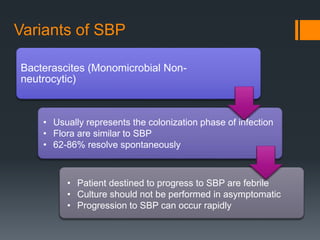
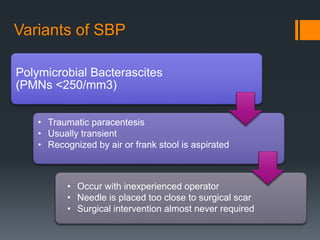
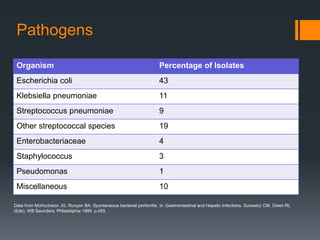
1) Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is an infection of the ascitic fluid without an evident intra-abdominal surgically treatable cause.
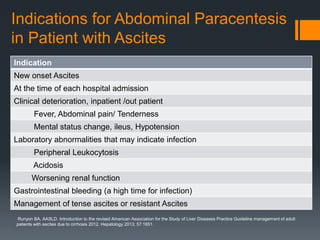
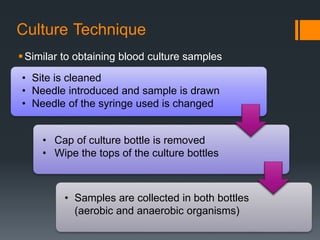
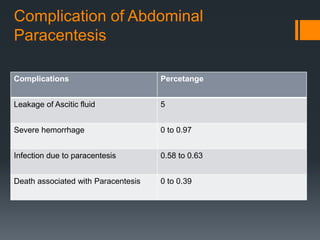
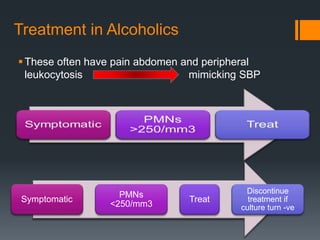
2) Abdominal paracentesis should be performed for patients with ascites who present with signs of infection like fever or abdominal pain. The ascitic fluid is examined for white blood cell count and cultured.
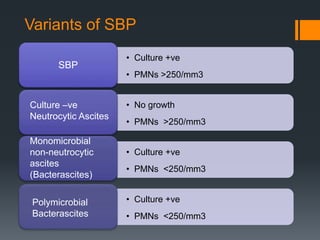
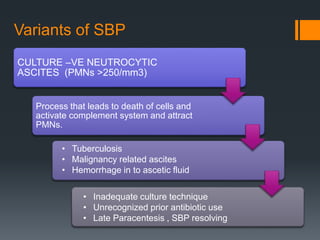
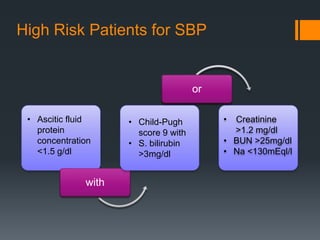
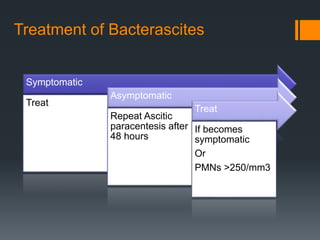
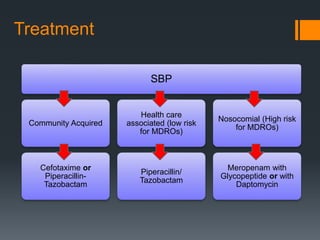
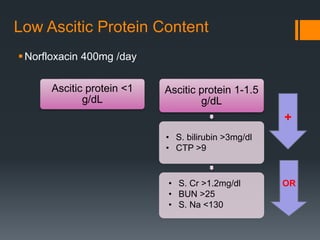
3) SBP is diagnosed if the ascitic fluid white blood cell count is above 250 cells/mm3 or has a positive culture. Treatment involves antibiotics like cefotaxime for 5 days along with intravenous albumin to prevent kidney injury.