1) A 60-year-old woman presented to the ER with chest pain and was found to have an anterior ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) on her ECG.
2) Anterior STEMIs result from occlusion of the left anterior descending artery and carry a worse prognosis due to larger infarct size.
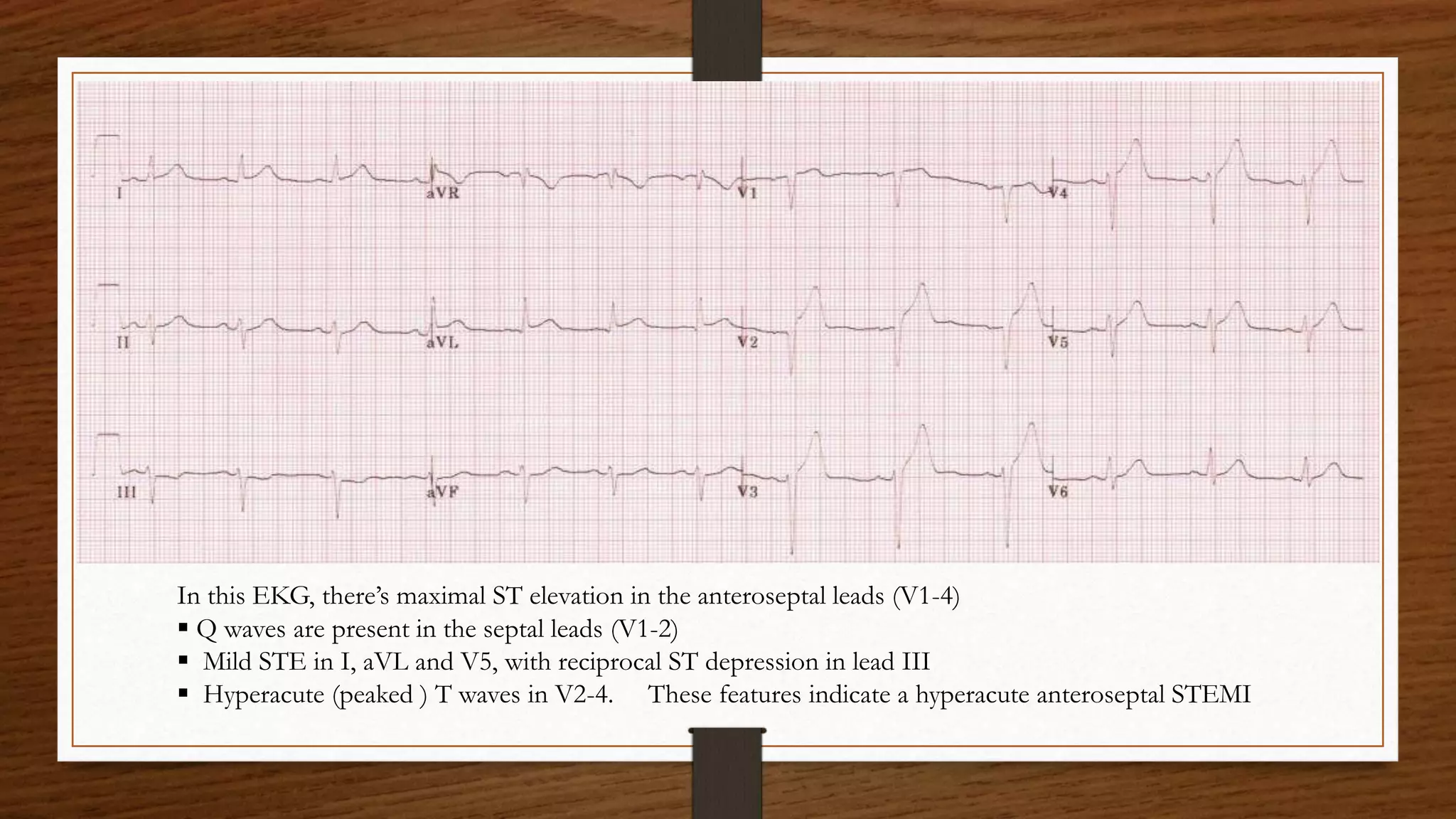
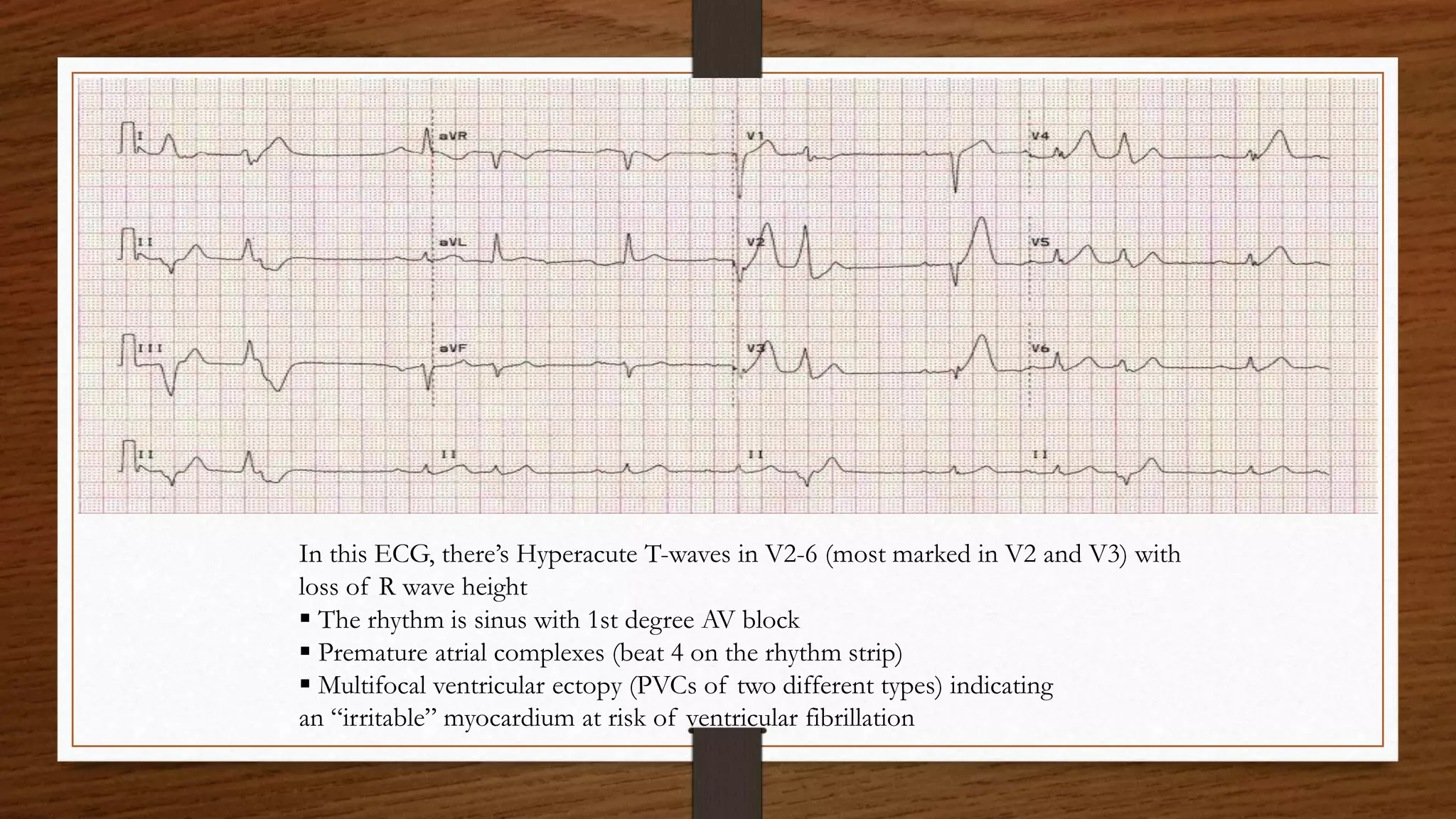
3) The ECG showed ST elevation in the precordial leads V1-V6 indicative of a large anterior wall infarction involving the proximal left anterior descending artery.