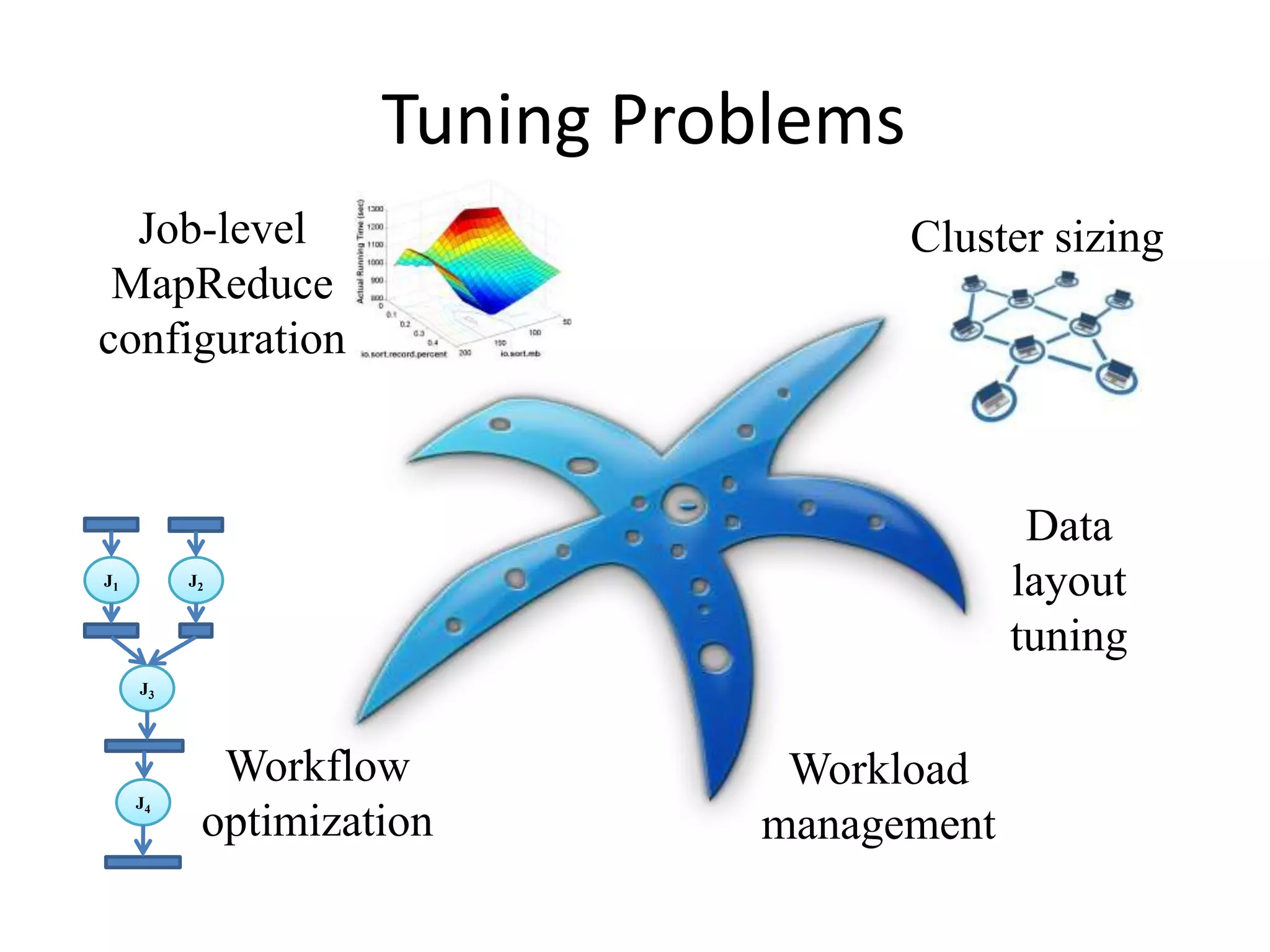
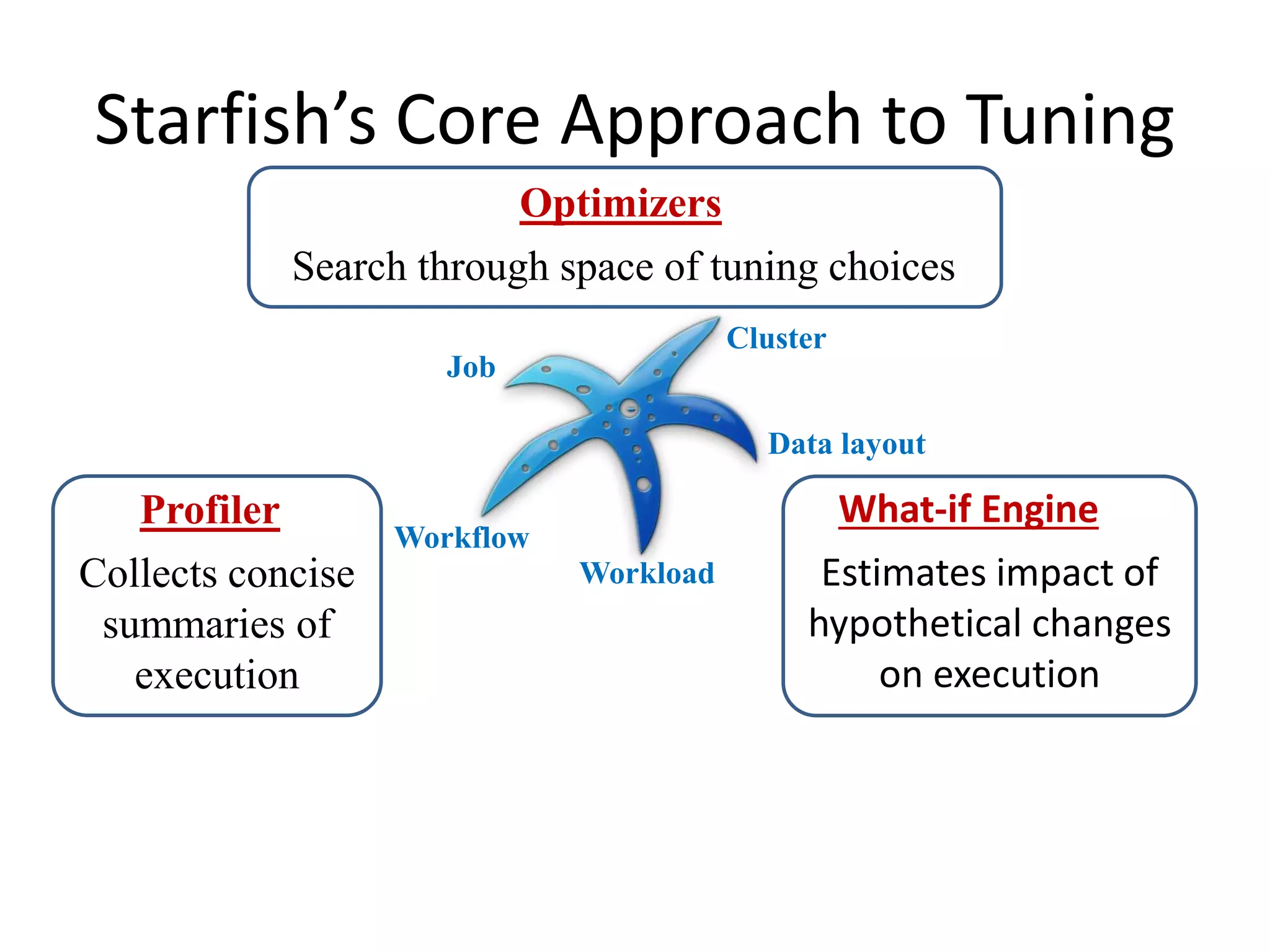
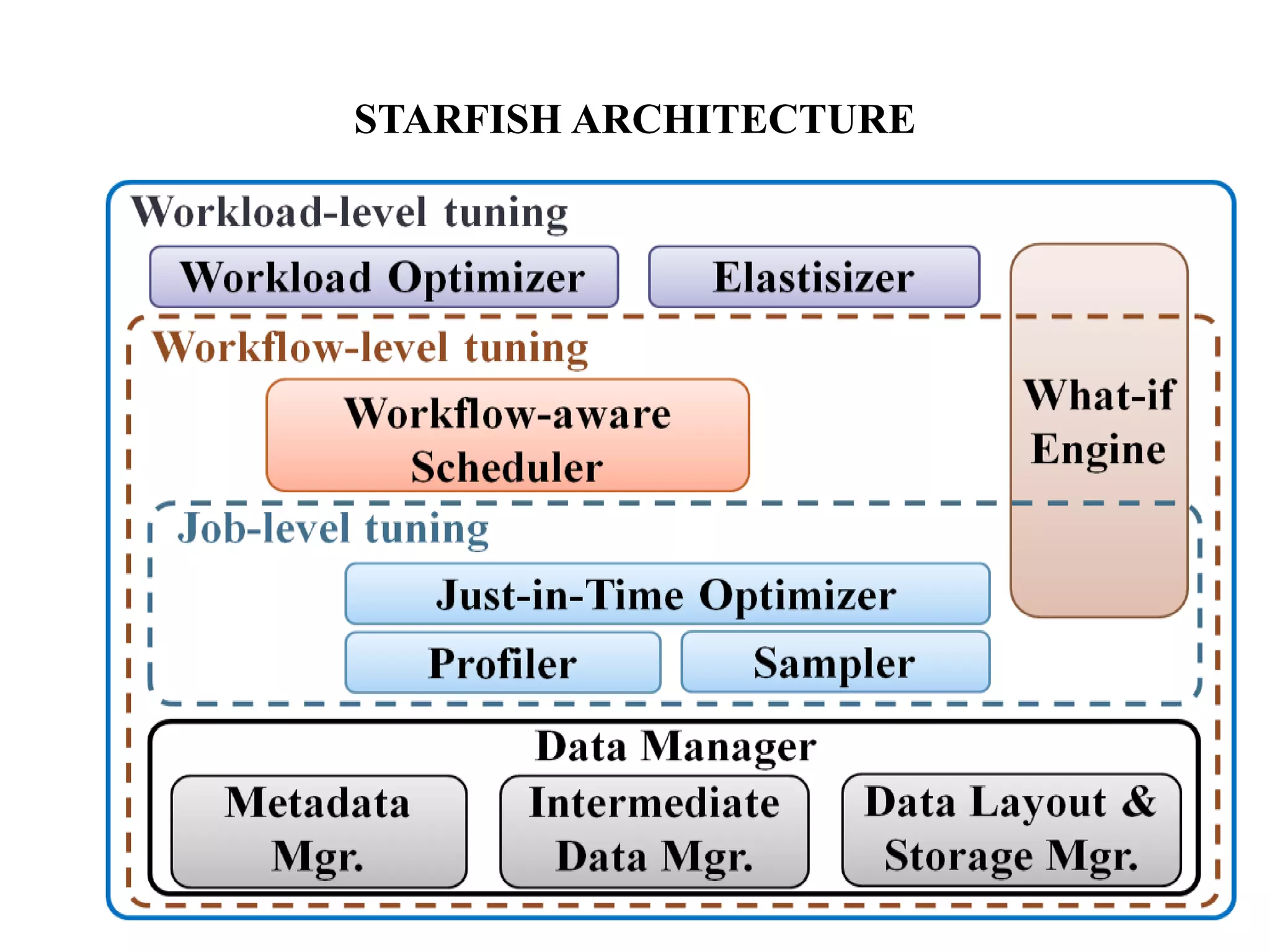
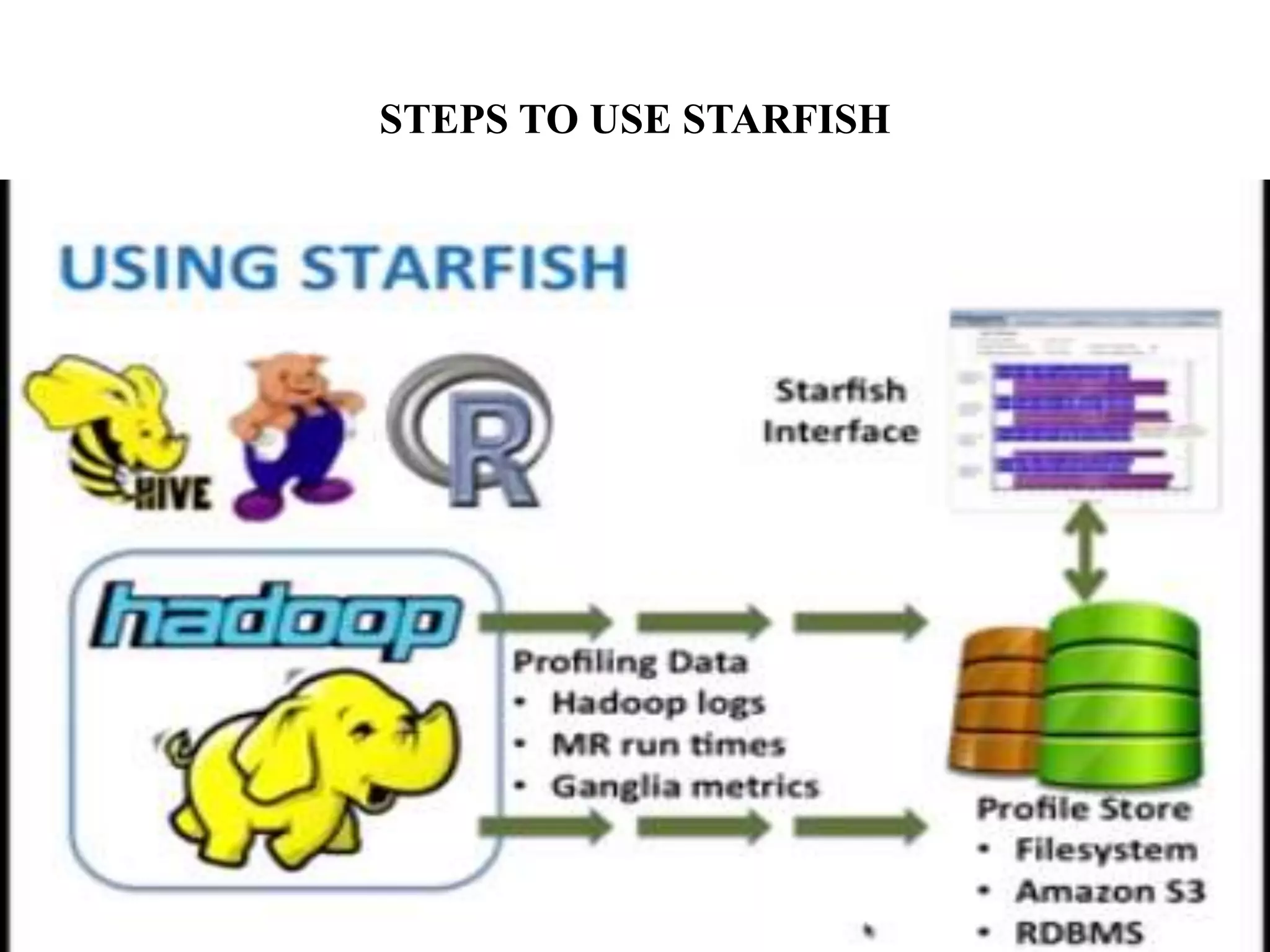
Starfish is a self-tuning system for improving performance in Hadoop big data analytics. It collects execution profiles from Hadoop clusters, then uses a what-if engine and optimizers to search for and estimate the impact of different tuning configurations on jobs, workflows, and workloads. The goal of Starfish is to enable users and applications to get good performance automatically throughout the data lifecycle in Hadoop.