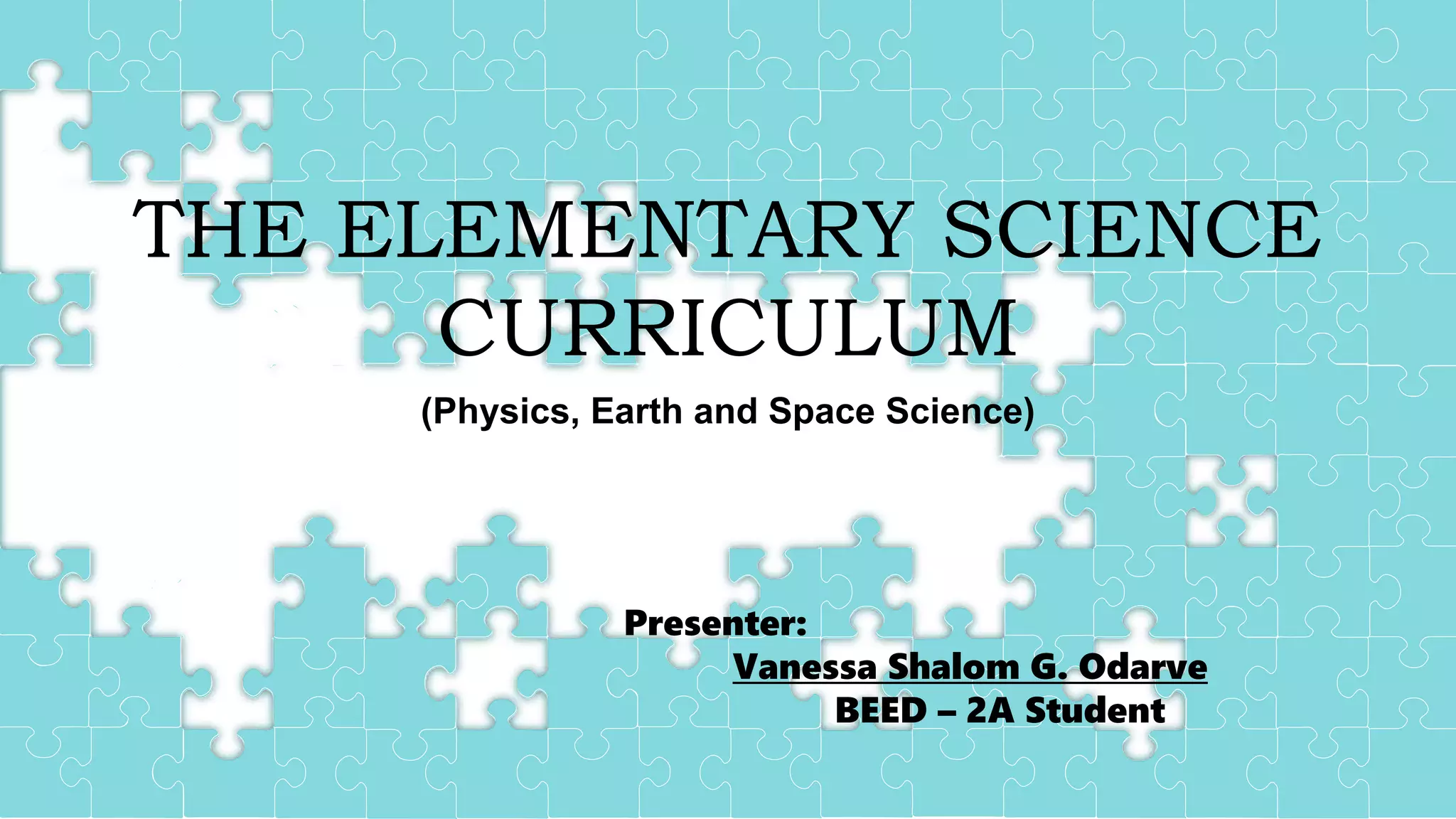
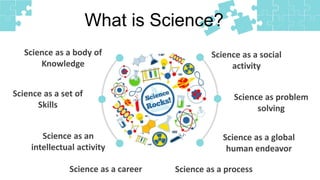
This document discusses key concepts in science education, including the definition of science, the scientific method, and qualities of effective science teachers. It defines science as a body of knowledge acquired through systematic processes of observation and experimentation. The scientific method is described as a set of steps including making observations, developing hypotheses, conducting experiments, analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. Finally, it notes that inspiring science teachers engage students through traits like creativity, stamina, involvement, and clear instruction.