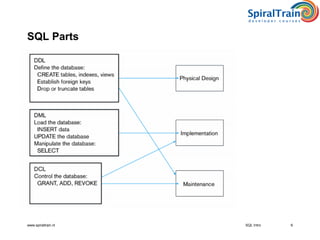
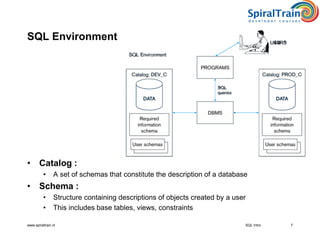
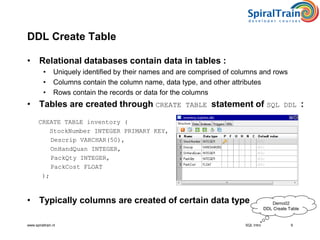
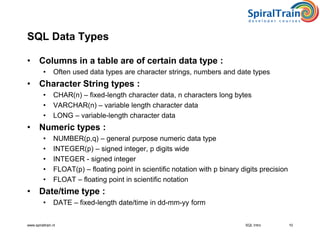
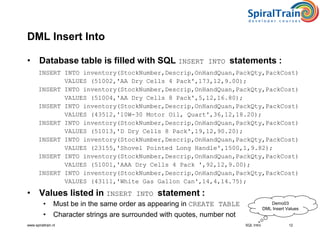
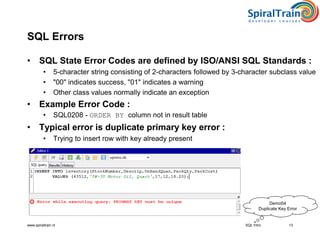
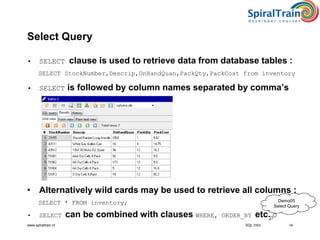
This document provides an overview of SQL, detailing its definition as a standard language for accessing relational database management systems, along with its various components including data definition, manipulation, and control languages. It covers the history of SQL, evolution of standards over the years, and the structure and types of SQL environment. Additionally, it explains SQL language elements, common data types, and examples of SQL commands and error handling.