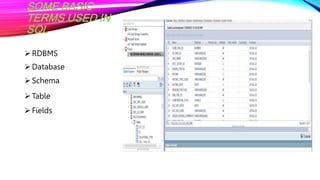
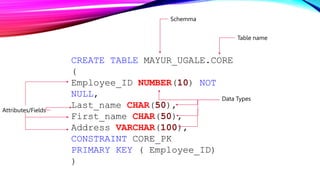
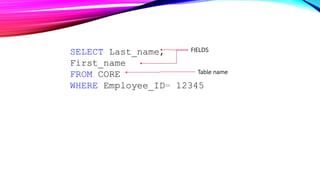
SQL is a standard language for accessing and manipulating databases. It allows users to create, retrieve, update, and delete data as well as manage database schemas. SQL commands include DDL commands like CREATE and ALTER for managing database structures and DML commands like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE for interacting with data. Writing SQL queries involves specifying elements like SELECT, FROM, WHERE to retrieve relevant data from database tables that are defined with attributes and primary keys.