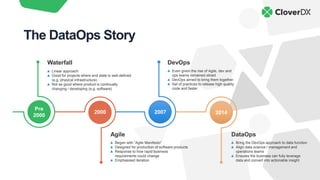
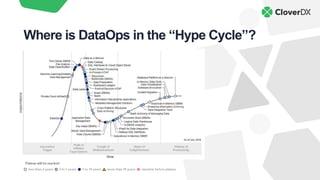
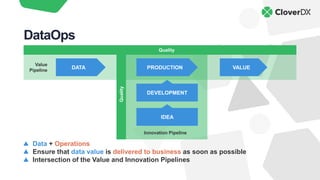
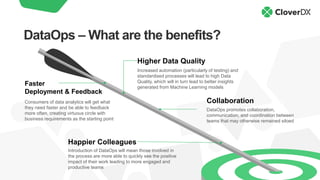
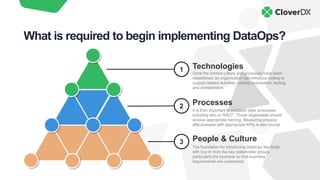
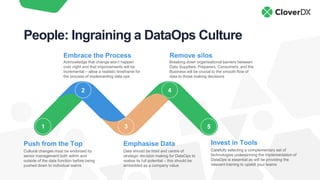
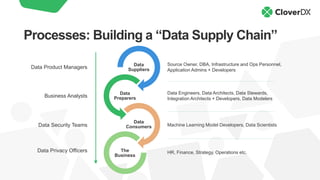
The document discusses DataOps as an evolution of Agile and DevOps, aimed at improving collaboration between data teams and the broader business to enhance data utilization for actionable insights. It outlines the benefits and principles of DataOps, emphasizing the importance of processes, people, culture, and technology in its implementation. Additionally, it provides a case study of Facebook's DataOps journey and highlights essential techniques for successful DataOps delivery.