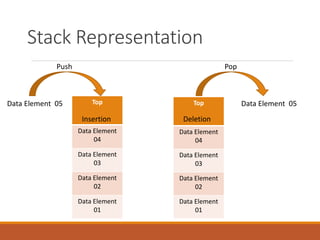
1) A stack is a linear data structure that follows LIFO (last in, first out) ordering. Data is inserted using push operations and removed using pop operations.
2) A queue is a linear structure that follows FIFO (first in, first out) ordering. Data is inserted at the rear of the queue and removed from the front.
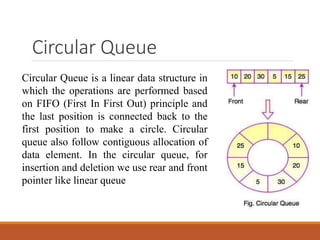
3) There are two main types of queues - linear and circular queues. Linear queues have separate front and rear pointers while circular queues connect the last position to the first to form a circle.


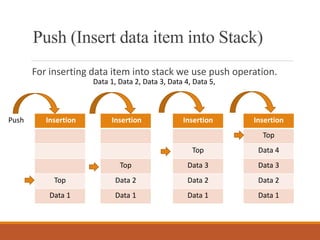
![Algorithm for insert data into stack
Step 1. Check stack if full
If Top=Max-1
Print stack is full and exit
Step 2: Increment to by one
Top=Top+1
Step 3: Insert data into stack
Stack[TOP]=data
Step 4: End
1
2
1
3
2
1
4
3
2
1
5
4
3
2
1
Push
2
Push
3
Push
4
Push
5
Push
1
Max
size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackandqueue-211110101458/85/Stack-and-queue-4-320.jpg)
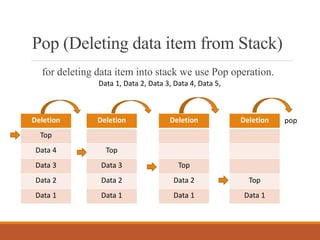
![Algorithm for insert data into stack
Step 1: Check stack is empty
If TOP=-1
Print Stack is empty and Exit
Step 2: delete an element from stack top
Set Del_element=Stack[Top]
Step 3: decrement stack size by one
Top=Top-1
Step 4: End
5
4
3
2
1
4
3
2
1
3
2
1
2
1
Max
size Pop
5
Pop
4 Pop
3
1
Pop
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackandqueue-211110101458/85/Stack-and-queue-6-320.jpg)


![Insertion Data item into Queue
Rear
Front
Front
Front
Front
Front
Rear
Rear
To insert data element into queue, we use rear pointer all data element inserted only rear end.
Algorithm for Insert an element into Queue
Step 1: Check if the queue is full.
If rear == max-size-1
Print Queue is full and exit
Step 2: Add and element into Queue
SET REAR = REAR + 1
Step 3: data element insert at rear pointer .
Set QUEUE[REAR] = NUM
Step 4: return success.
10
10 20
10 20 30
10 20 30 40
Rear
Rear
10 20 30 40 50
Rear
Front](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackandqueue-211110101458/85/Stack-and-queue-10-320.jpg)
![Deletion Data item From Queue
Algorithm for Delete an element From Queue
Step 1: Check if the queue is Empty.
If FRONT == -1 or FRONT >REAR
Print Queue is Empty and exit
Step 2: Delete an data element from Queue
SET FRONT = FRONT + 1
Step 3: data element insert at rear pointer .
Set Data element = QUEUE[FRONT]
Step 4: return success.
To Delete data element from queue, we use front pointer all data elements delete
only front end.
10 20 30 40 50
Front
Rear
20 30 40 50
30 40 50
40 50
50
Front
Front
Front
Front
Rear
Rear
Rear
Rear](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackandqueue-211110101458/85/Stack-and-queue-11-320.jpg)