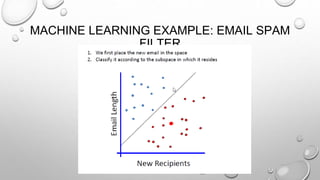
The document discusses the significance of big data from both business and technical perspectives, highlighting benefits such as cost savings, time reductions, and improved product development. It emphasizes the necessary infrastructure for managing big data, including the use of tools like Hadoop and Apache Spark, and strategies for effective implementation. Additionally, it outlines the importance of understanding customer behavior and market conditions to enhance business operations and decision-making.