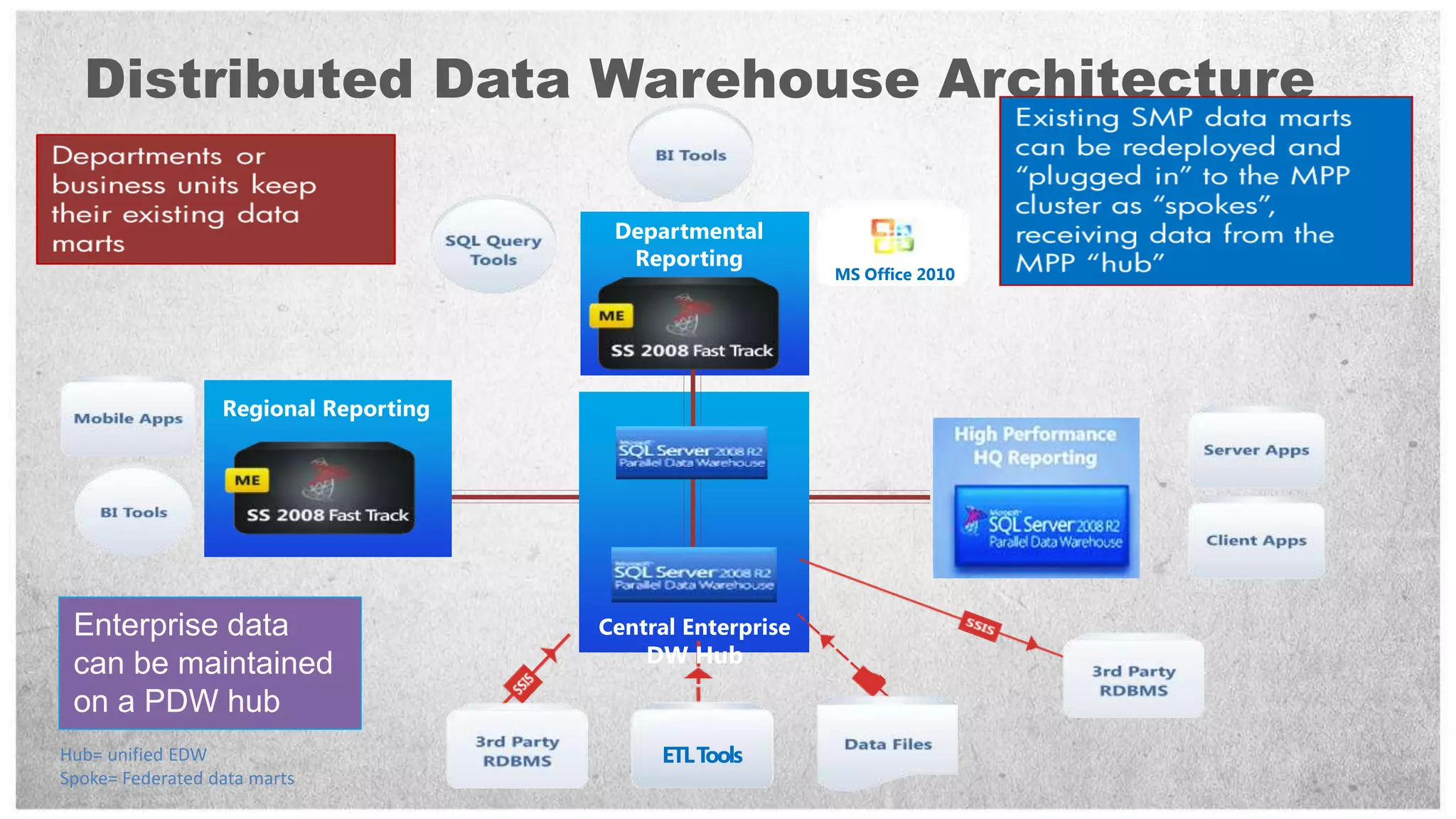
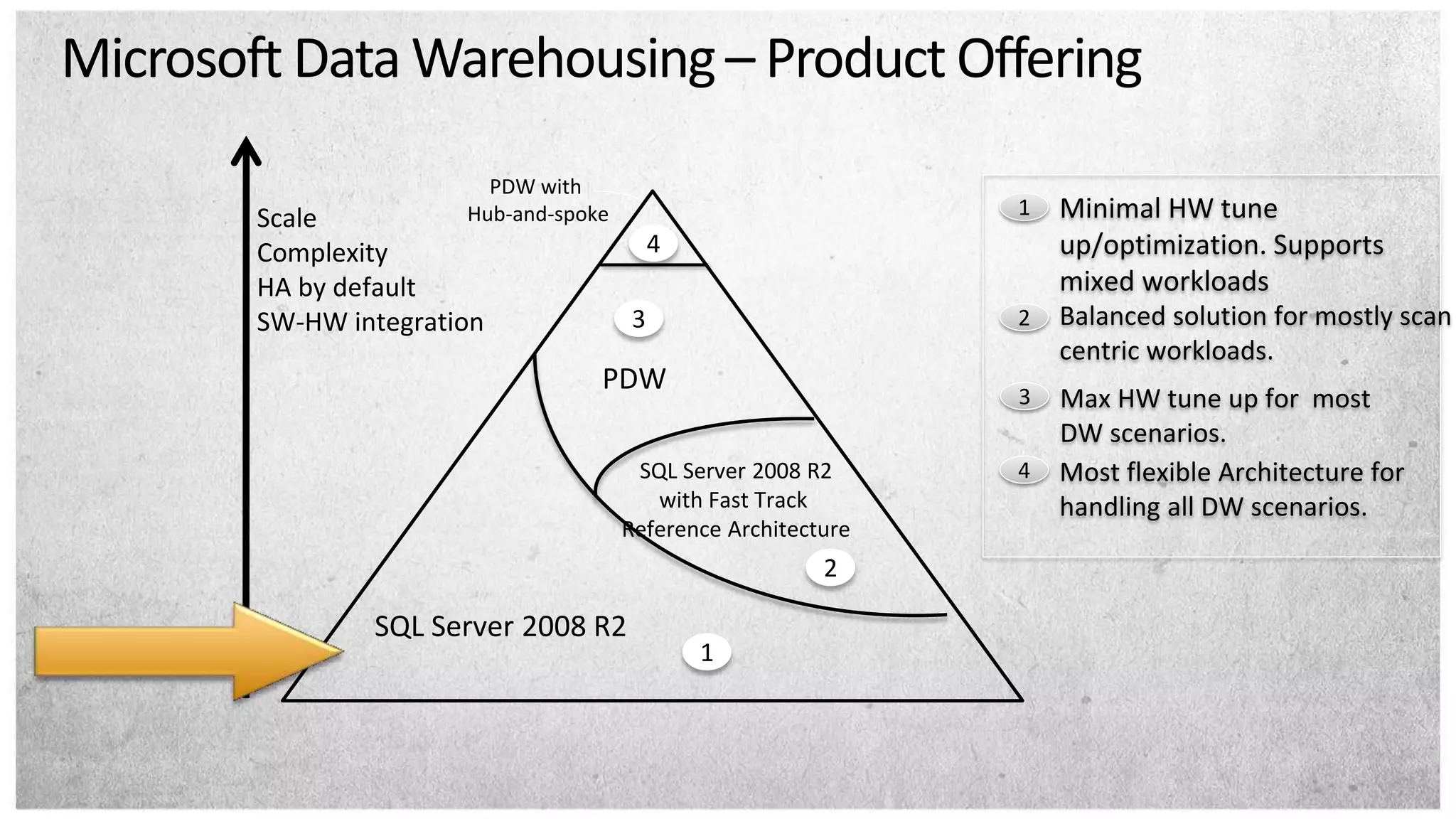
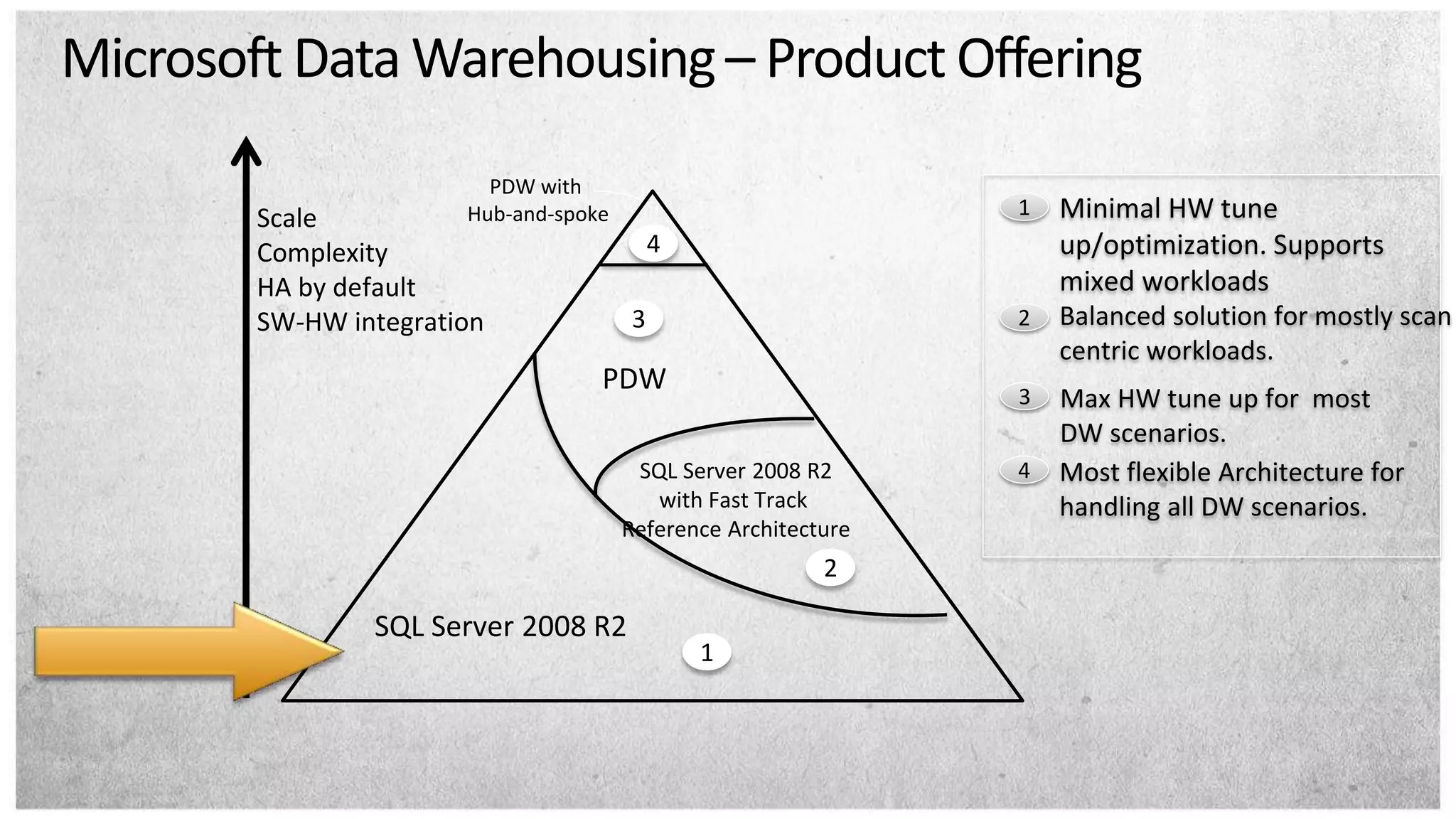
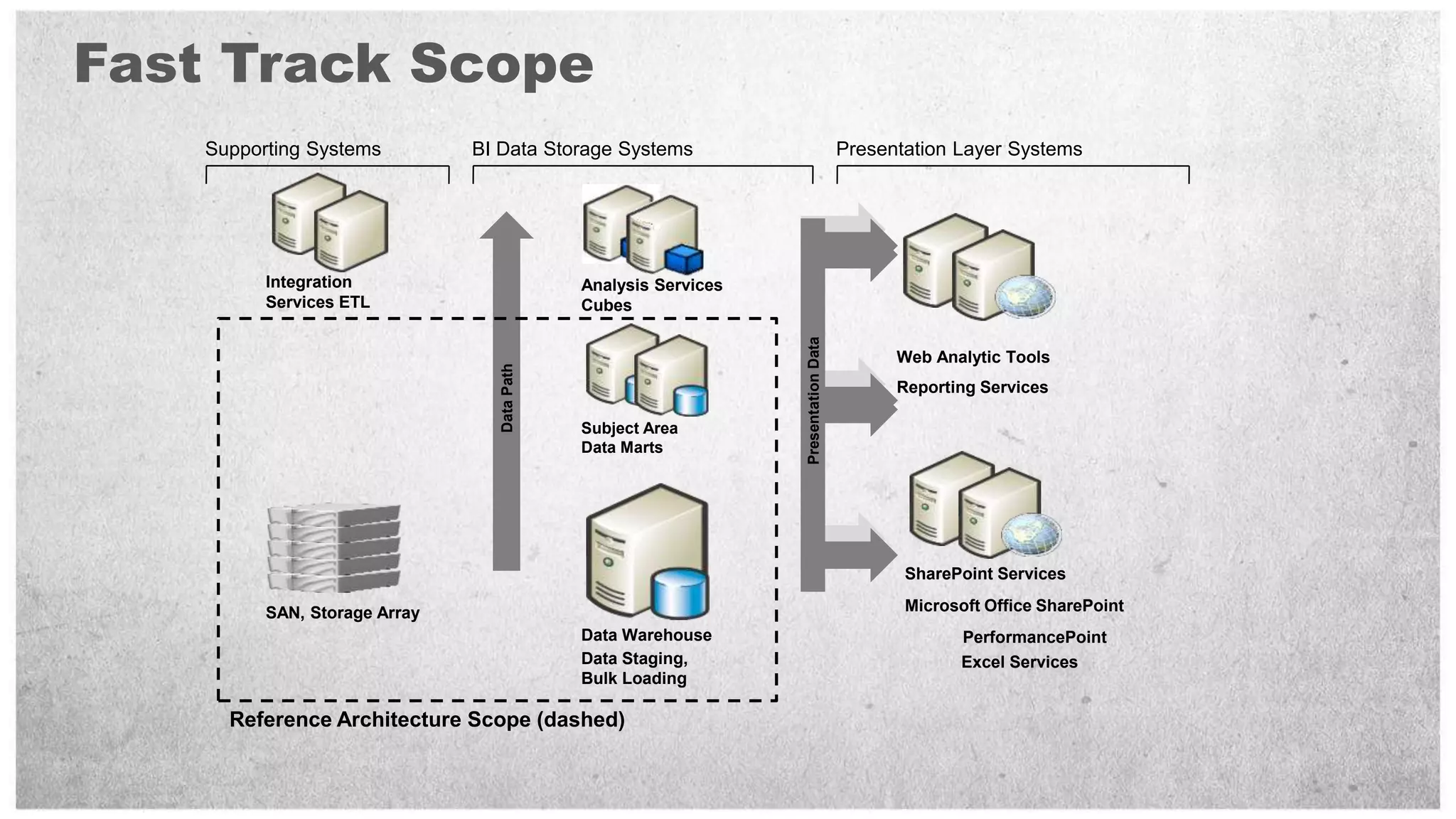
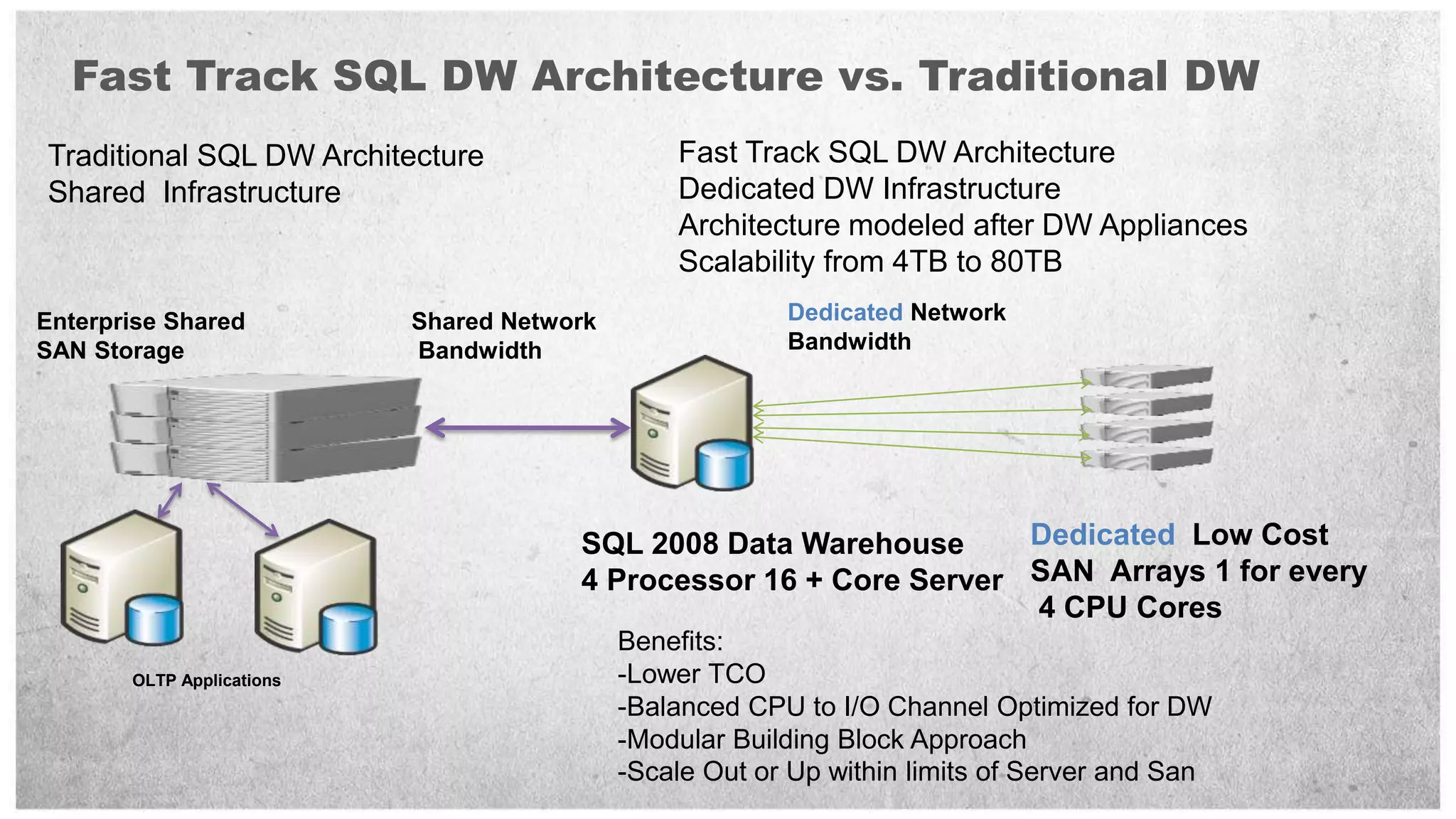
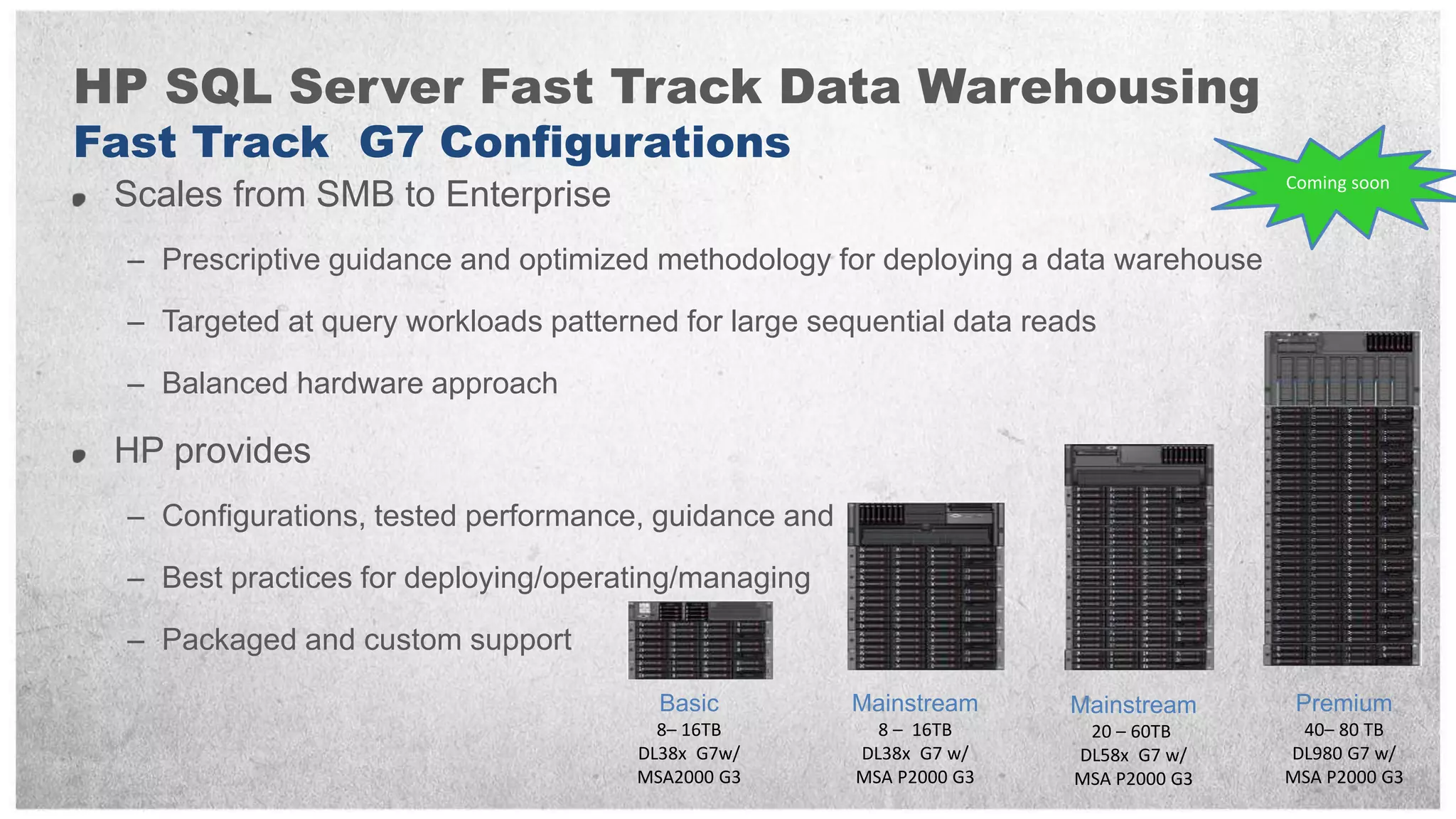
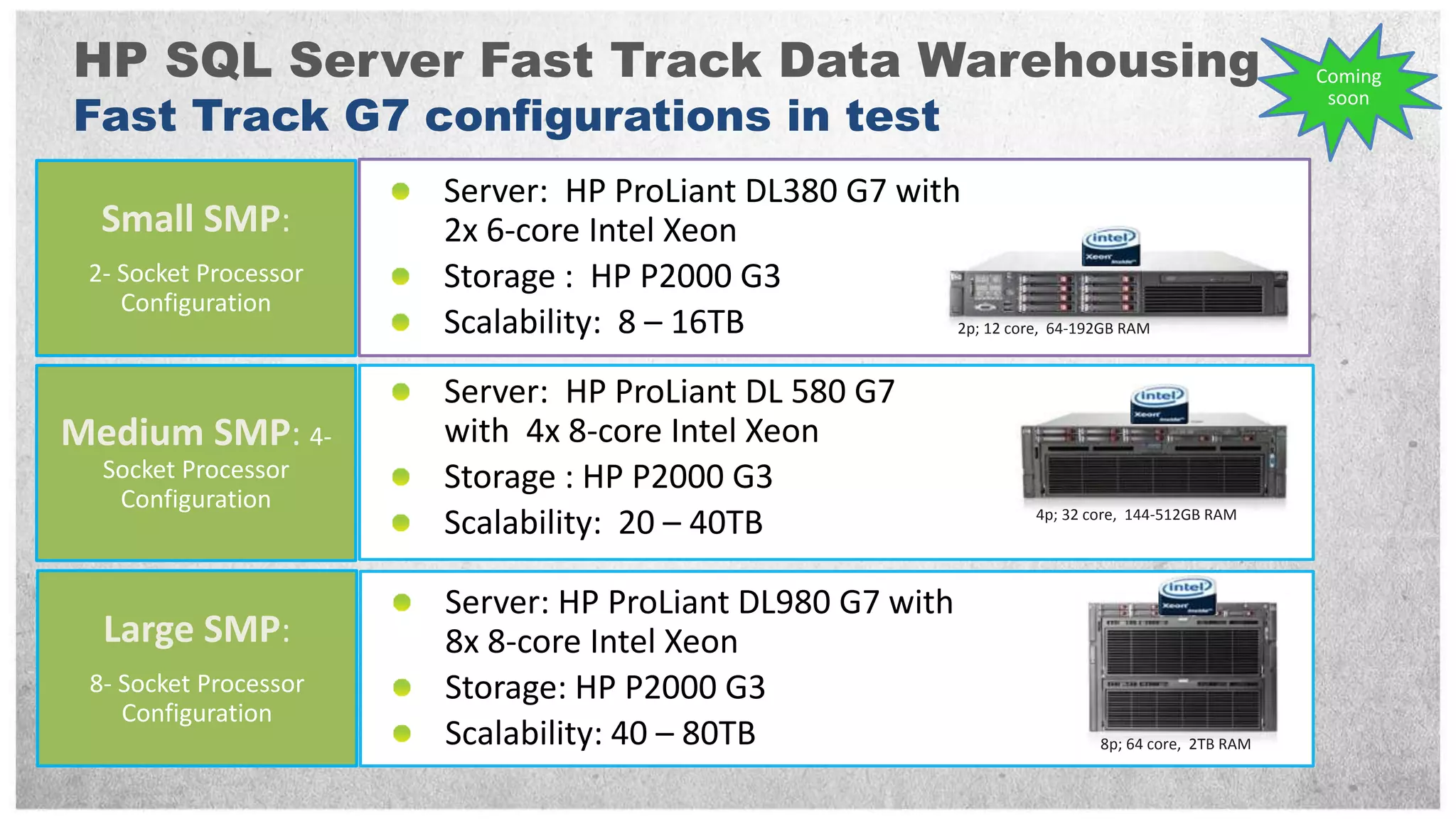
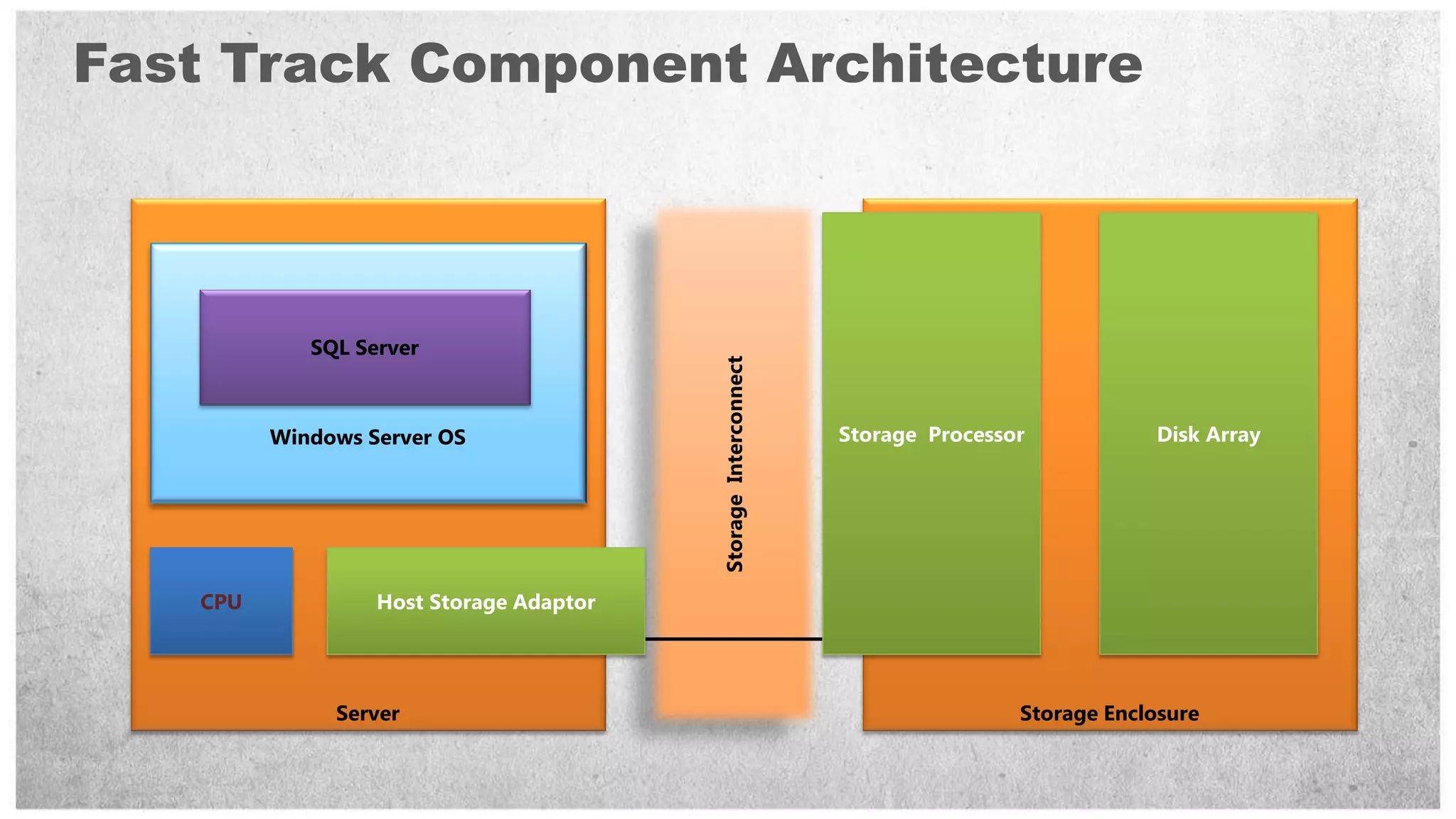
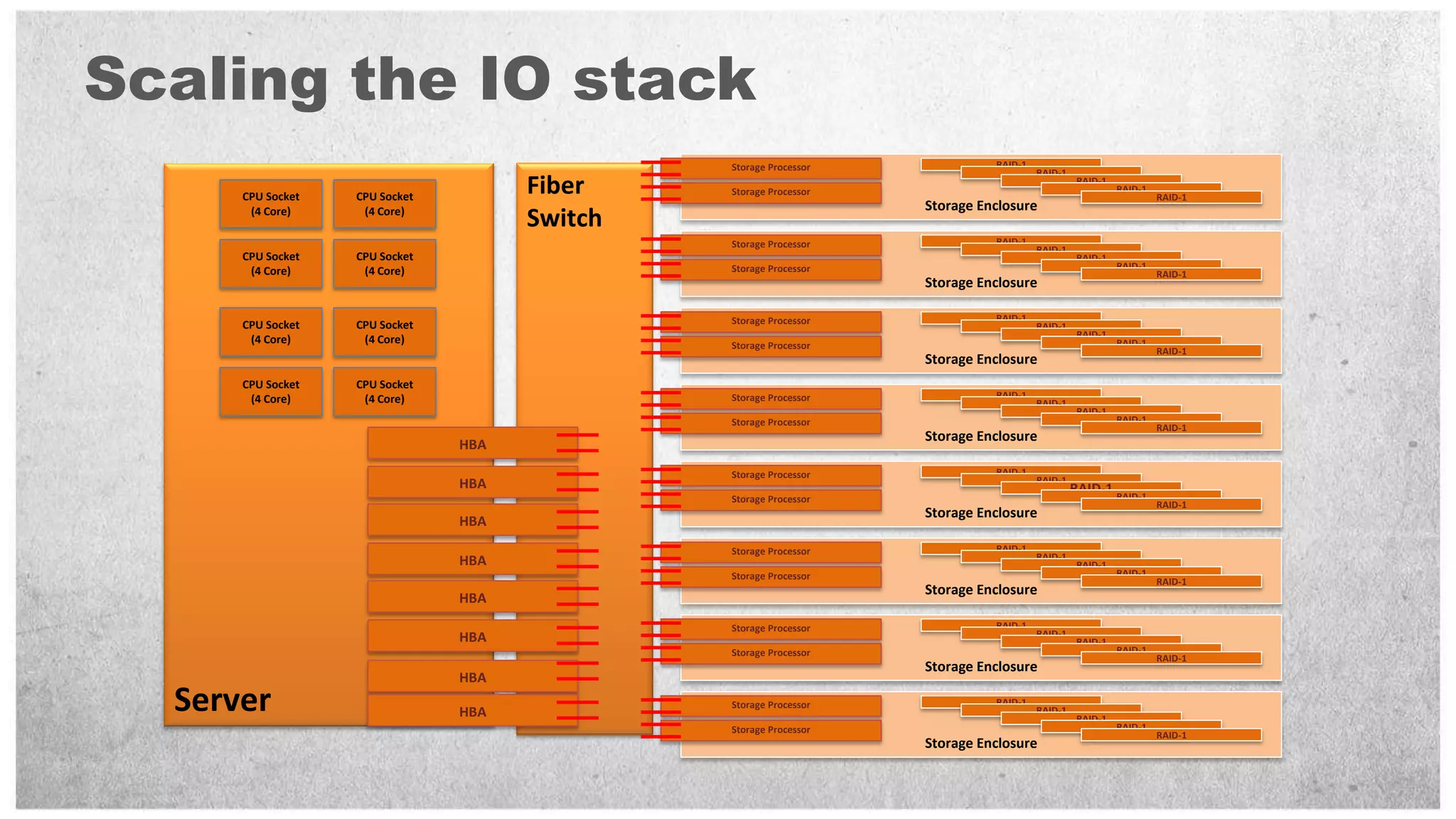
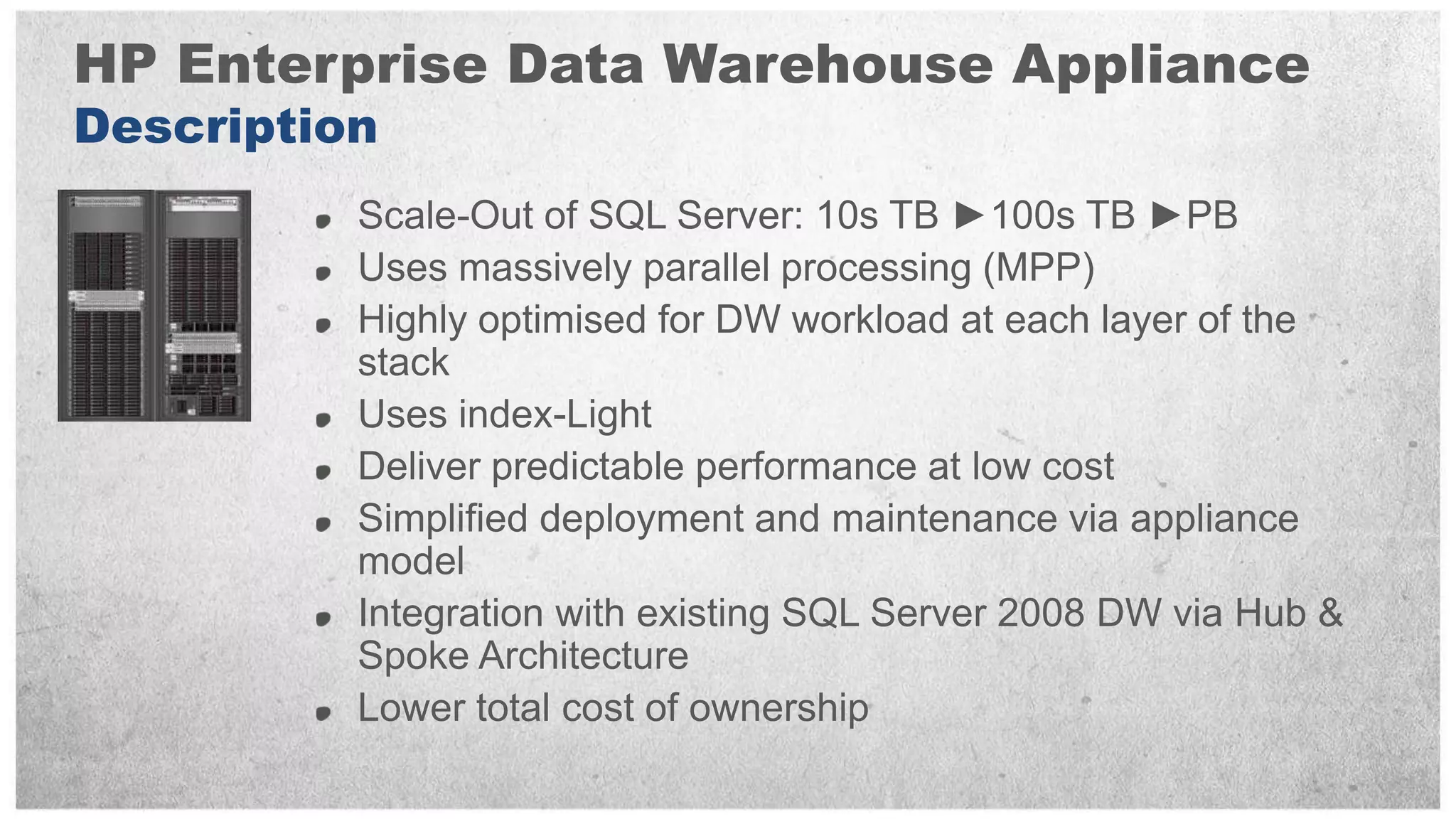
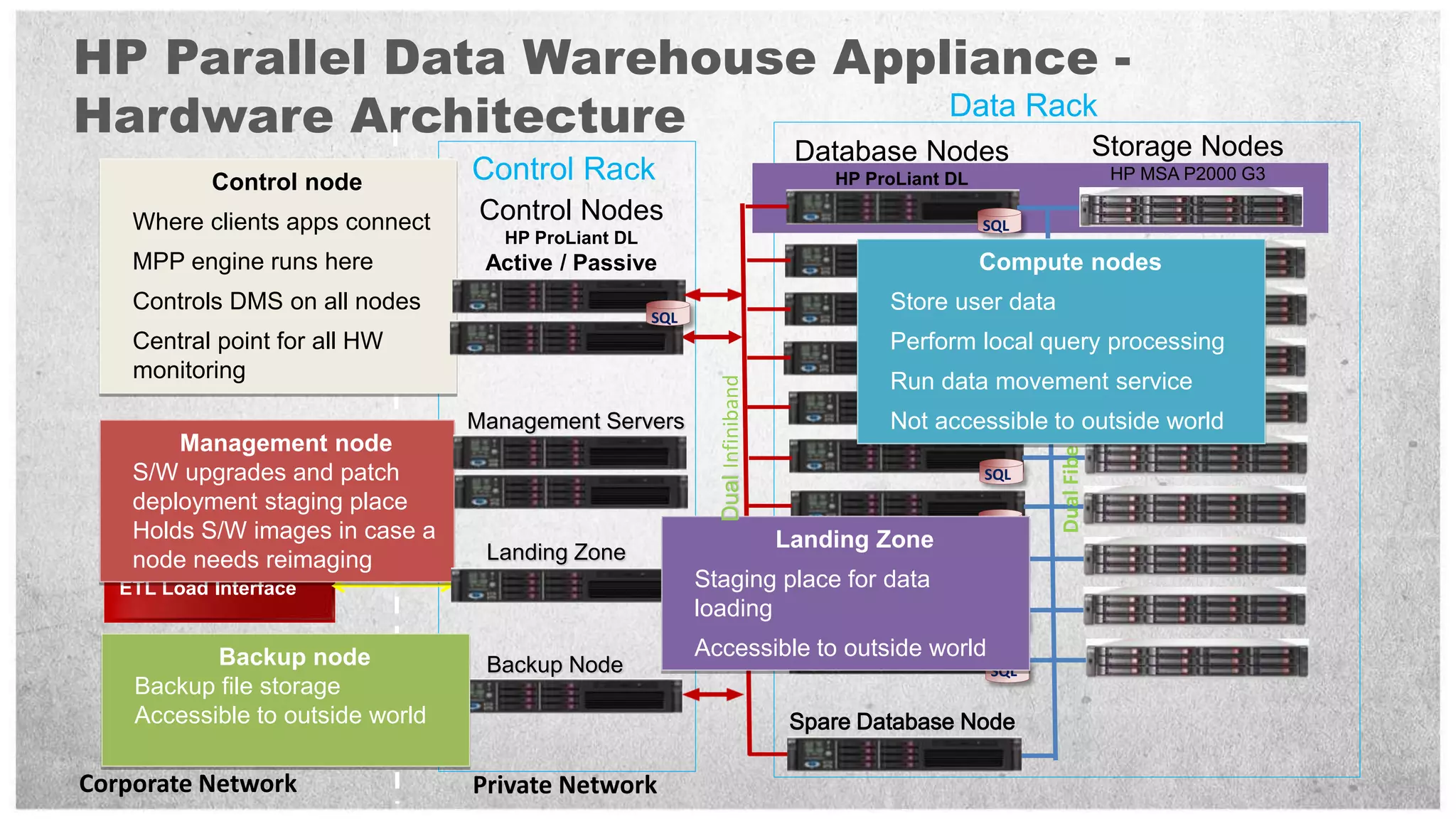
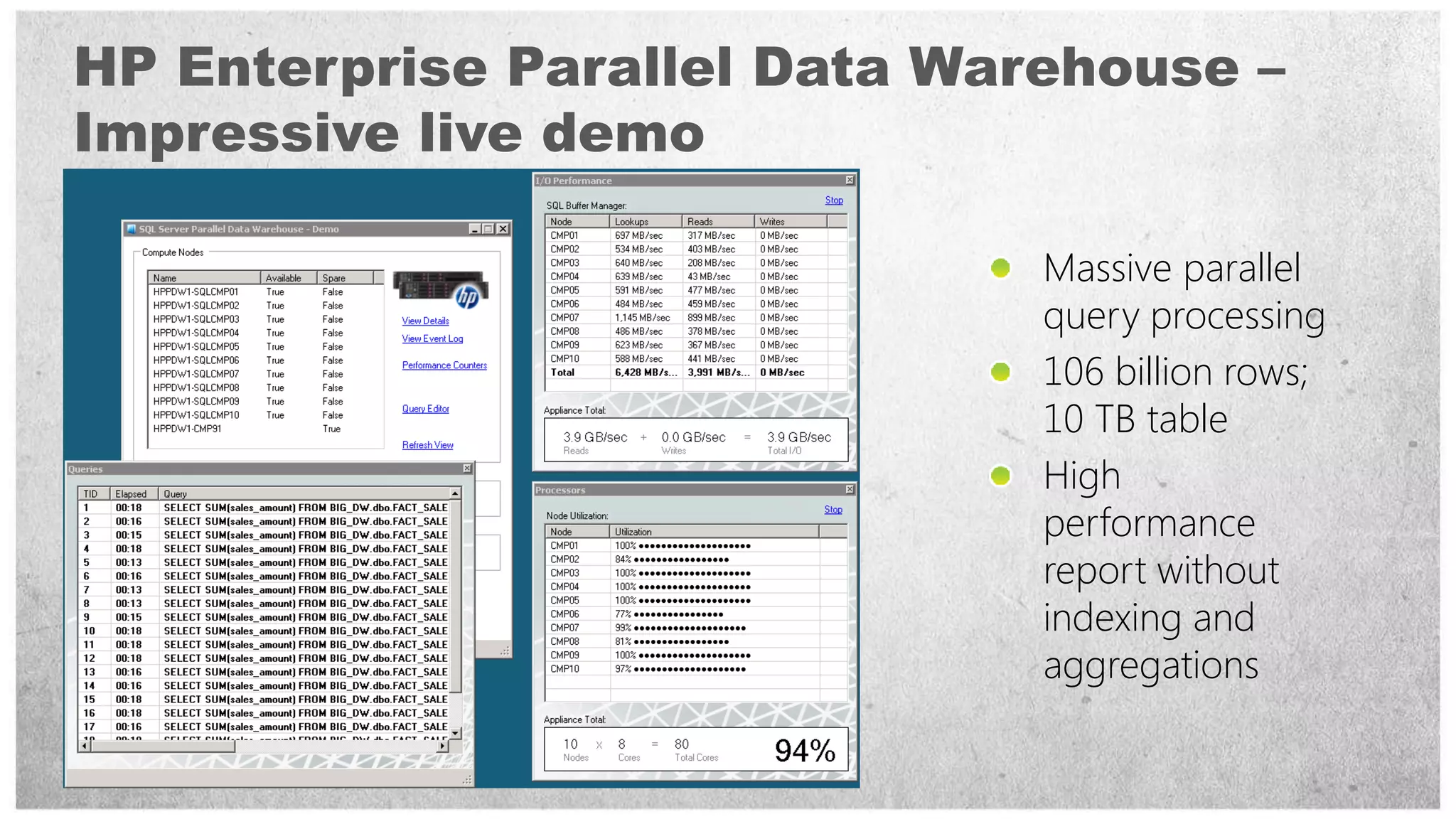
HP offers two solutions for data warehousing - Fast Track and Parallel Data Warehouse. Fast Track provides reference architectures using SQL Server for balanced deployments scaling from 8-80TB. Parallel Data Warehouse uses a massively parallel processing architecture to scale SQL Server deployments to petabytes of data. It uses a scale-out architecture with distributed data and query processing. This provides very high performance for large and complex workloads.




















![Data Distribution with replication
Database
Date Dim
Customer D_DATE_SK
D_DATE_ID
C-CUSTOMER_SK D_DATE
D_MONTH
C_CUSTOMER_ID Item
C_CURRENT_ADDR …
… I_ITEM_SK
I_ITEM_ID
I_REC_START_DATE
I_ITEM_DESC
…
SS[1] Store Sales
Ss_sold_date_sk
SS[2] Ss_item_sk
Ss_customer_sk
Ss_cdemo_sk
SS[3] Ss_store_sk
Ss_promo_sk
Ss_quantity
Promotion
SS[4]
Customer
…
Demographics P_PROMO_SK
P_PROMO_ID
CD_DEMO_SK P_START_DATE_SK
P_END_DATE_SK
CD_GENDER Store …
CD_MARITAL_STATUS
CD_EDUCATION
… S_STORE_SK
S_STORE_ID
S_REC_START_DATE
S_REC_END_DATE
S_STORE_NAME
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bi303datawarehousingwithfasttrackandpdw-120210052214-phpapp01/75/Bi303-data-warehousing-with-fast-track-and-pdw-Assaf-Fraenkel-37-2048.jpg)