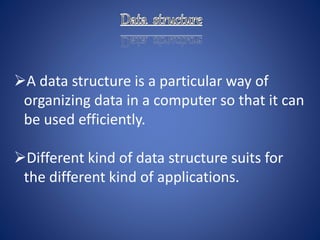
This document discusses queues, which are linear data structures that follow a first-in, first-out (FIFO) principle. Elements are added to the rear of the queue and removed from the front. Circular queues are also covered, which connect the rear and front to address limitations of linear queues. Real-world applications of queues include lines at stores, waiting on hold, escalators, and bookstore checkouts. Algorithms for enqueue and dequeue operations on both linear and circular queues are provided.





![12 9 7 18 5
A[0] A[1] A[2] A[3] A[5] A[6]
Queue
rearfront
12 9 7 18 5 14
9 7 18 5 14
Queue after insertion of new element rearfront
Queue after deletion of an element
rearfront](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-180919144500/85/Queue-8-320.jpg)
![Algorithm:- enqueue
Input:-queue[Max],FRONT,REAR,VALUE
Output:-queue of elements
Begin:-
STEP:1- IF REAR= MAX-1
Print “Queue is OVERFLOW”
Return.
STEP:2- If (FRONT=-1)
FRONT=FRONT+1
STEP:3- REAR = REAR+1
queue[REAR] = VALUE
STEP:4- END.
INITIALLY
REAR = -1
FRONT =-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-180919144500/85/Queue-9-320.jpg)
![Algorithm:- de_queue
Input:- queue[MAX],REAR,FRONT
Output:-deleted data ITEM
Begin:-
Step:1-If (REAR=-1)
Print “Queue is UNDERFLOW”
Return.
Step:2-ITEM=queue[FRONT]
Step:3-If (REAR=FRONT)
{
REAR=FRONT=-1
}
Else
FRONT=FRONT+1
Step:4- print deleted data ITEM
END.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-180919144500/85/Queue-10-320.jpg)

![STEP-1 If FRONT = (REAR+1)%MAX
write OVERFLOW
go to step 4
STEP-2 If (REAR=FRONT = -1)
{
REAR = FRONT = +1
}
Else
REAR = (REAR +1)%MAX
STEP-3 CQ[REAR] = NUM
STEP-4 EXIT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-180919144500/85/Queue-12-320.jpg)
![STEP-1 If FRONT = -1
write UNDERFLOW
go to step 3
STEP-2 ITEM =c_queue[FRONT]
STEP-3 If (FRONT = REAR)
{
FRONT = REAR= -1
}
Else{
FRONT = (FRONT +1)%MAX
}
STEP-3 EXIT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queue-180919144500/85/Queue-13-320.jpg)

