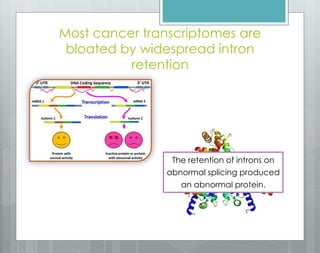
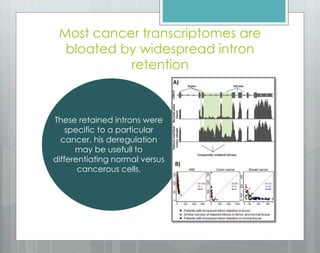
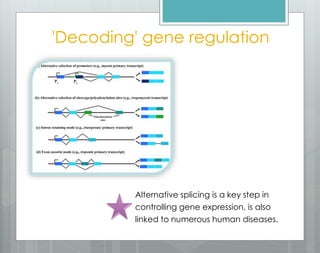
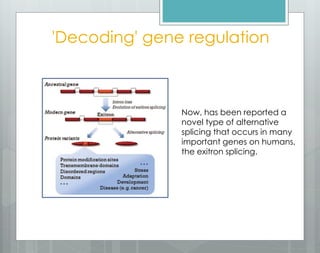
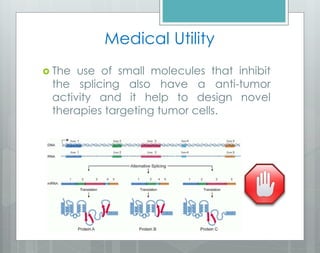
The document discusses the role of splicing in protein creation and its implications in cancer, highlighting that abnormal RNA splicing is linked to tumor initiation and metastasis. It mentions that retained introns could differentiate between normal and cancerous cells, while alternative splicing presents new targets for therapeutic intervention. The author notes the potential for developing novel therapies and preventative measures against cancer through deeper understanding of splicing and gene regulation.