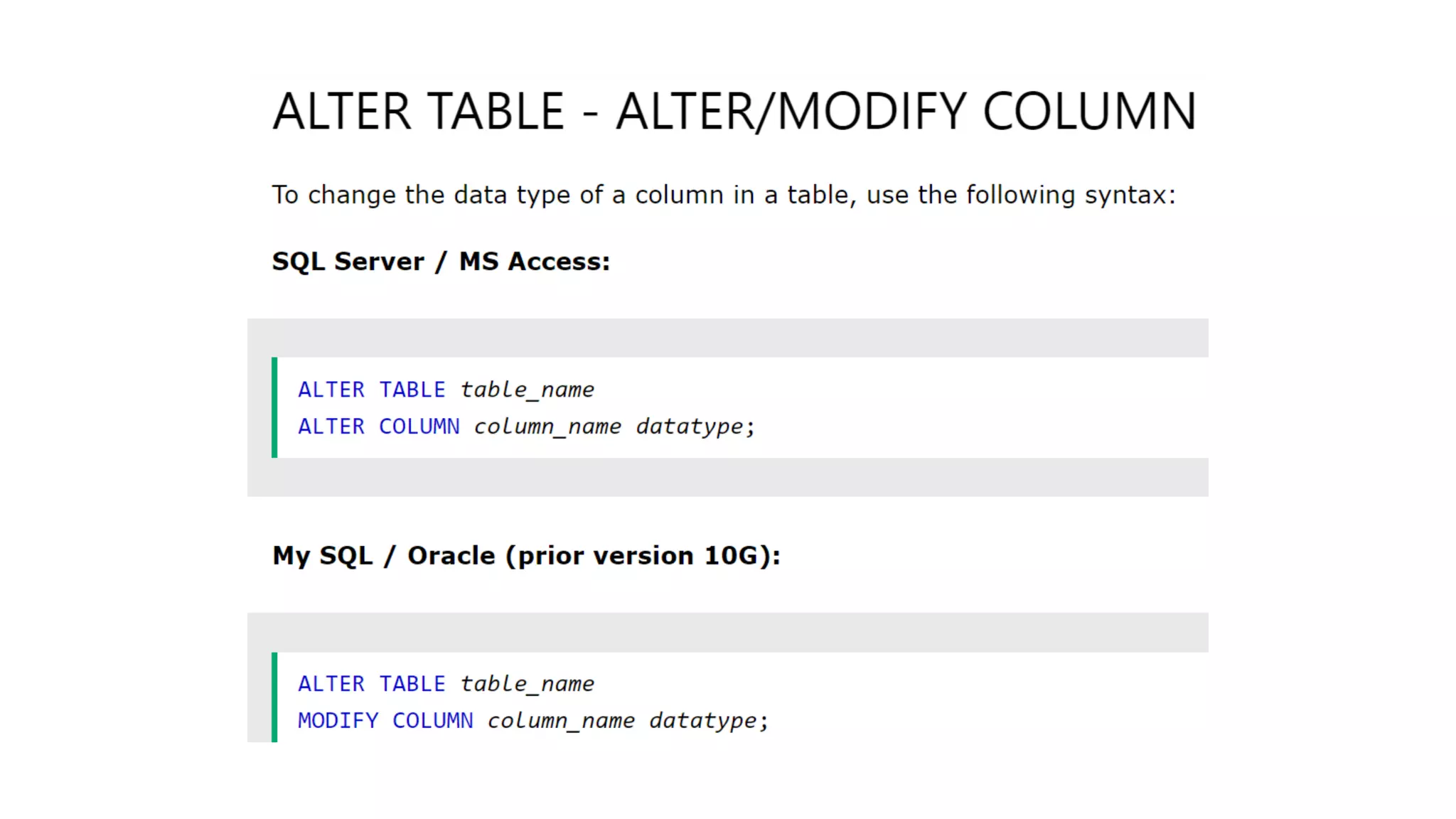
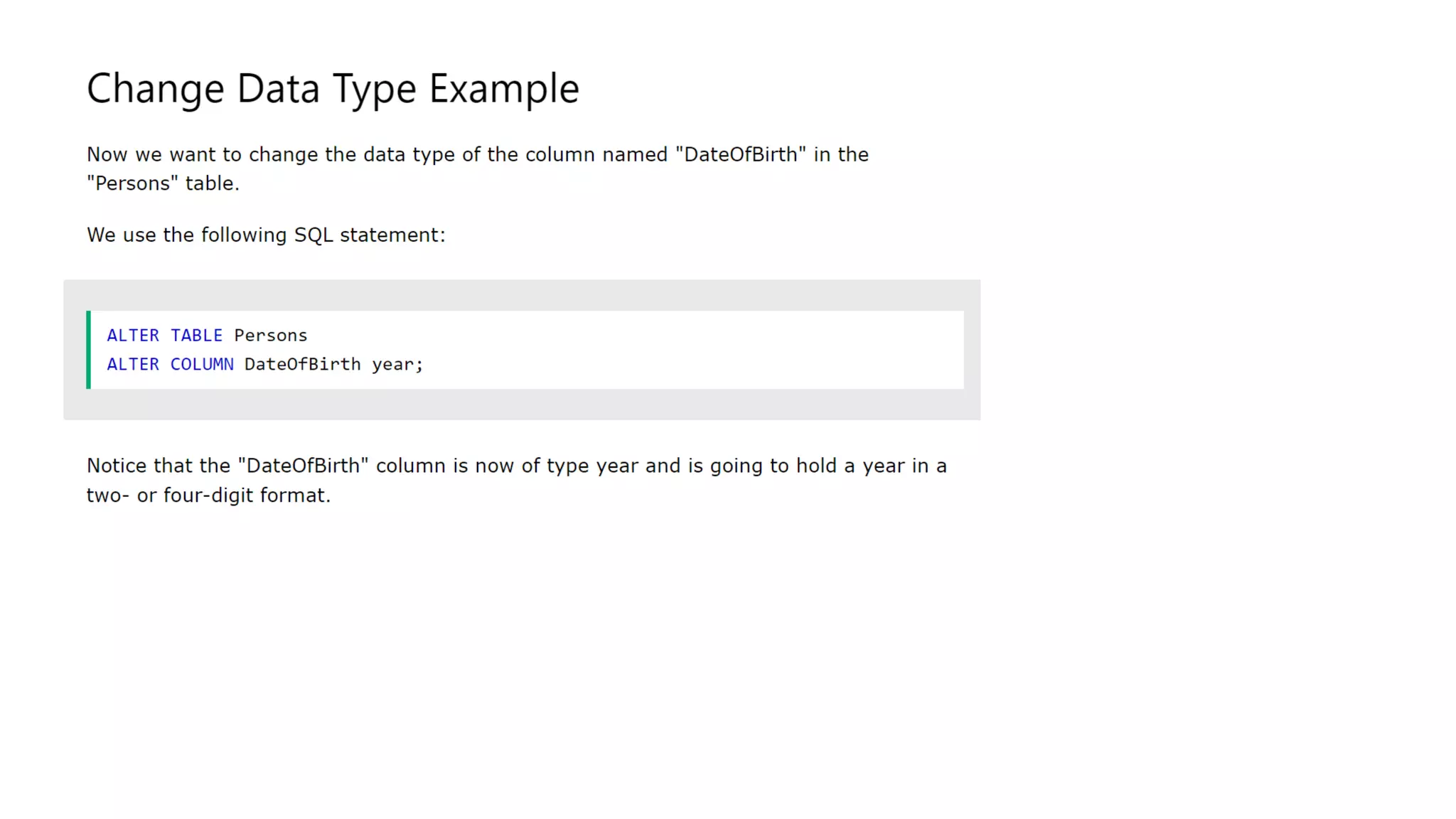
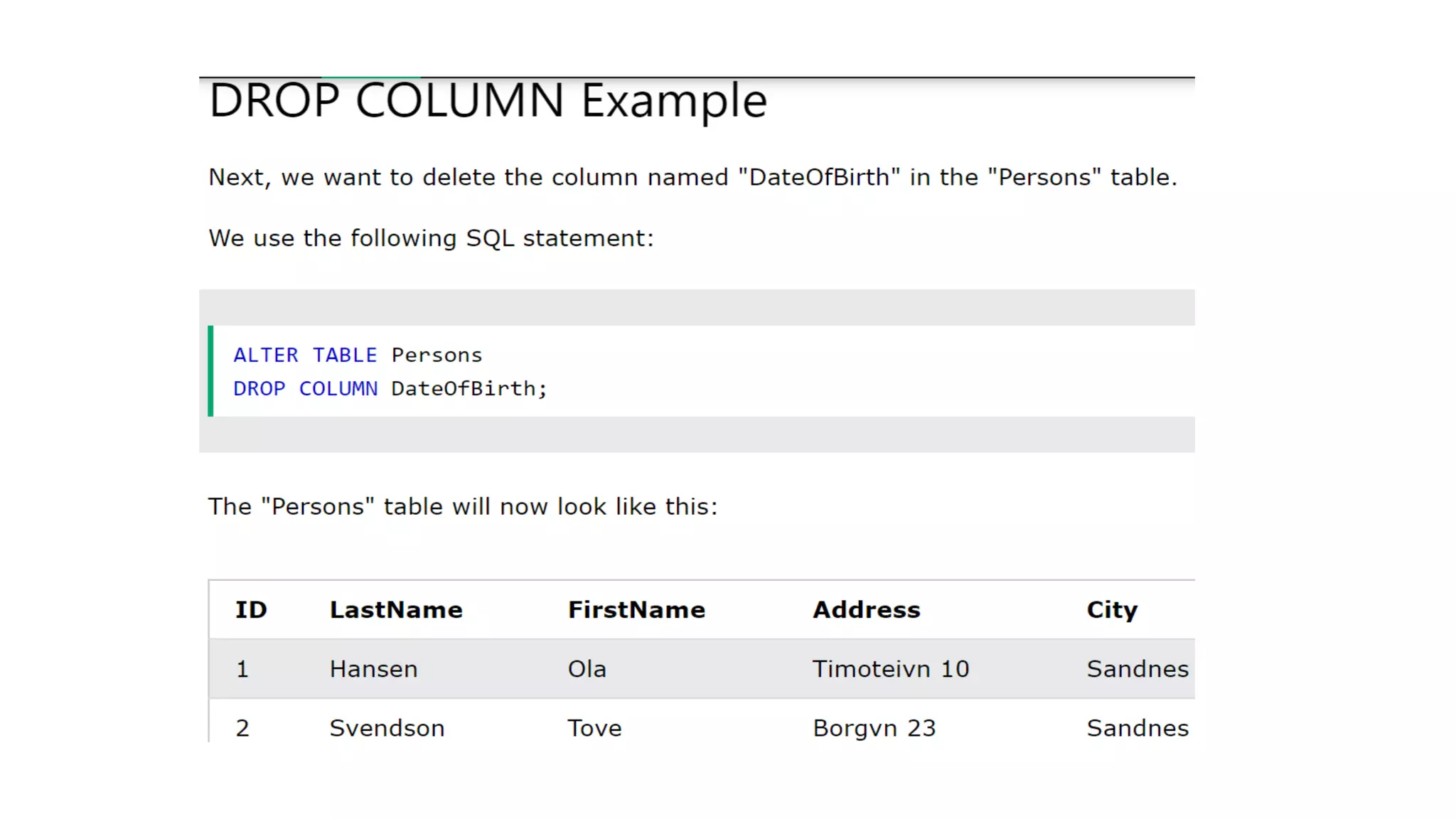
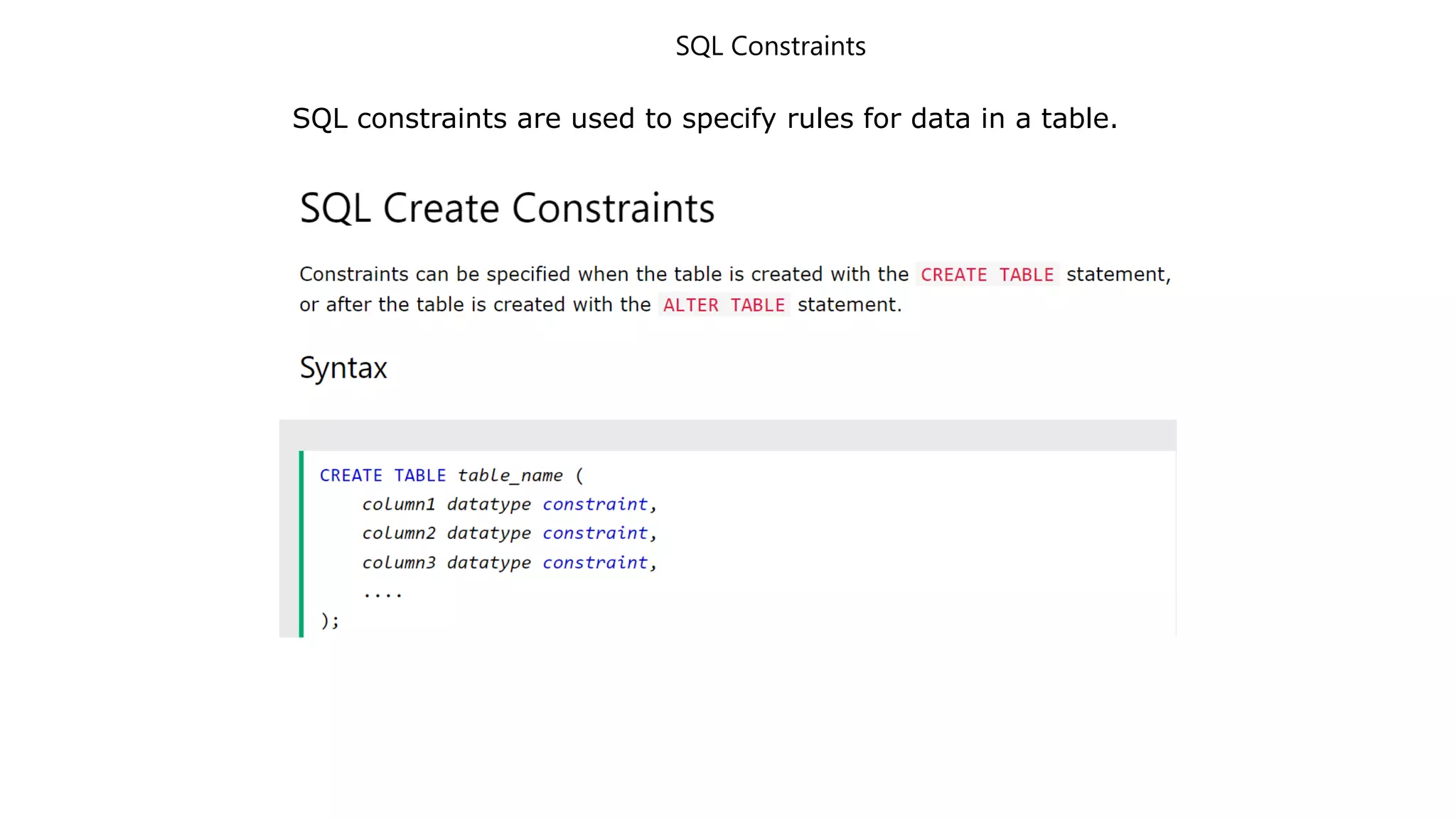
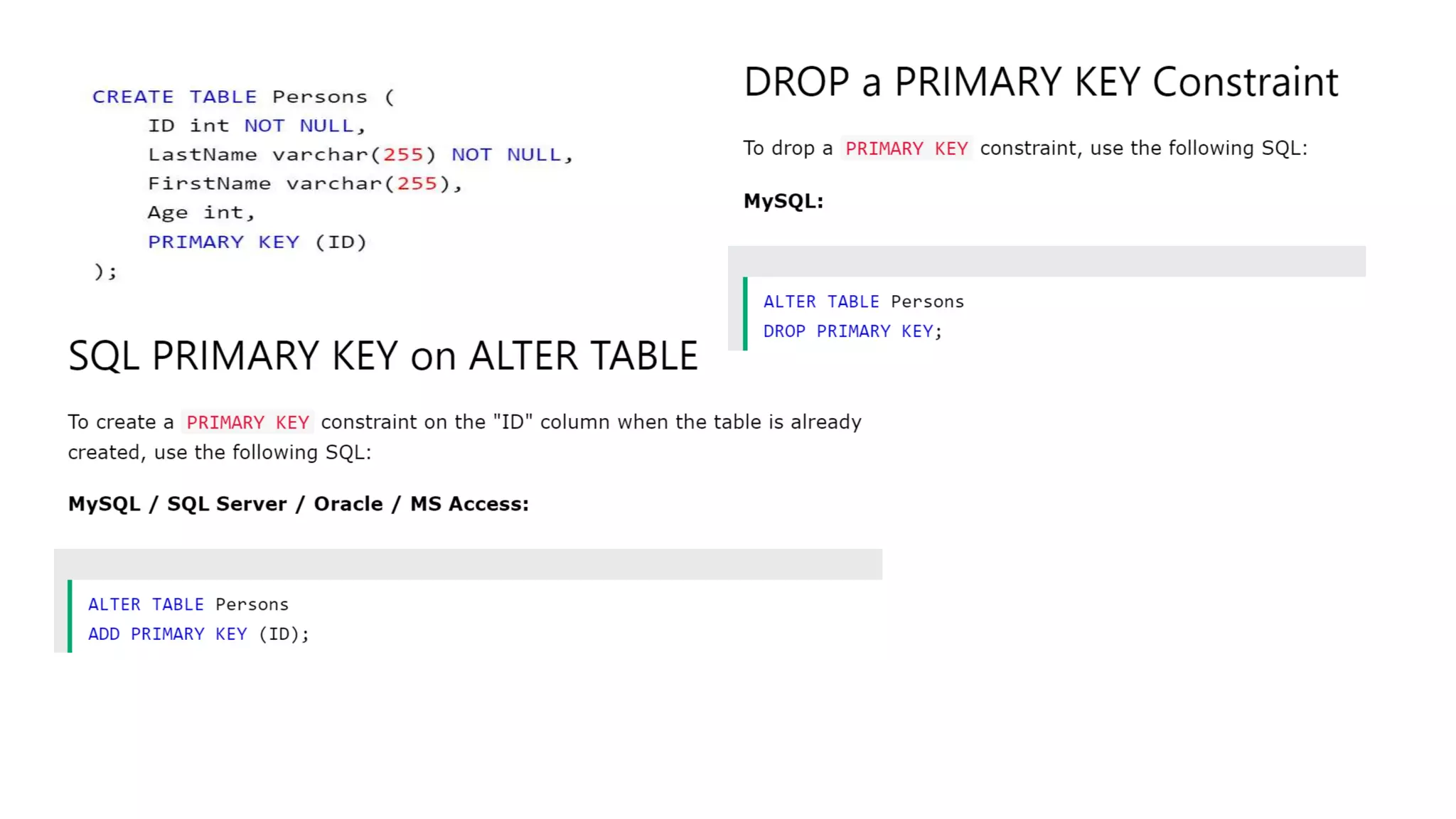
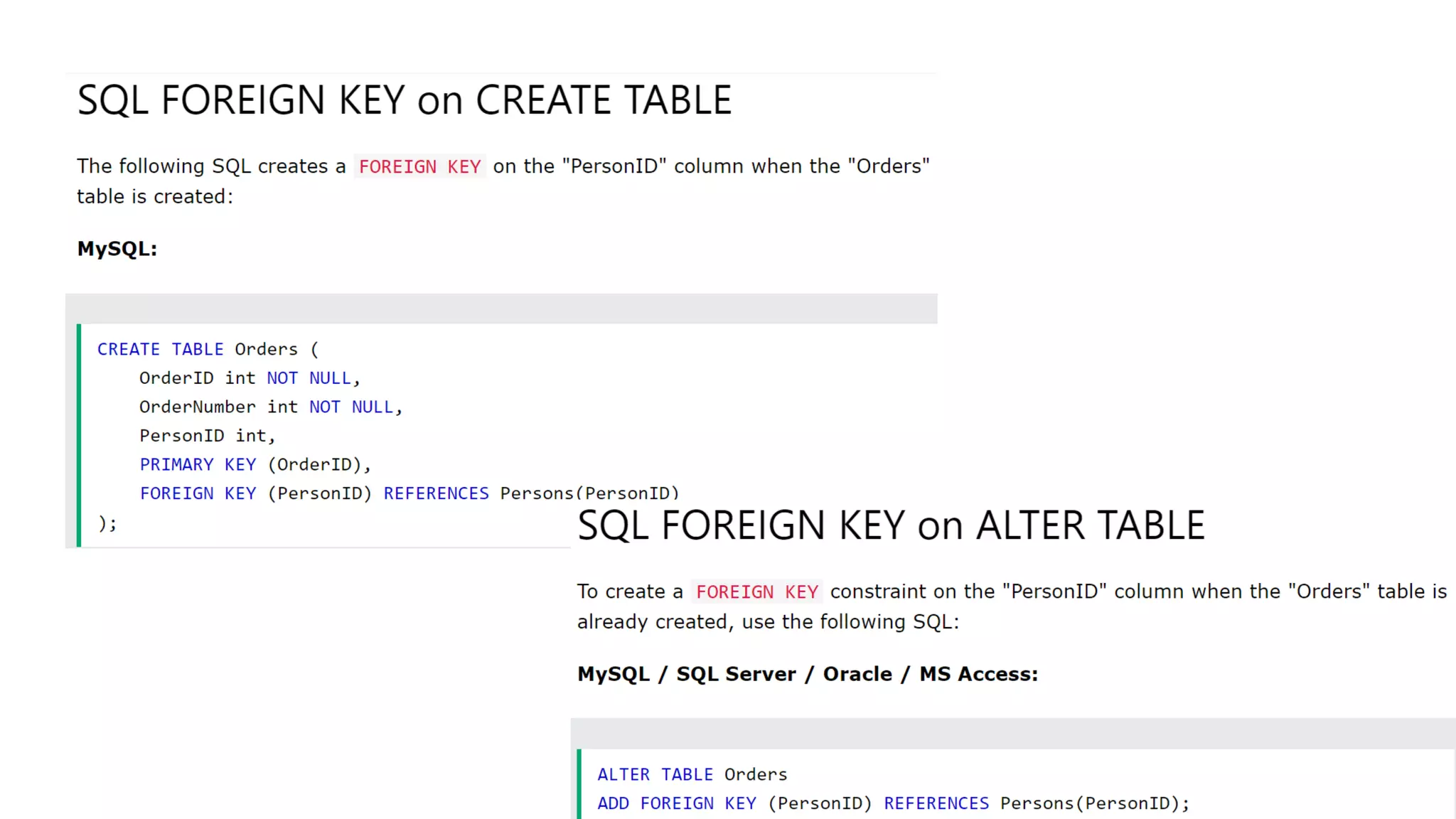
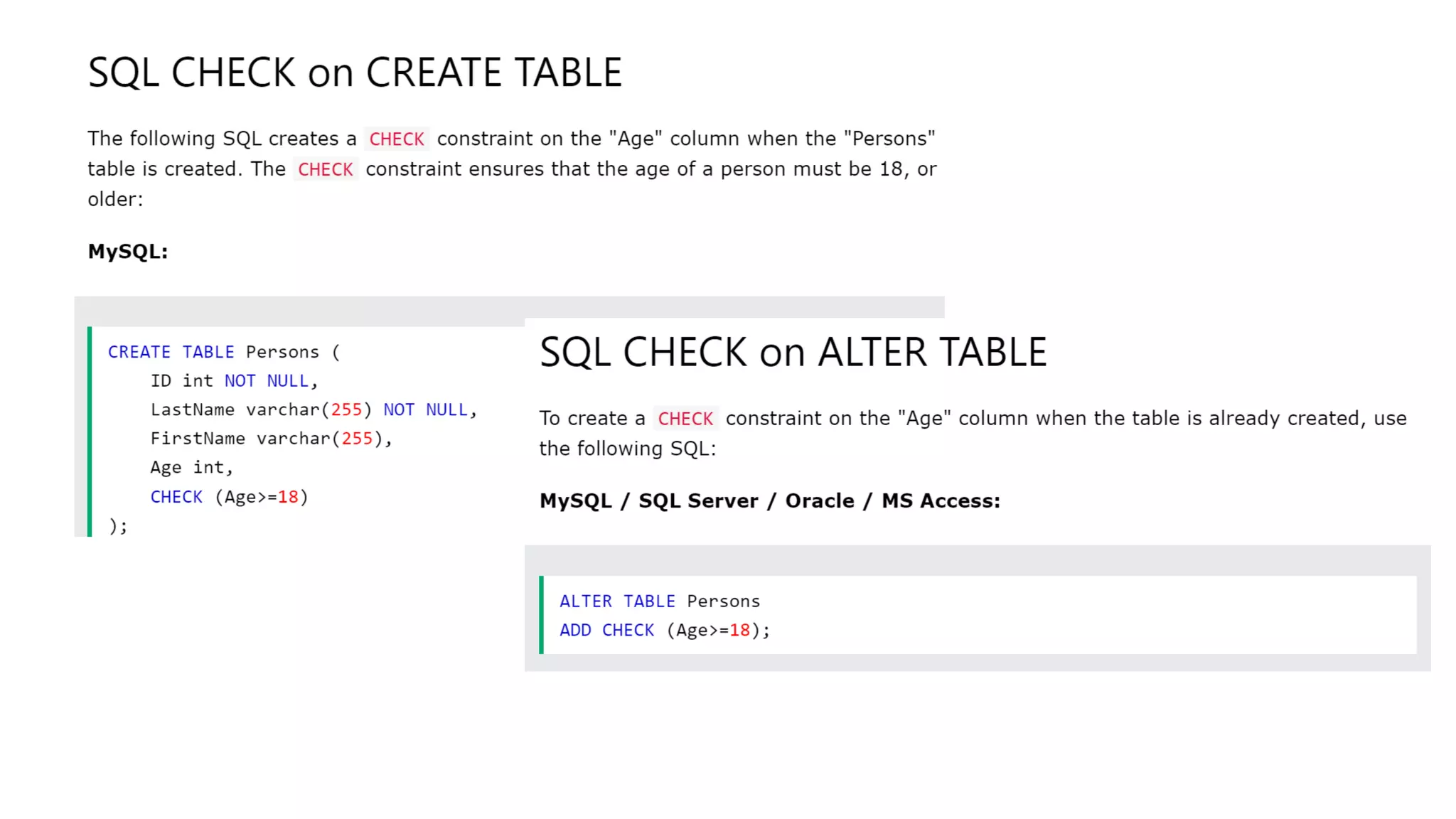
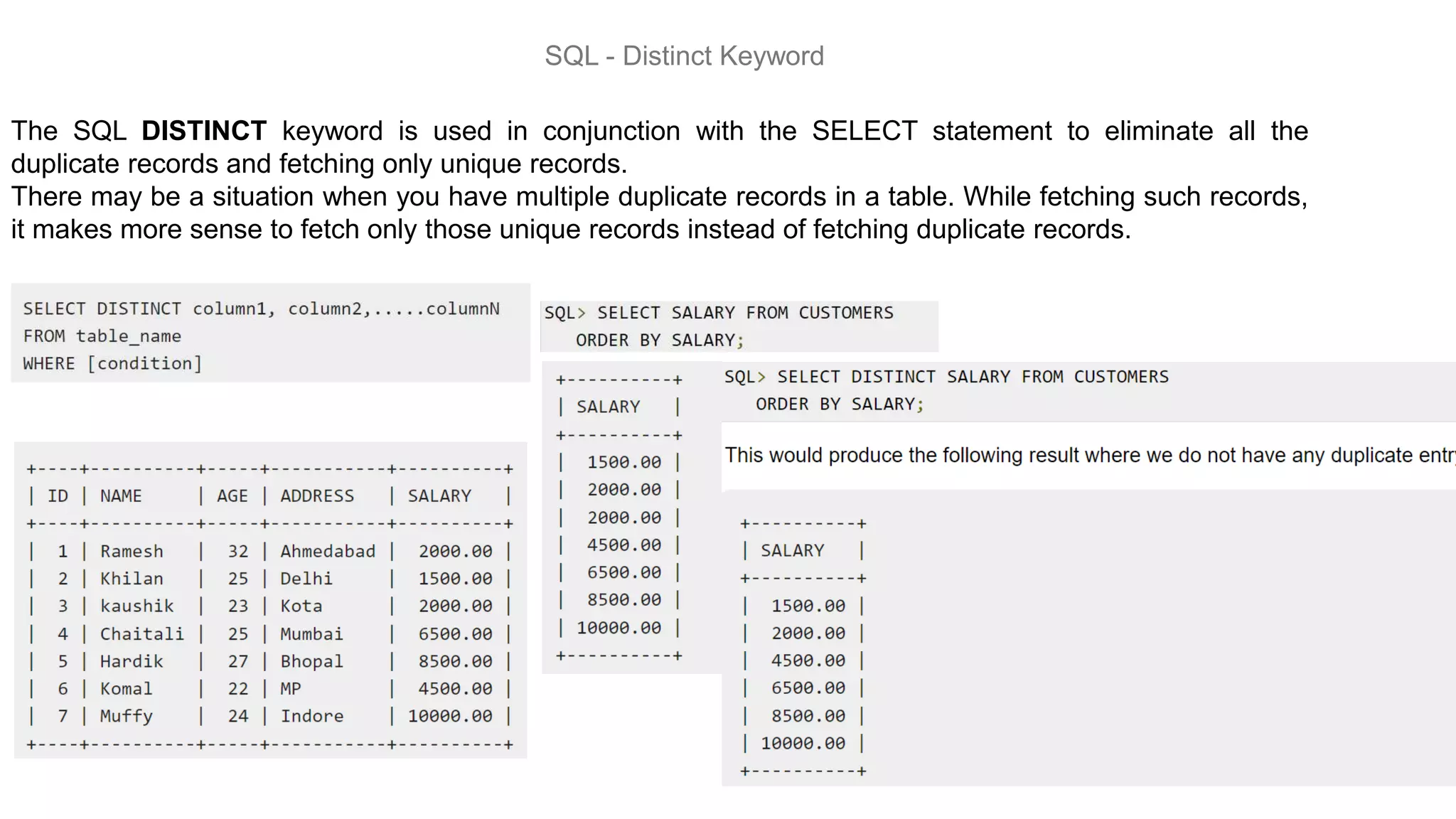
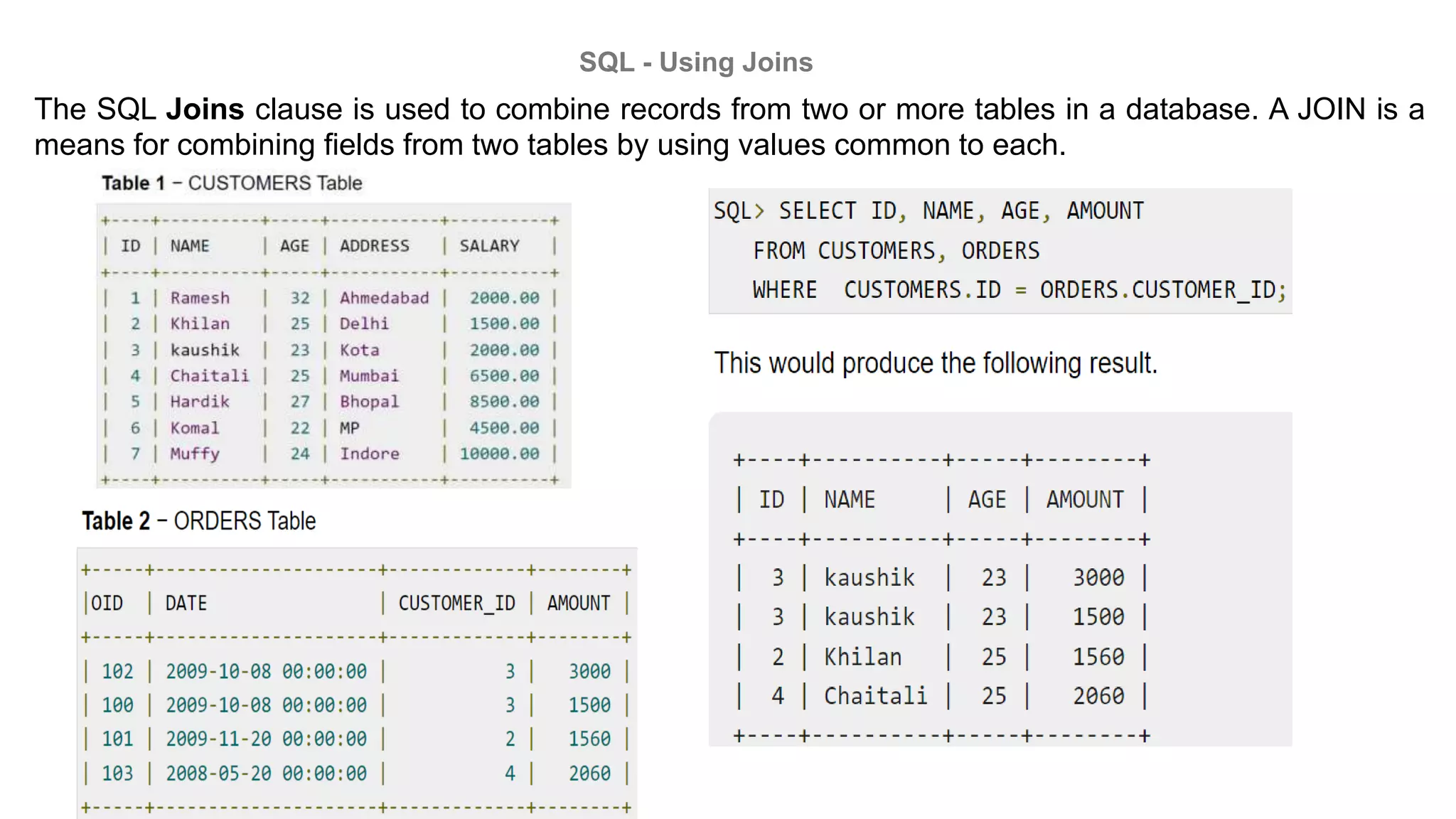
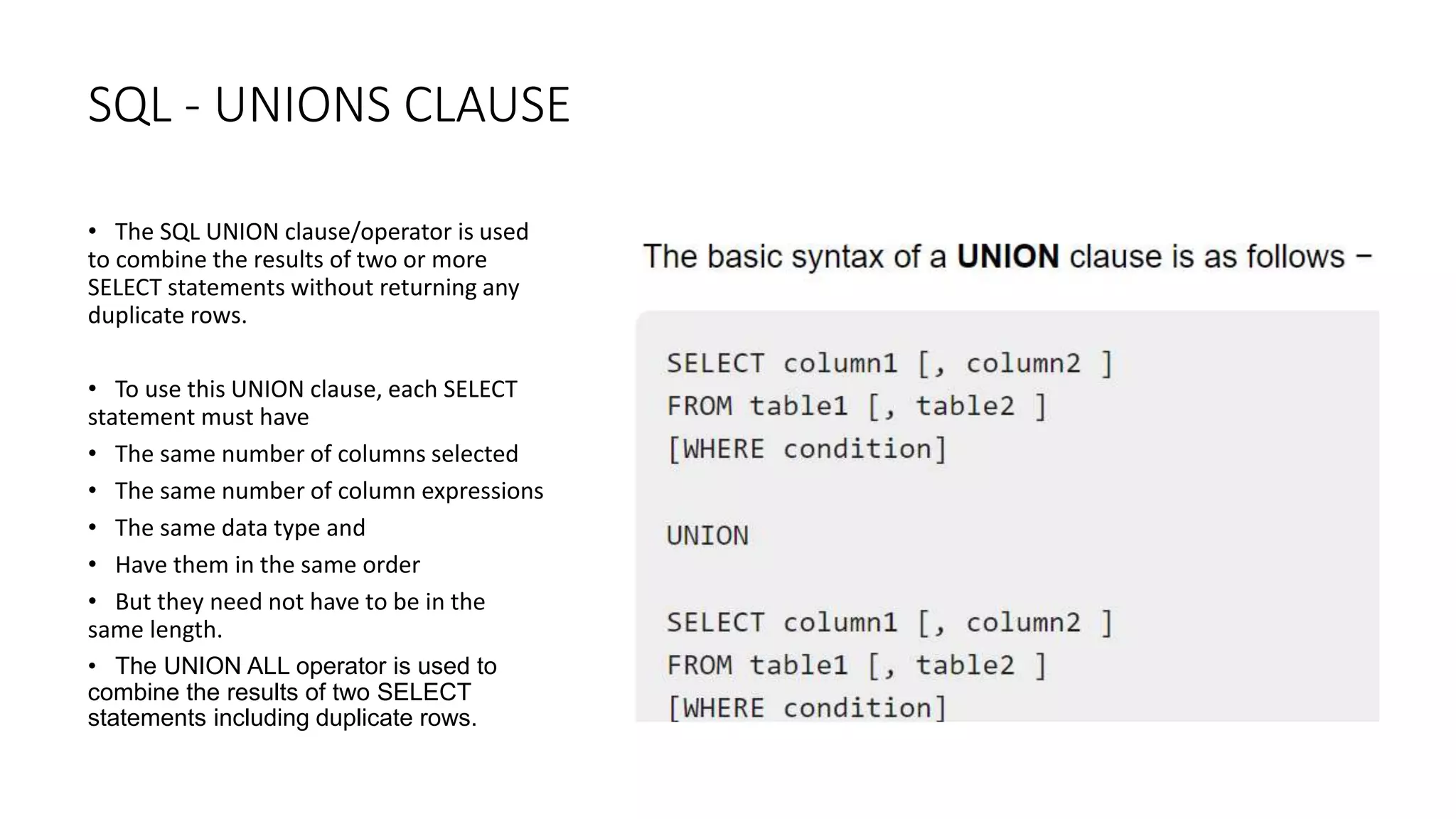
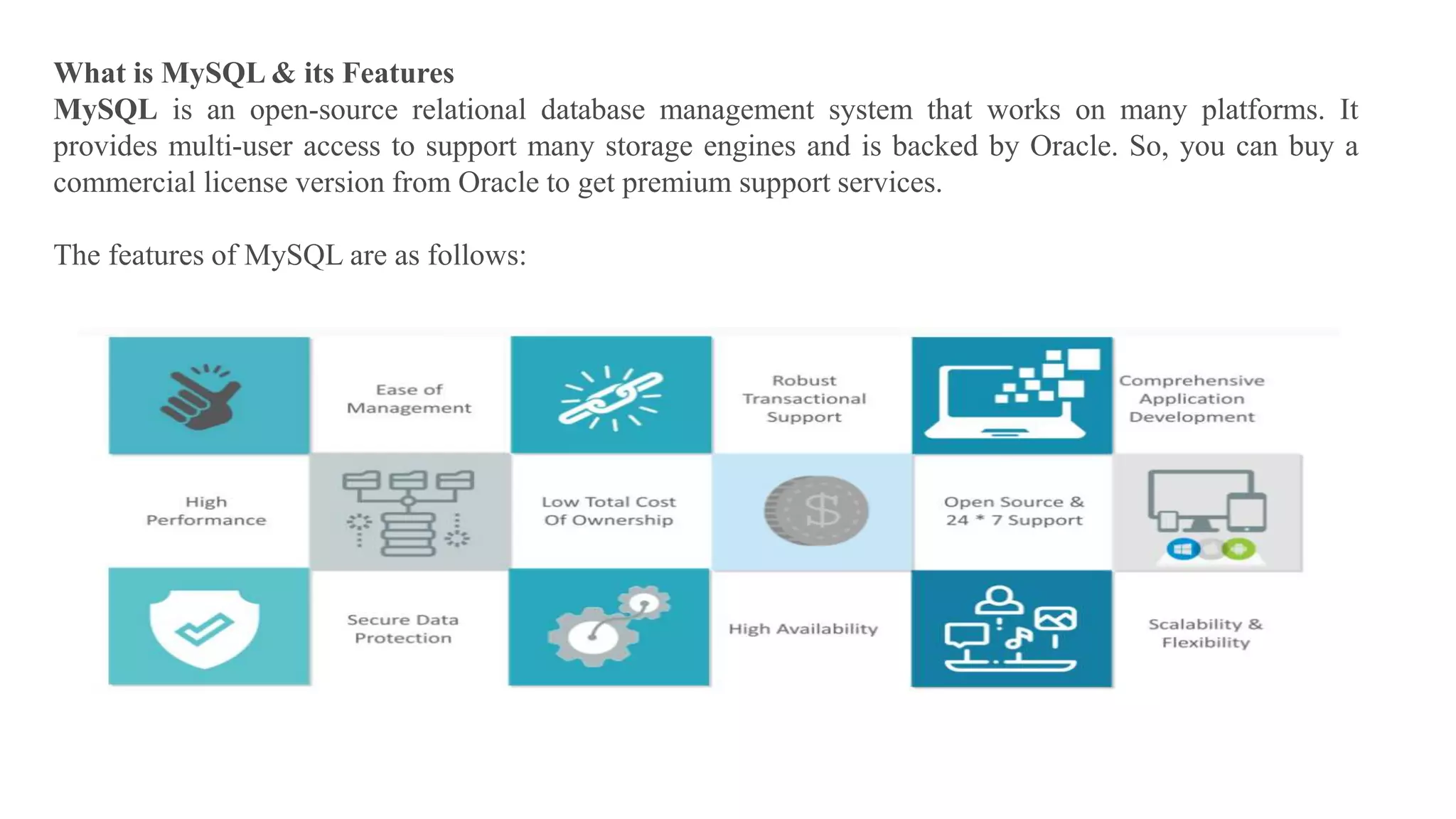
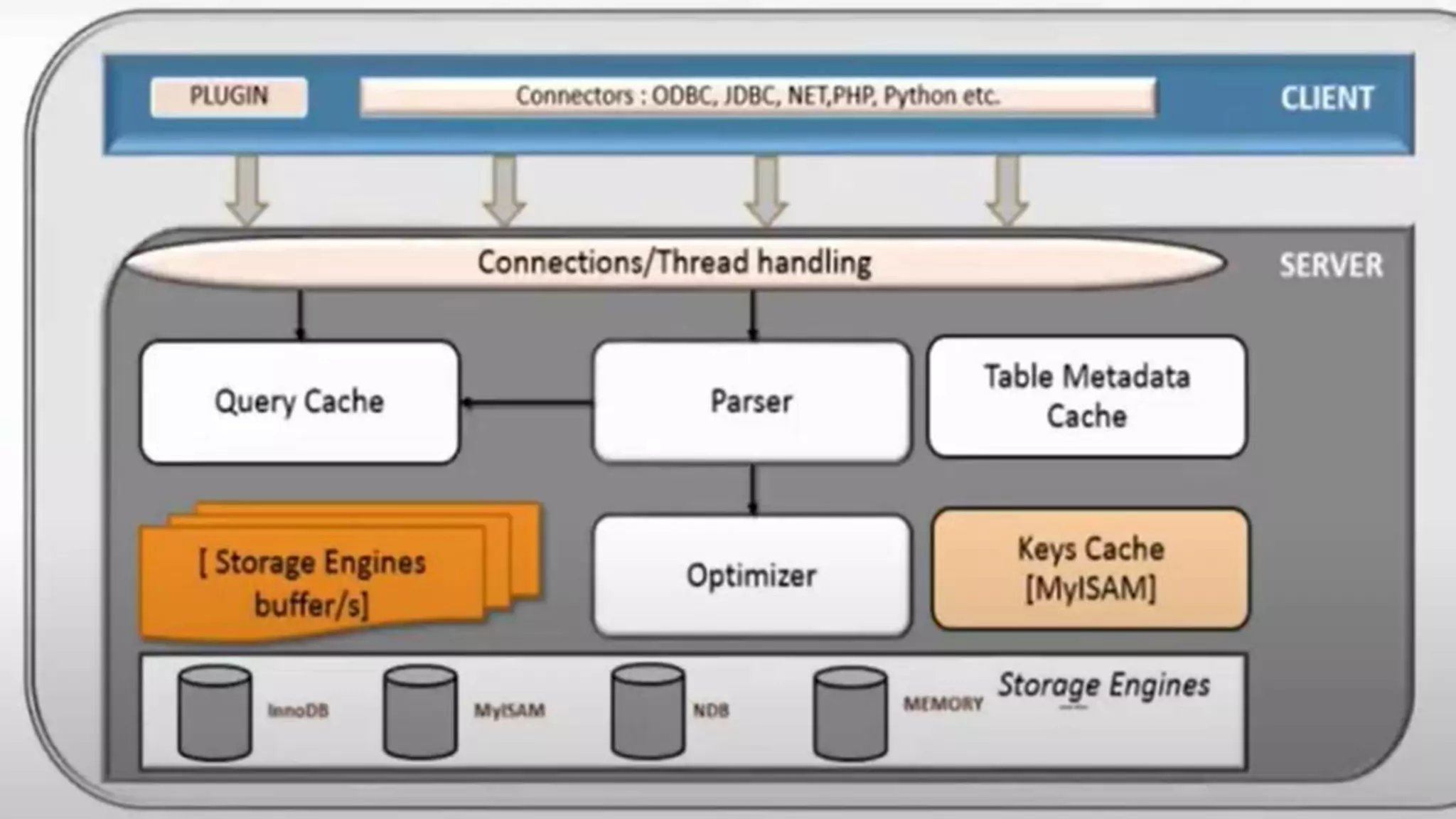
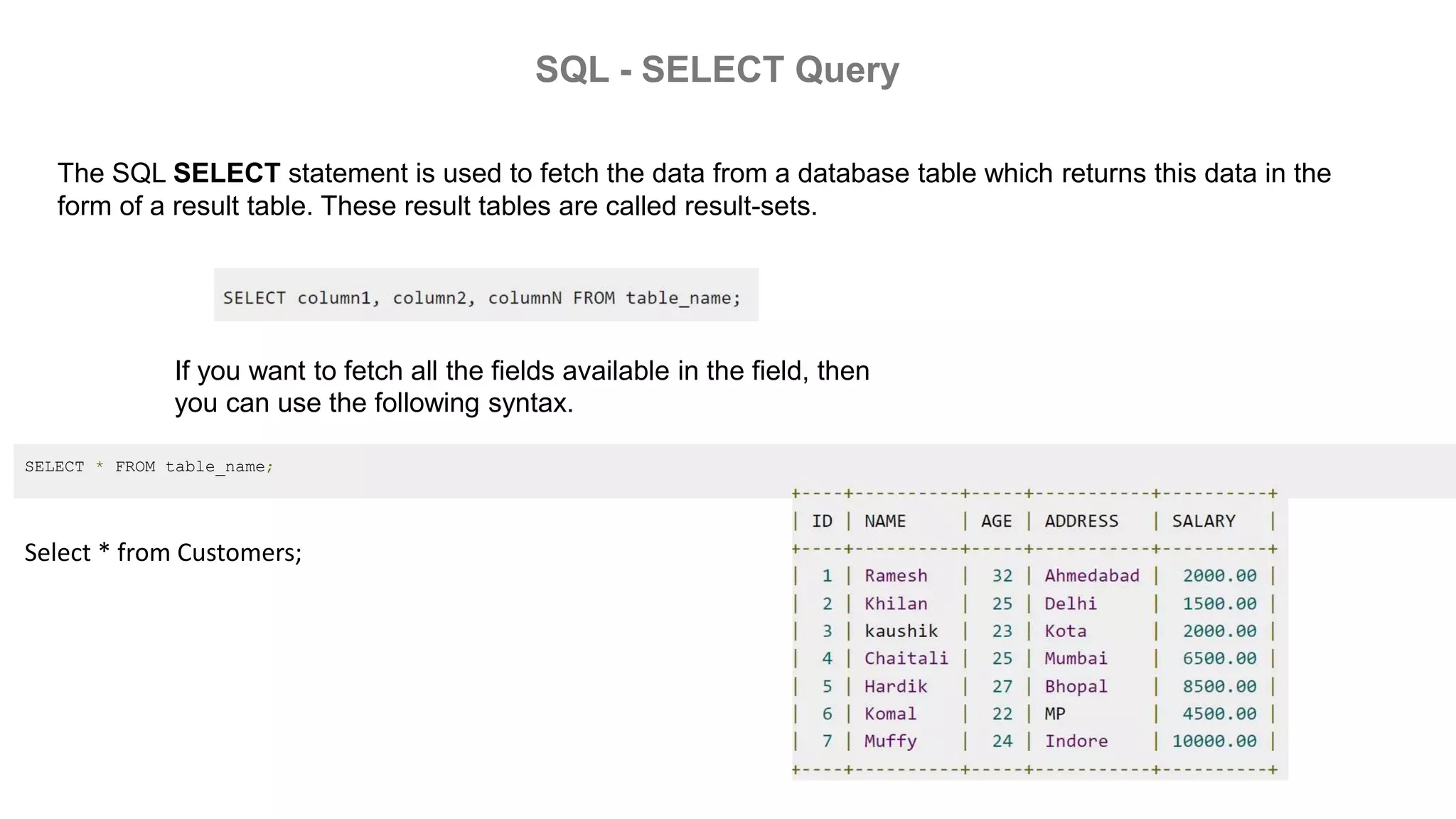
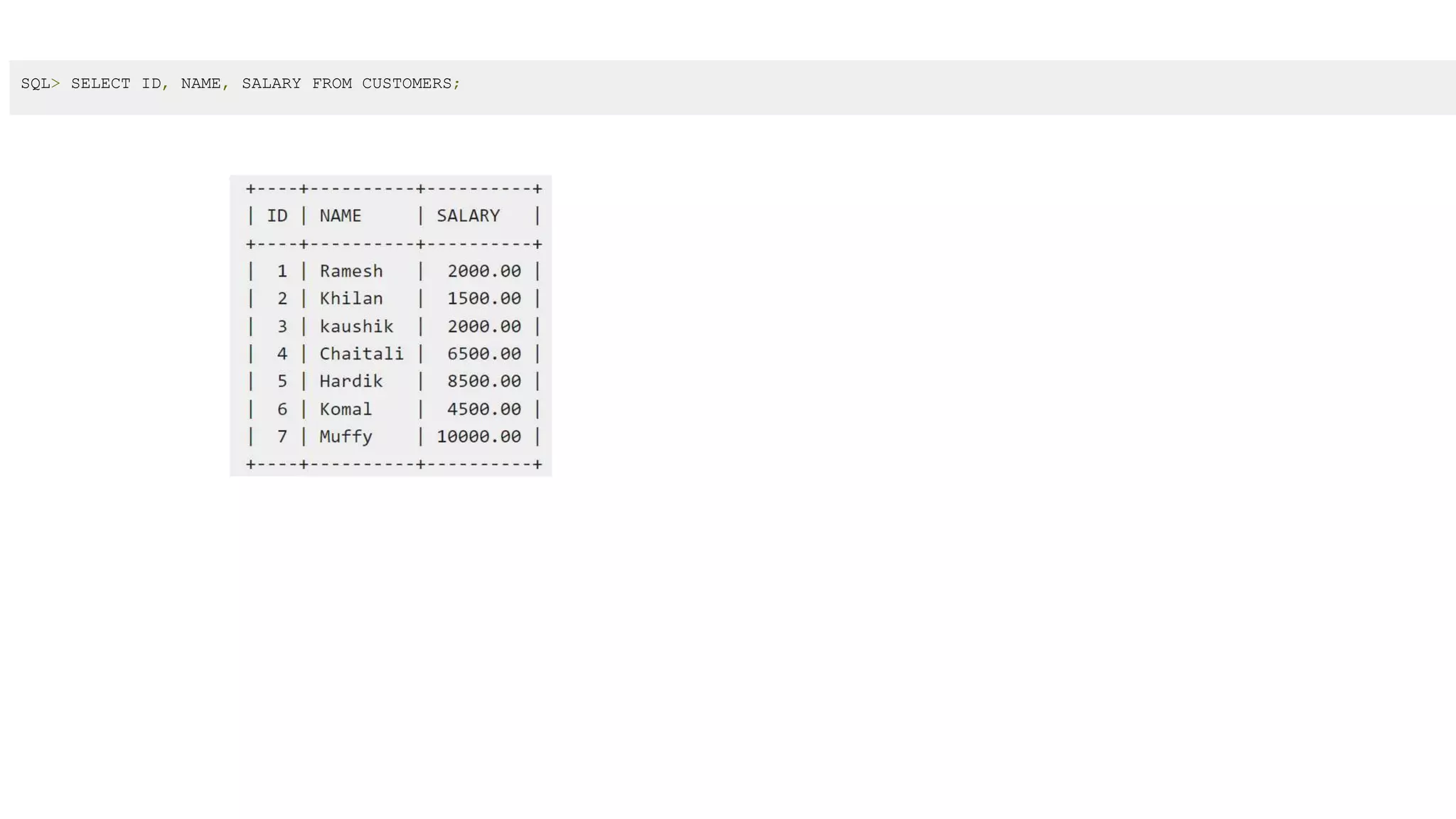
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system that works on many platforms. It provides multi-user access to support many storage engines and is backed by Oracle. SQL is the core of a relational database which is used for accessing and managing the database. The different subsets of SQL are DDL, DML, DCL, and TCL. MySQL has many features including ease of management, robust transactional support, high performance, low total cost of ownership, and scalability.












![SQL - WHERE Clause
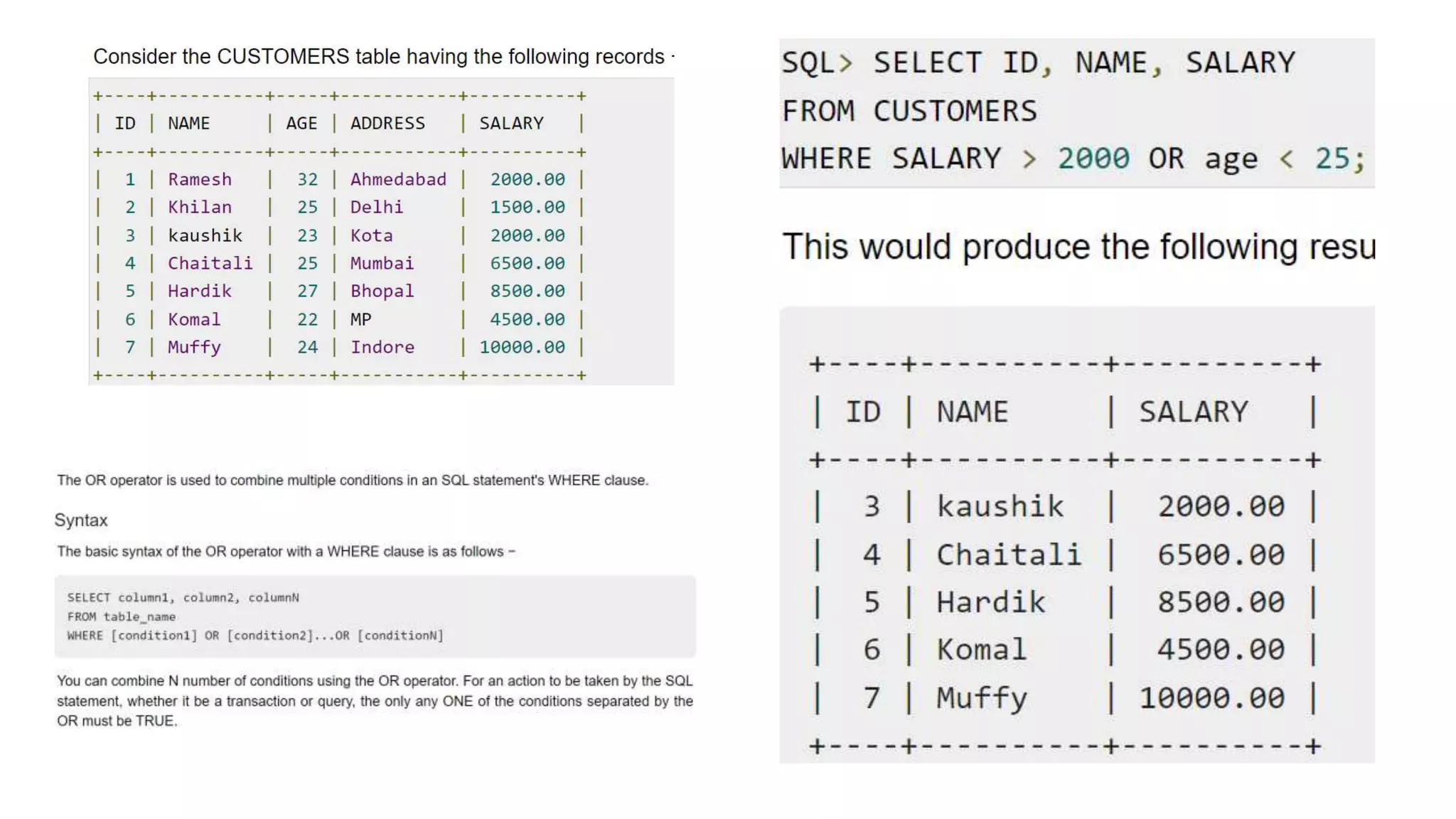
The SQL WHERE clause is used to specify a condition
while fetching the data from a single table or by joining
with multiple tables. If the given condition is satisfied, then
only it returns a specific value from the table. You should
use the WHERE clause to filter the records and fetching
only the necessary records.
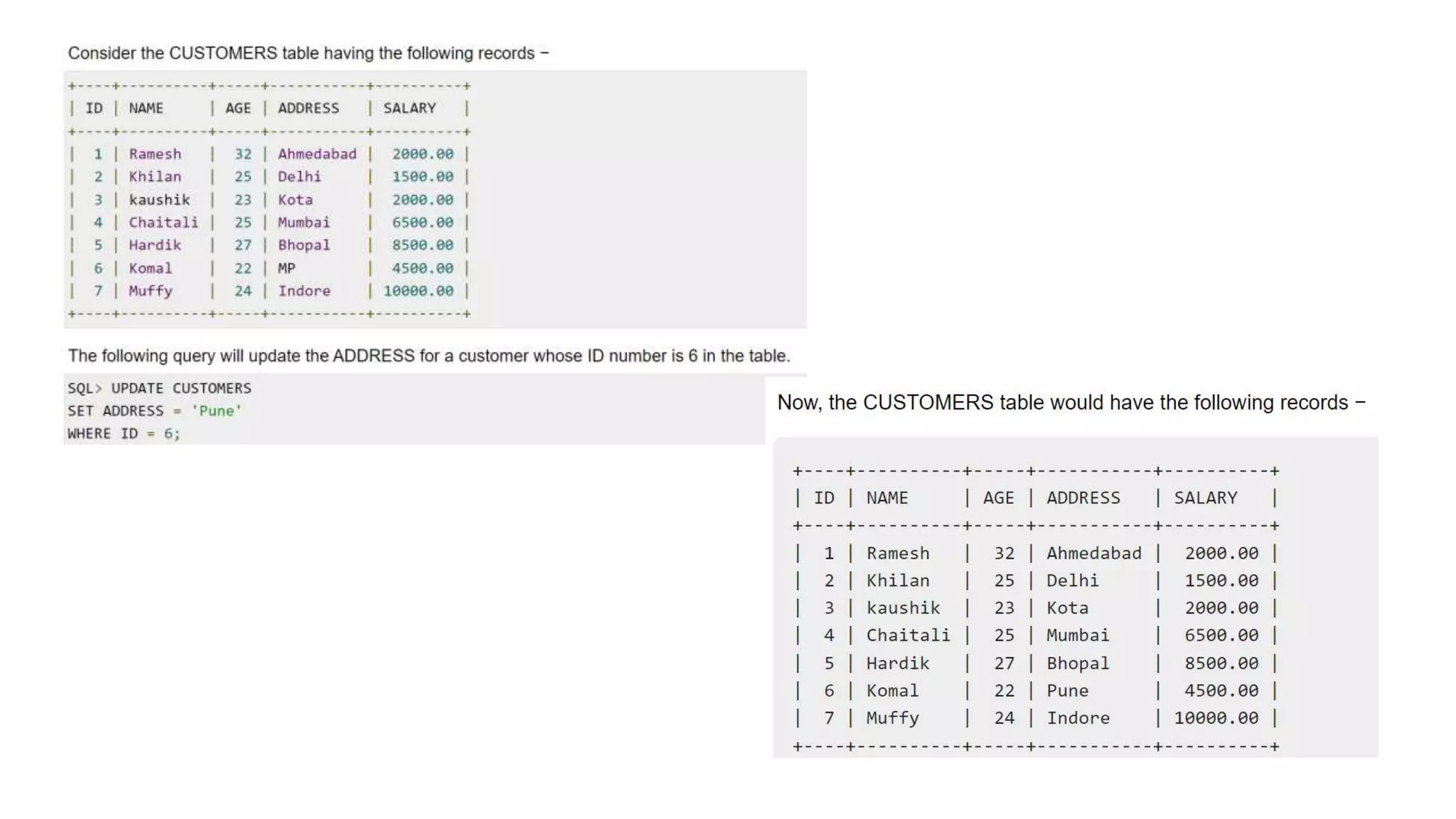
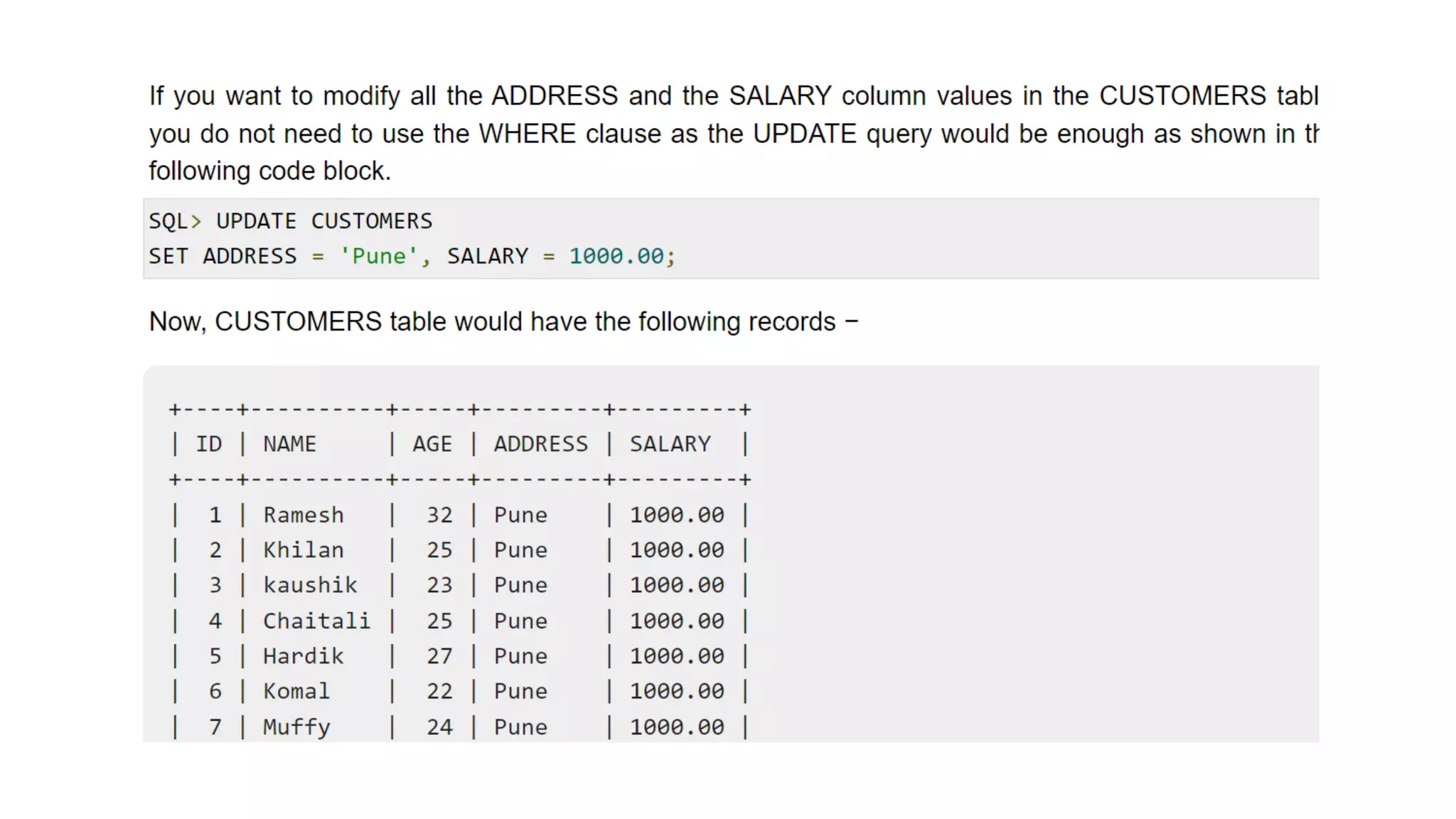
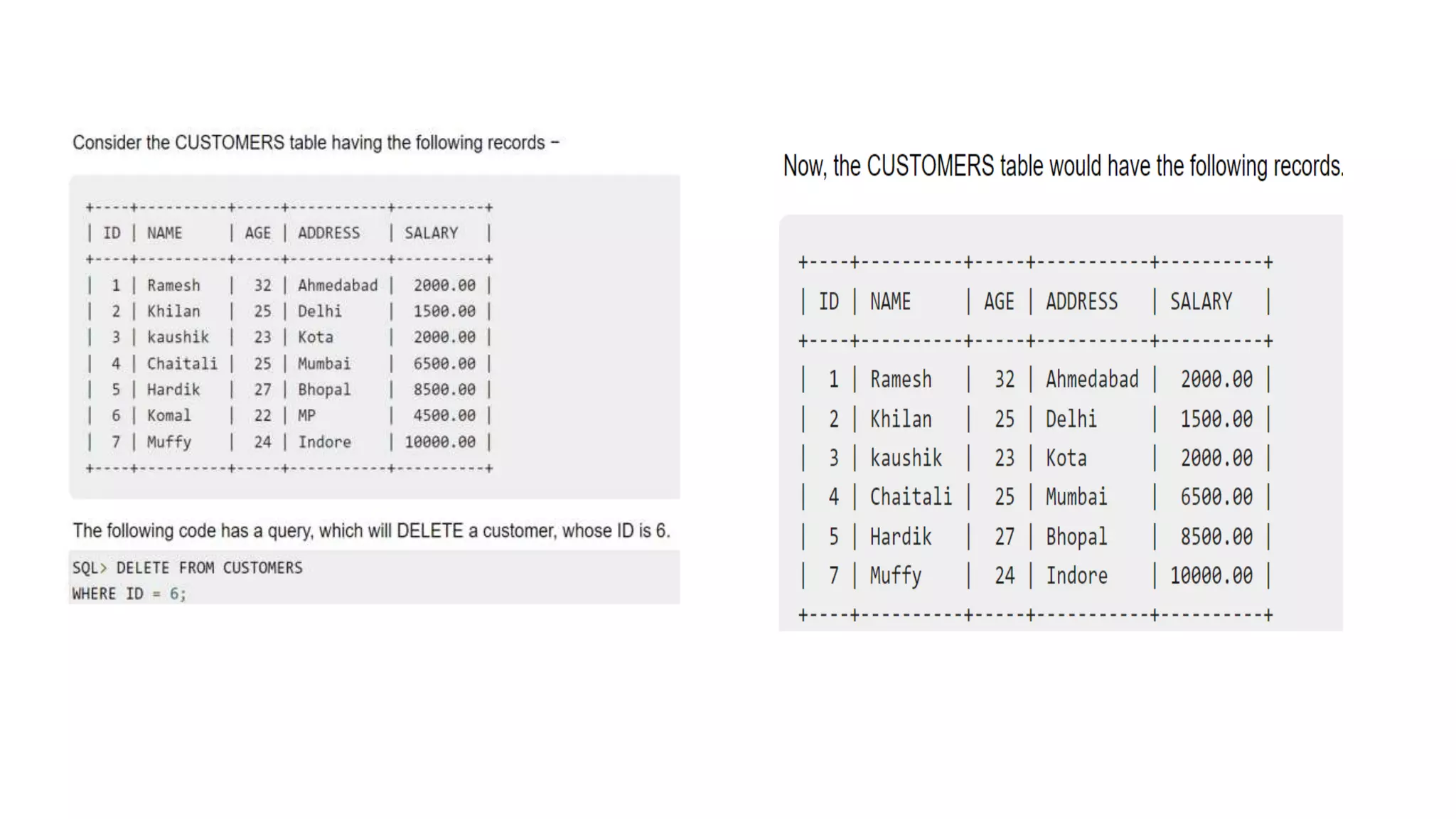
The WHERE clause is not only used in the SELECT
statement, but it is also used in the UPDATE, DELETE
statement, etc., which we would examine in the
subsequent chapters.
SELECT column1, column2, columnN FROM table_name WHERE [condition]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlppt-221116104448-b586141f/75/SQL-PPT-pptx-21-2048.jpg)