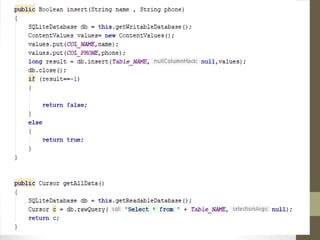
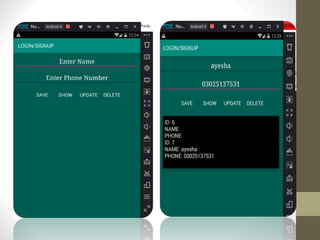
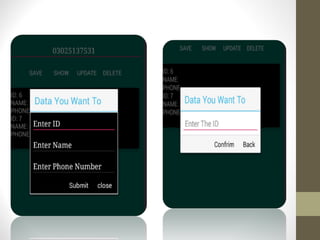
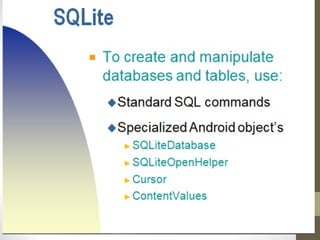
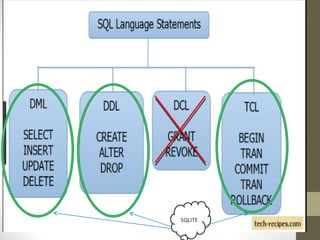
SQLite is a lightweight, relational database that is embedded into applications. It was designed to have a small memory footprint and not require administration. SQLite supports basic data types like text, integer, and real numbers. It uses a B-tree disk-based file format for storage. In Android, SQLite is commonly used through objects like SQLiteDatabase, SQLiteOpenHelper, and Cursor to create, open, and query databases. Common SQL commands like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE can be executed to manage data in SQLite tables.



















![Simple Queries
• SQL - "SELECT * FROM ABC;"
SQLite - Cursor c = mdb.query(abc,null,null,null,null,null,null);
• SQL - "SELECT * FROM ABC WHERE C1=5"
SQLite - Cursor c = mdb.query(
abc,null,"c1=?" , new String[ ] {"5"},null,null,null);
• SQL – "SELECT title,id FROM BOOKS ORDER BY title ASC"
SQLite – String colsToReturn [ ] {"title","id"};
String sortOrder = "title ASC";
Cursor c = mdb.query("books",colsToReturn,
null,null,null,null,sortOrder);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlitedatabase-190601112541/85/Sq-lite-database-23-320.jpg)