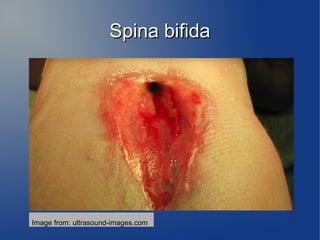
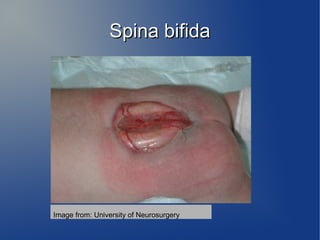
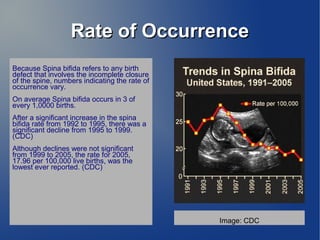
Spina bifida is a neural tube defect that results from the spine failing to close properly during early embryonic development between the third and fourth week of pregnancy. It can cause varying degrees of paralysis in the lower body. The most common type is myelomeningocele, where the bones of the spine do not fully form, leaving the spinal cord and its surrounding tissues exposed. Risk factors include family history, folate deficiency, certain medications, diabetes, and obesity. It is typically diagnosed during pregnancy through blood tests and ultrasound exams. The prognosis depends on the severity of the condition and any associated complications.