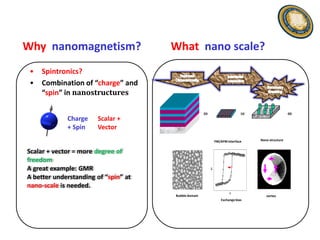
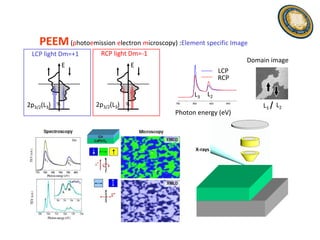
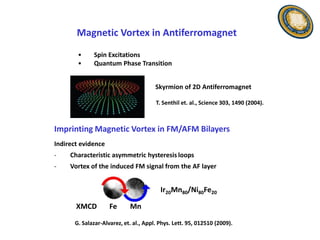
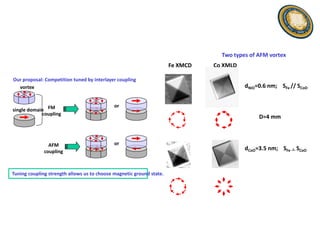
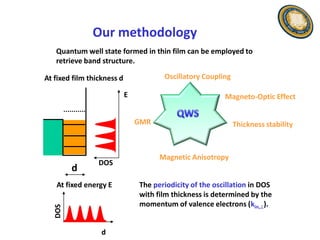
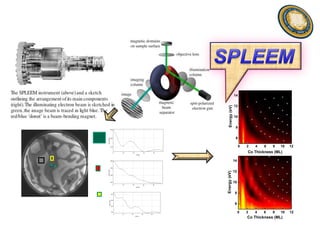
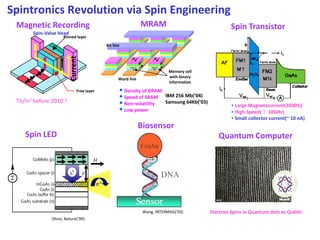
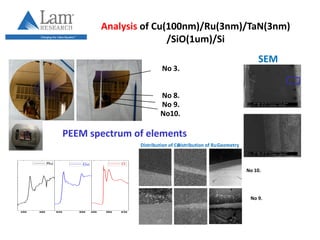
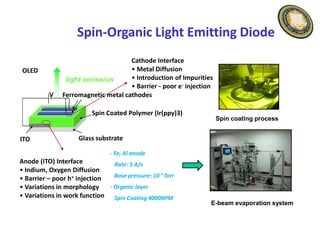
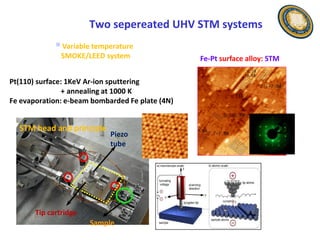
This document discusses the research and expertise of Jusang Park in the area of spintronics and nanomagnetism. It provides details of his education background including PhD in condensed physics from Hanyang University. It outlines his research experience studying nano-magnetism at UC Berkeley and previous positions. It also lists his technical expertise in areas such as thin film growth, structural analysis, and magnetic characterization techniques. Finally, it provides examples of his research investigating topics like interlayer coupling in magnetic multilayers, magnetic vortices in antiferromagnets, and potential applications of spintronics.