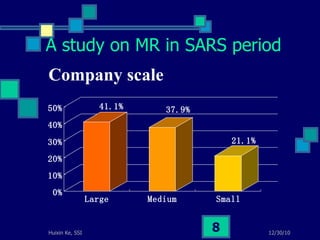
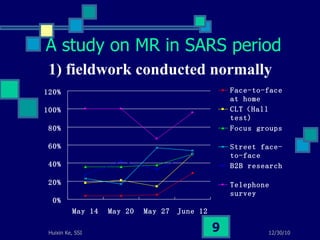
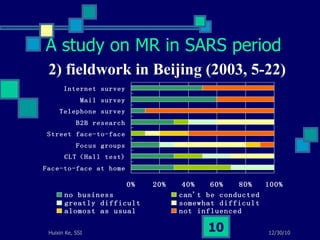
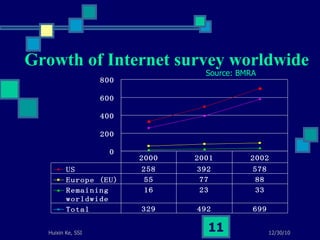
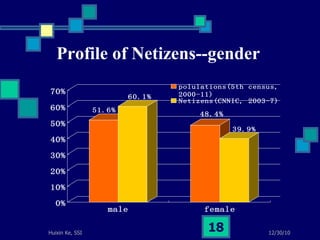
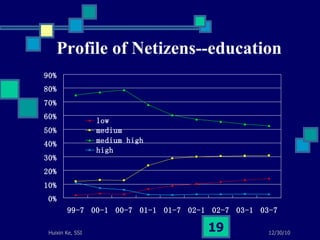
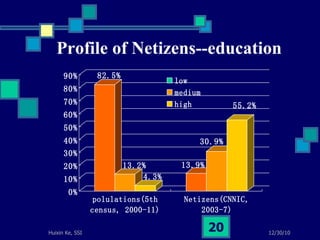
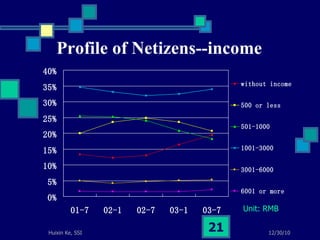
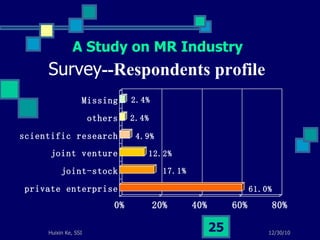
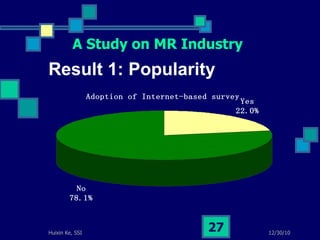
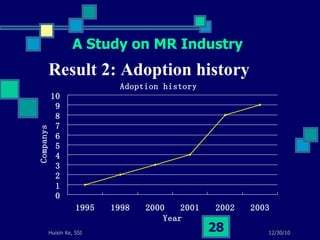
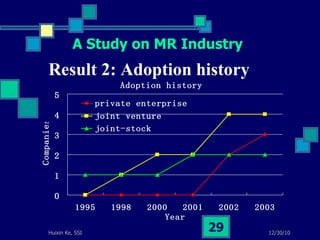
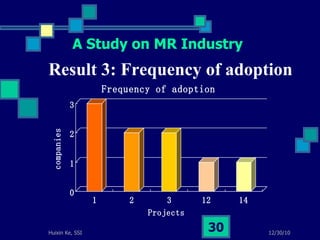
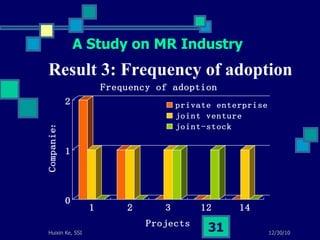
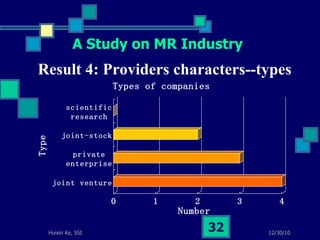
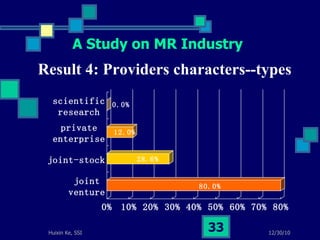
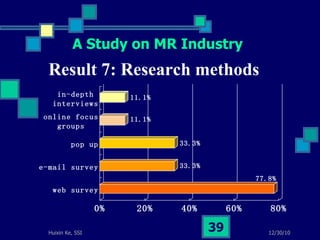
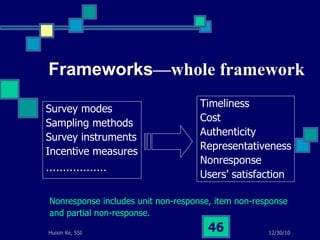
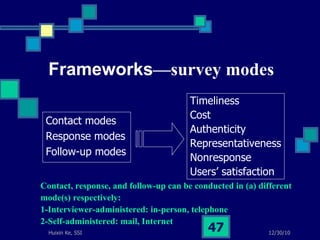
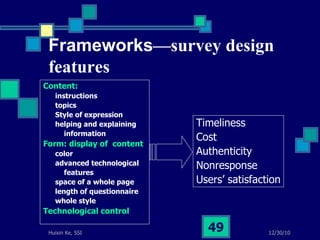
This document summarizes a study on internet-based survey methodology in China. It discusses the background and rise of internet surveys, current adoption and applications in China, obstacles and problems, and orientations for future research. Some key findings are that internet surveys are growing in popularity due to advantages like low cost and timeliness. However, there are also challenges regarding representativeness, response rates, and a lack of scientific methodology. The document proposes frameworks for future research focusing on new survey methods, sampling techniques, questionnaire design, and incentive strategies to address these issues.
![A Study of Internet-based Survey Methodology --Where can we go? Ke Huixin, Huang Gang Beijing Broadcasting Institute Email: hxke@public.bta.net.cn [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-101229211010-phpapp01/85/slide-1-320.jpg)