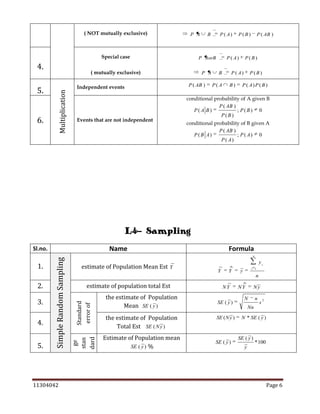
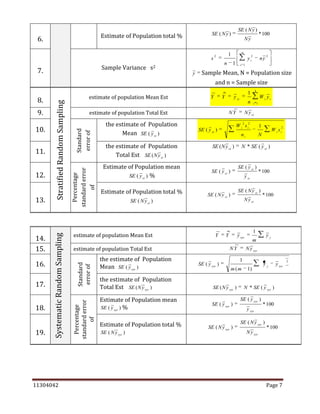
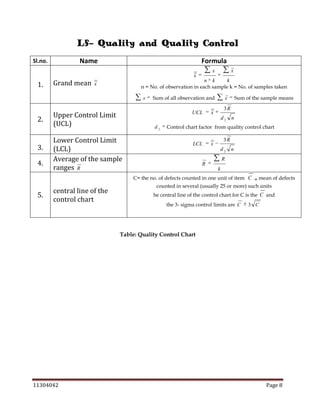
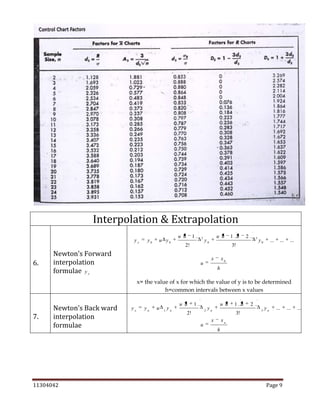
The document is a comprehensive statistics formula sheet detailing various statistical concepts including measures of central tendency, probability, sampling, quality control, and index numbers. It presents formulas for calculating means (arithmetic, geometric, harmonic), standard deviations, regression models, correlation coefficients, and several probability rules. Additionally, it includes methods for interpolation, extrapolation, and time series analysis, along with control chart parameters for quality control.
![18.
19.
20.
21.
Coeff.
Coefficient of QD
U
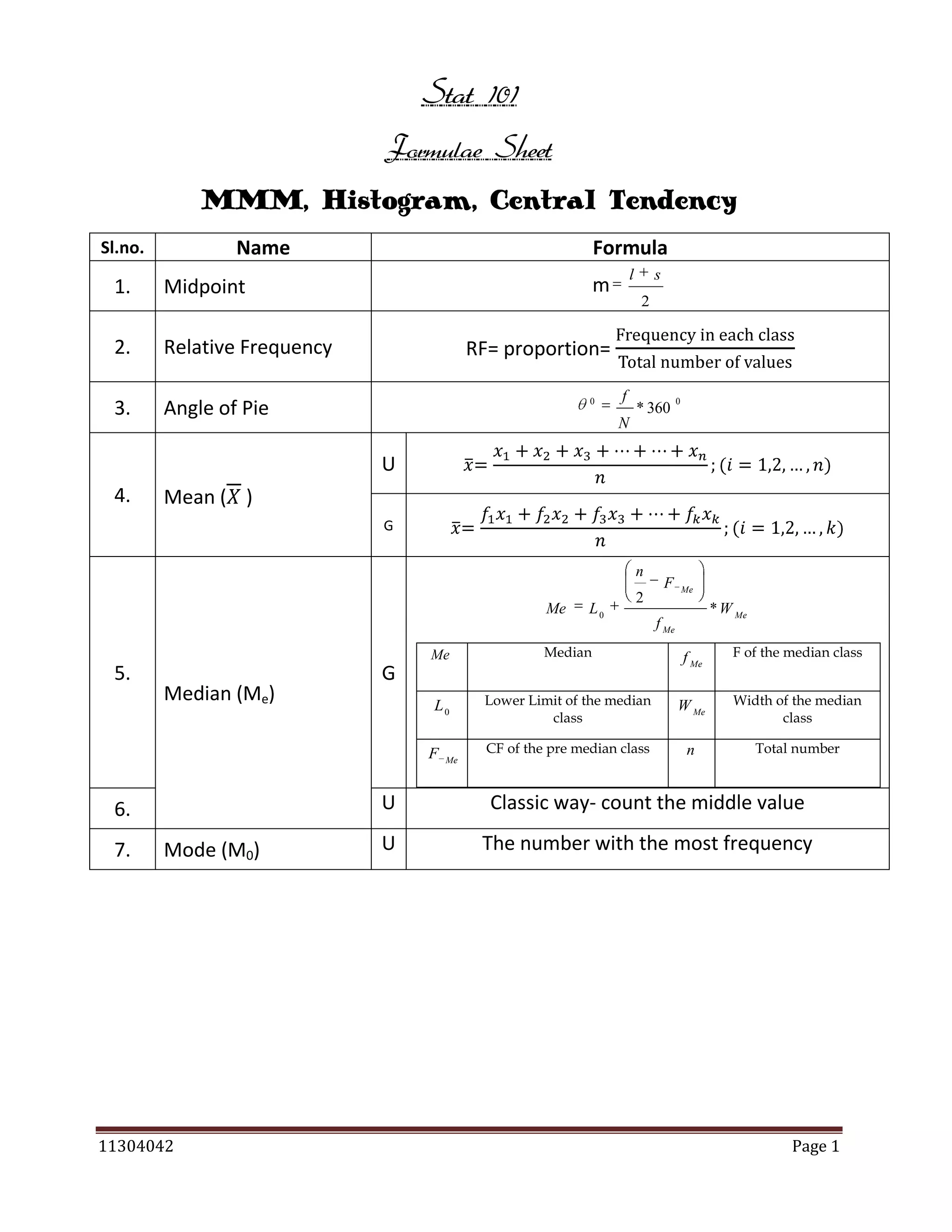
Mean Deviation (MD)
Where A can be mean/
median/mode
1
MD
Population
i
1
i
2
i
1
N
R
2
Sample
1
i
k
1
i
i
1
23.
1
N
1
2
2
k
1
s
n
1
2
n
f 1 x1
k
1
Ungroup data
22.
i
2
fi xi
N
fi x
i
Sample
n
2
xi
2
f 1 x1
xi
N
1
2
fi Di
N
k
i
N
s
A =
A
1
Population
x
Di
N
Group data
x
N
1
2
N
1
R
Coeff. MD =
Ungroup data
N
A =
fi X i
N
Coefficient of MD
2
Q1
Xi
N
G
Q1
Q3
1
MD
Q3
QD
2
i
i
1
1
n
Group data
Standard Deviation
SD X
[SD(X)]
Coefficient of
VAR X
CV
Variation (CV)
VAR(X) =
=
SD ( X )
2
/ s2
A
.
R
AM ( X )
Mean
Skewness
11304042
Mode
The distribution is positively skewed
Mean
Median
Mode
The distribution is negatively skewed
Mean
24.
Median
Median
Mode
The distribution is symmetric
Page 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stat101formulaesheet-140222123345-phpapp01/85/Stat-101-formulae-sheet-3-320.jpg)
![L5- Index Number
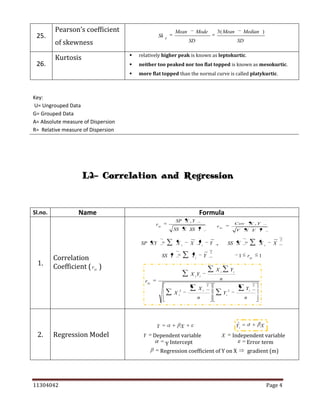
Name
Sl.no.
1.
Un-weighted Index
Numbers (Simple
Aggregative Method)
Formula
2.
Total of base year prices for various commodities
P
1
* 100
P
0
N
P
01
Where N refers to no. of items
log[
P
1
* 100 ]
P
0
log P
01
log P
or
N
Where
3.
* 100
P0
Total of current year prices for various items
P1
P0
Un-weighted Index
Numbers (Simple
Average Relative of
Method)
P1
P01
P01
Laspeyres Method
N
P1
P
* 100
P2
PQ
1 0 * 100
P Q
0 0
Weight is Base year quantity
4.
P
01
Paasche Method
PQ
1 1
* 100
P Q
0 1
Weight is Current year quantity
5.
6.
Dorbish and Bowley’s
Method
P1 Q 0
[Where L
Fisher’s ‘Ideal’ Method
8.
Marshall – Edgeworth
Method
Kelly’s Method
P
01
P
P0 Q 1
2
P1Q 0
L*P
Paasche Index]
P1Q1
*
P0 Q 0
(Q 0
Q1 ) P1
(Q 0
Q1 ) P0
Paasche Index]
P1Q 0
P1Q
P1Q1
P0 Q 0
* 100
P
01
* 100
P0 Q1
Laspeyres Index and P
[Where Q
11304042
* 100
2
Lasperes Index and P
P
01
[Where L
7.
L
P
01
P1 Q 1
P0 Q 0
P0 Q1
* 100
* 100
P0 Q
Q0
Q1
2
]
Page 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stat101formulaesheet-140222123345-phpapp01/85/Stat-101-formulae-sheet-10-320.jpg)
