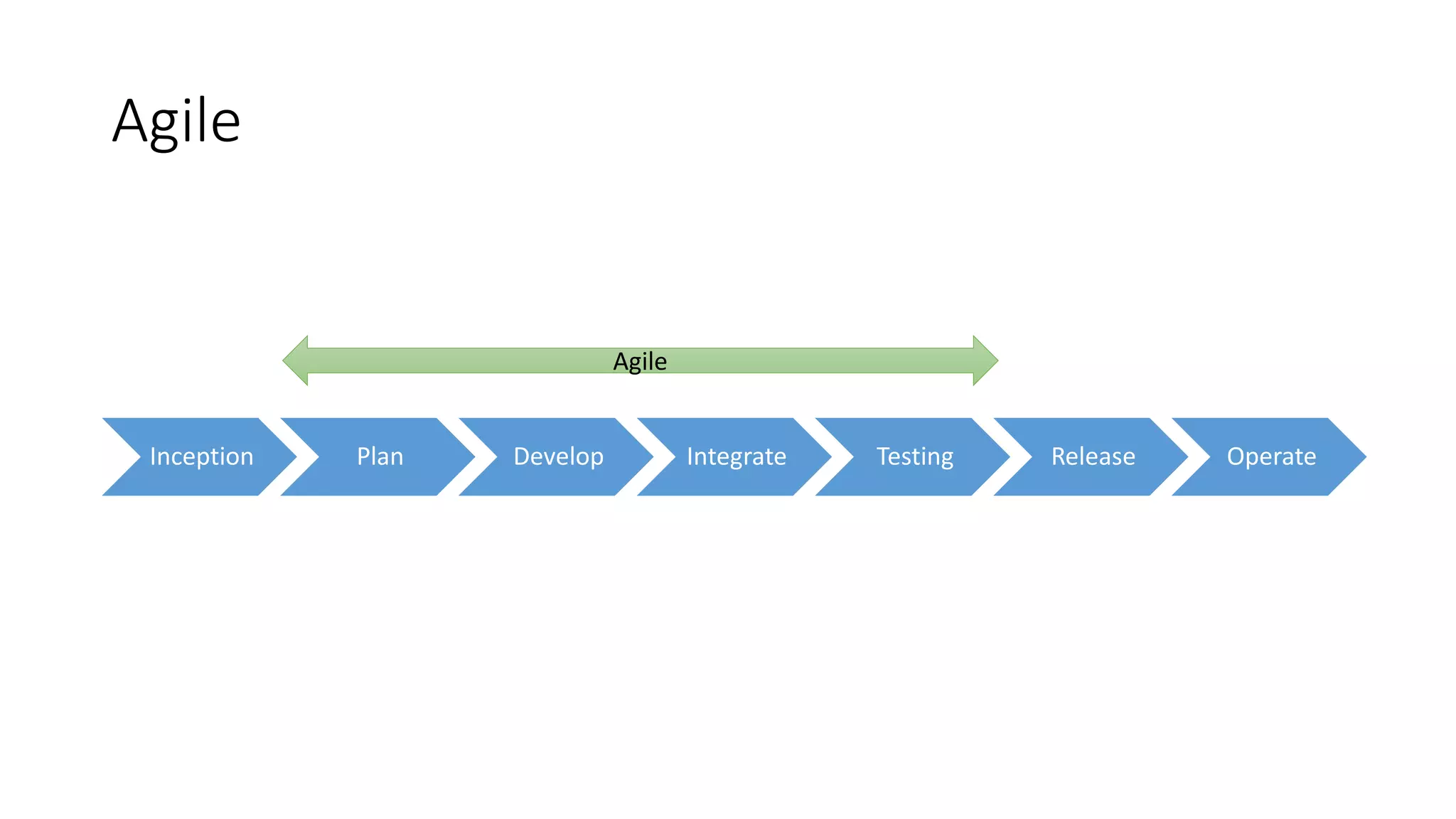
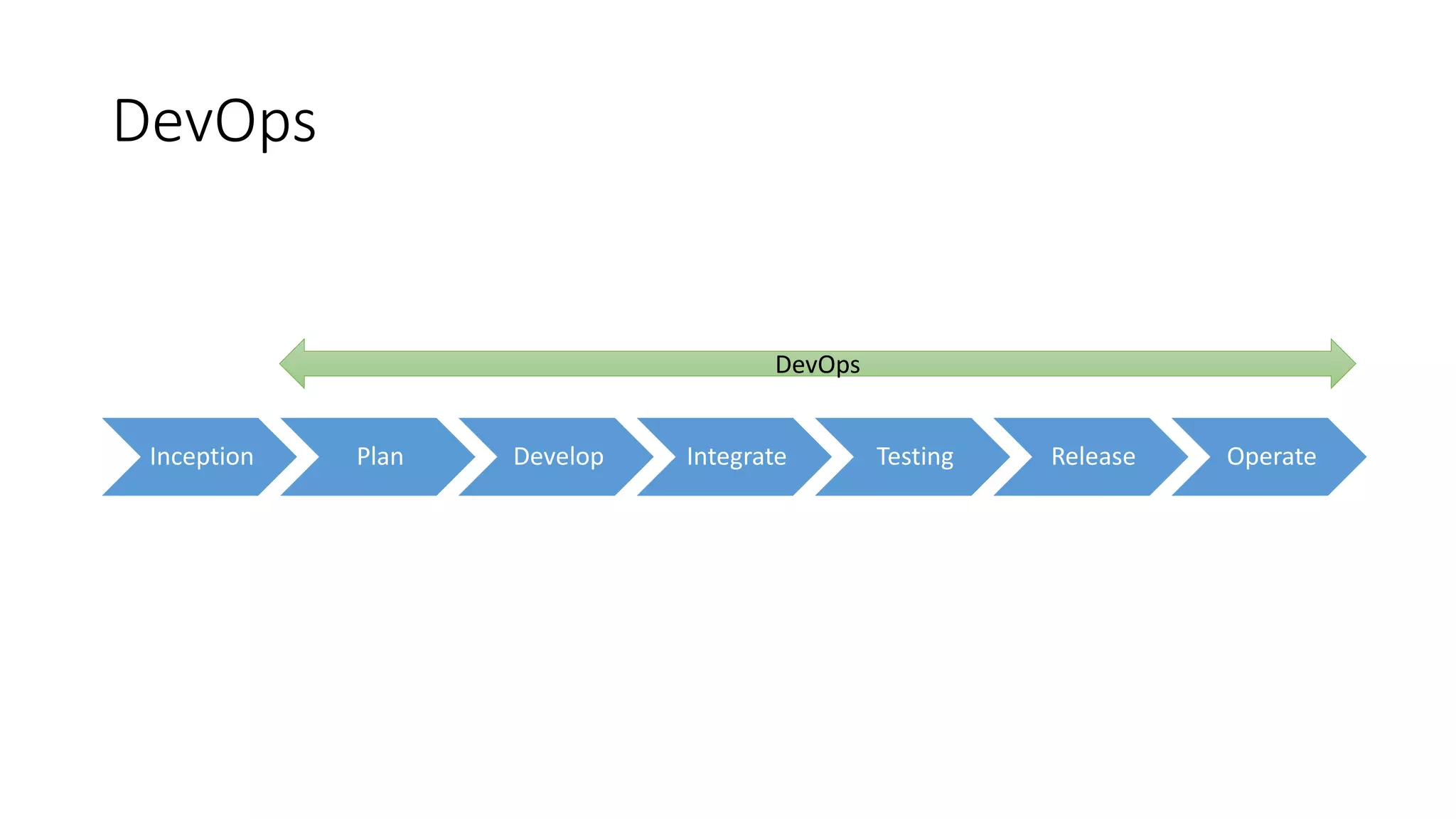
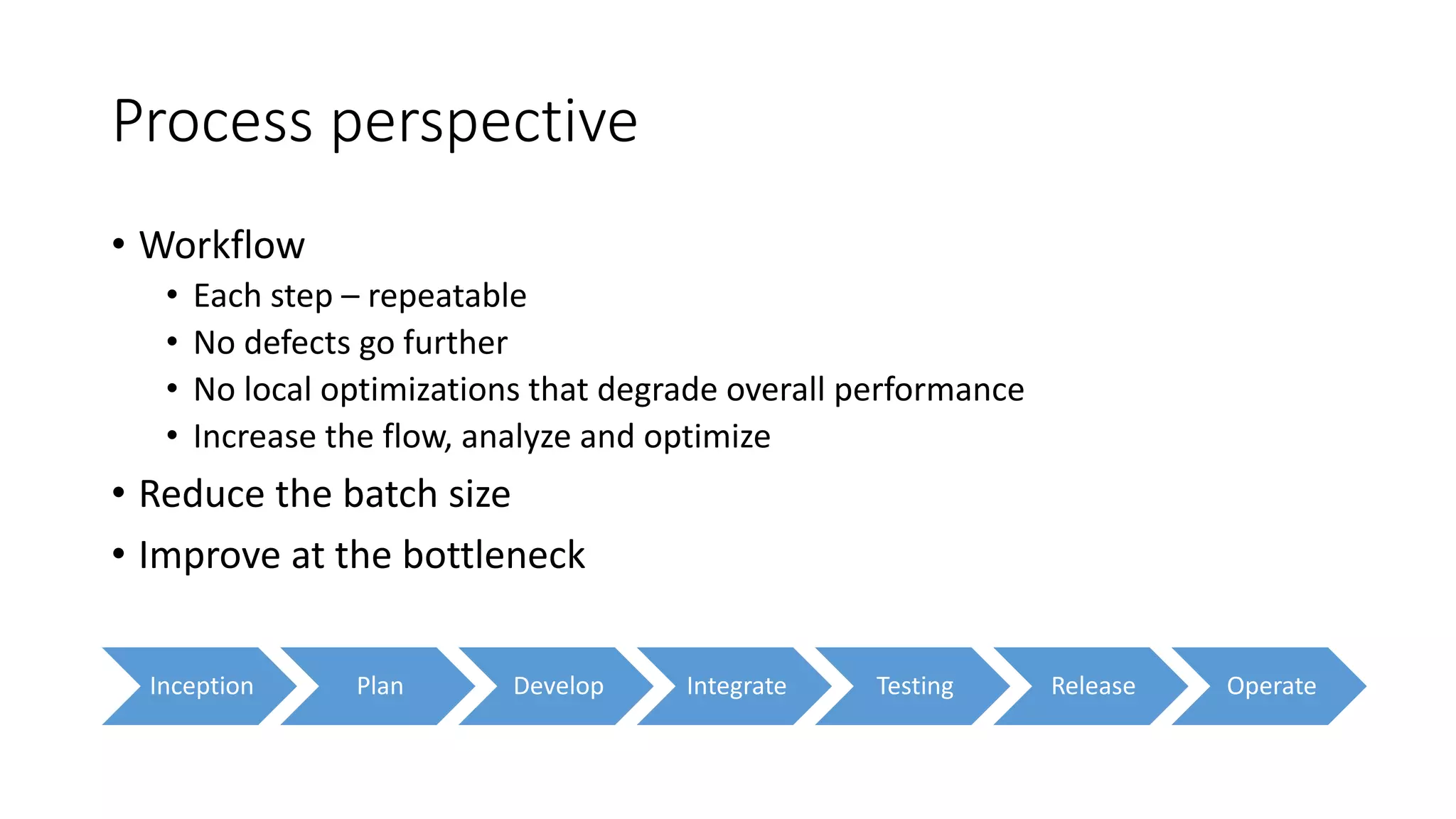
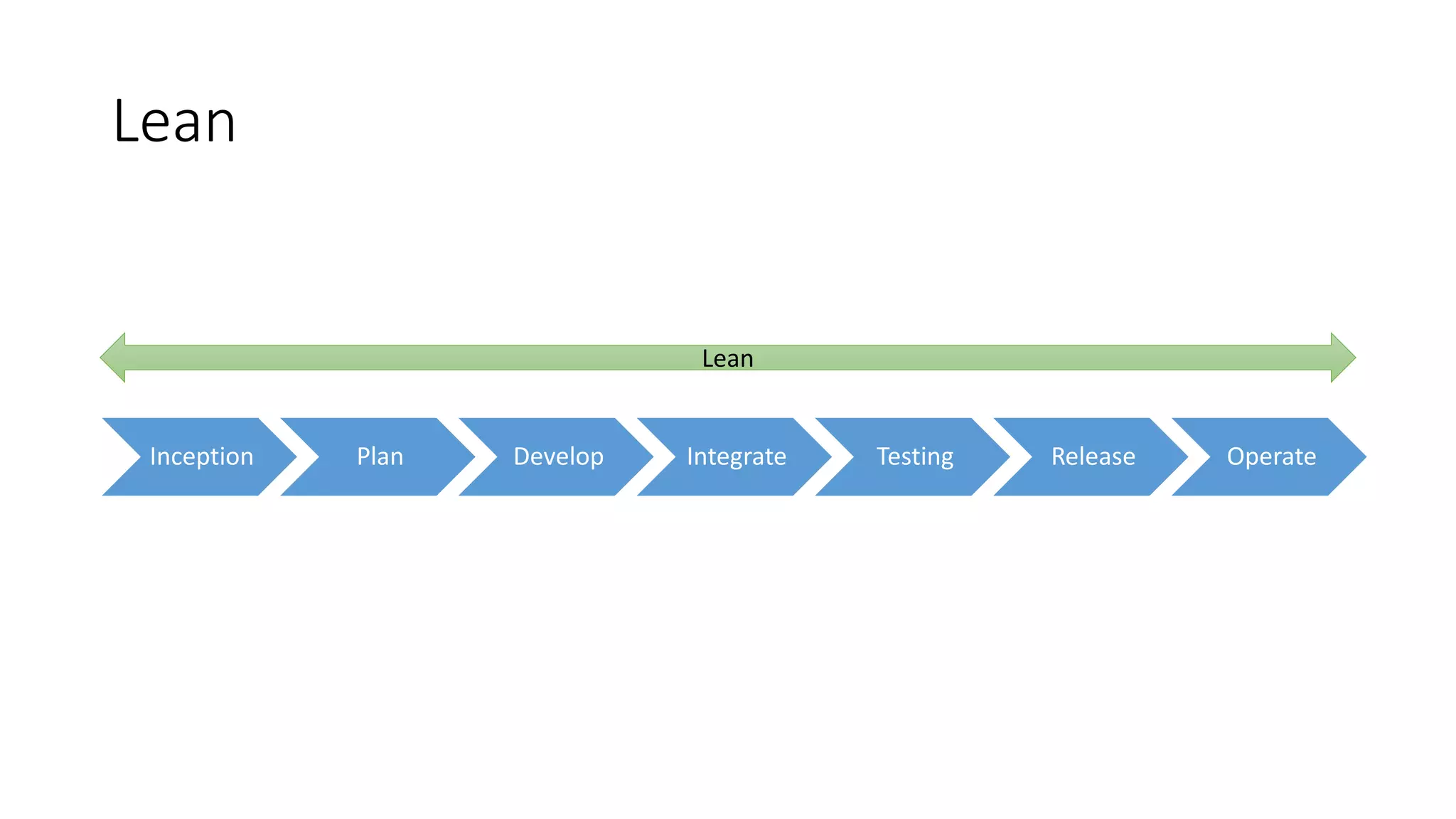
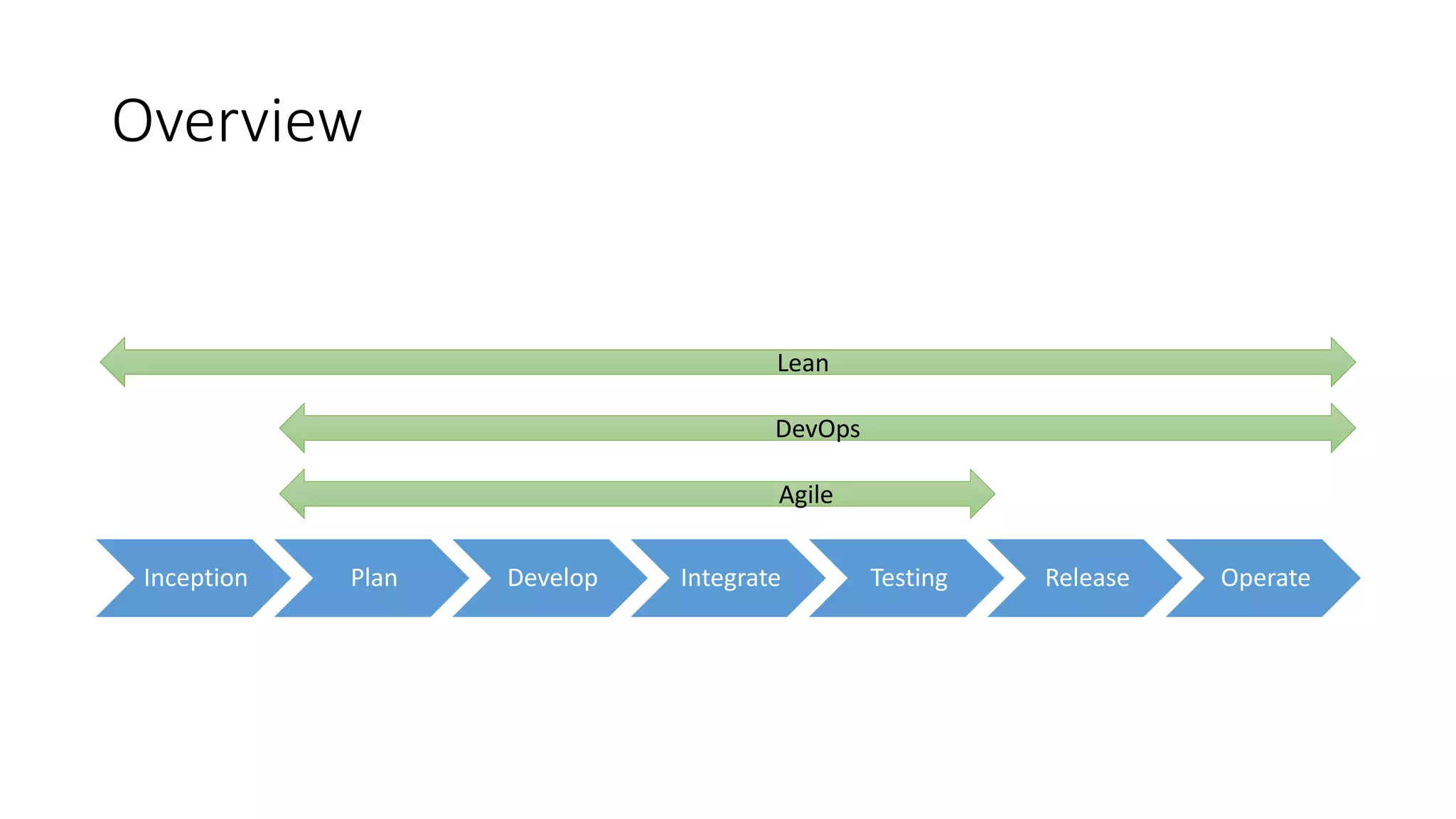
The document discusses the state of continuous delivery in 2015, emphasizing the goal of delivering valuable software quickly and reliably to customers while minimizing costs. Key principles include creating a repeatable release process, automating various stages, building quality into the process, and ensuring shared responsibility and communication within teams. It highlights the importance of agile practices and continuous improvement in optimizing software delivery and development processes.