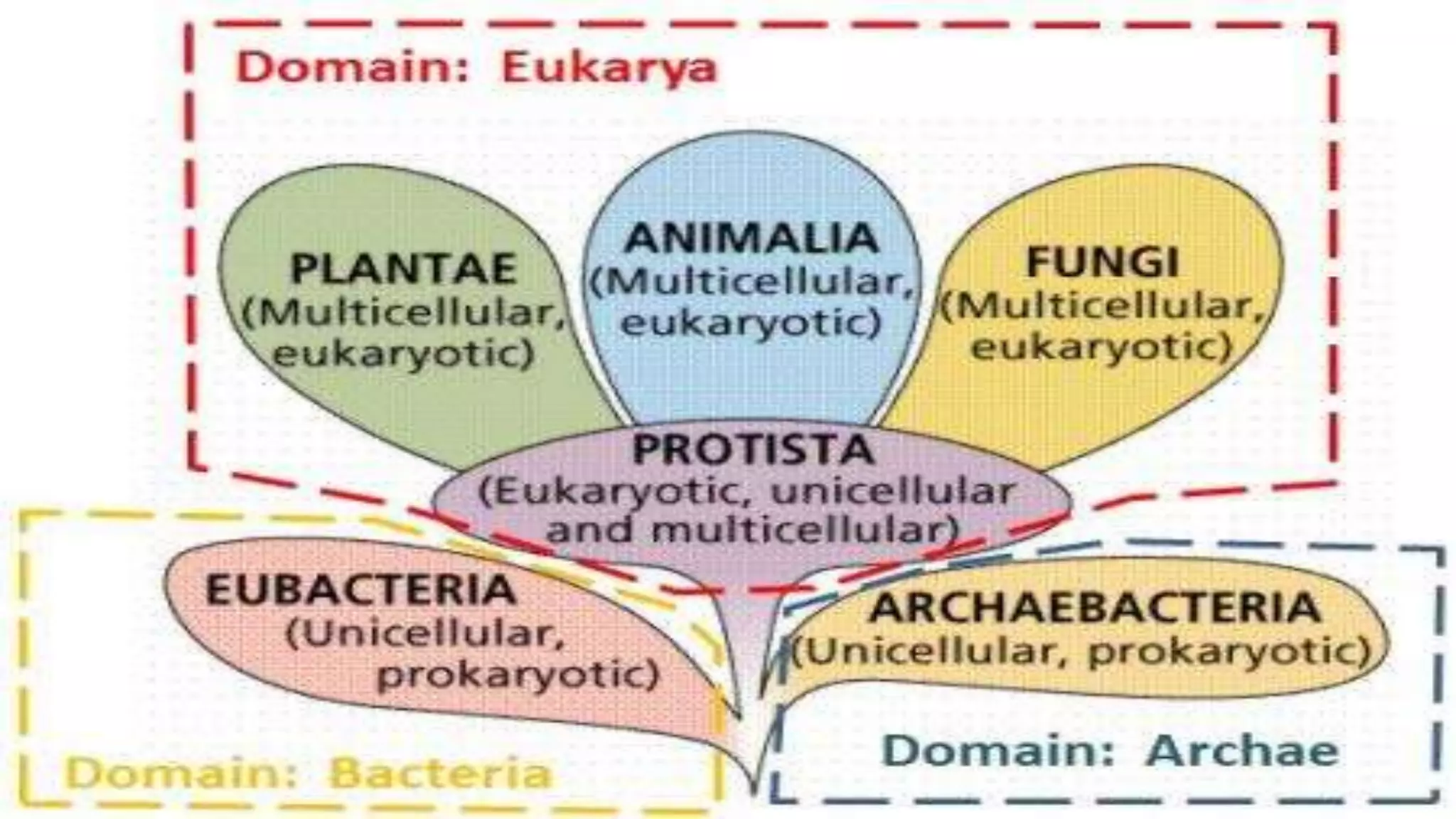
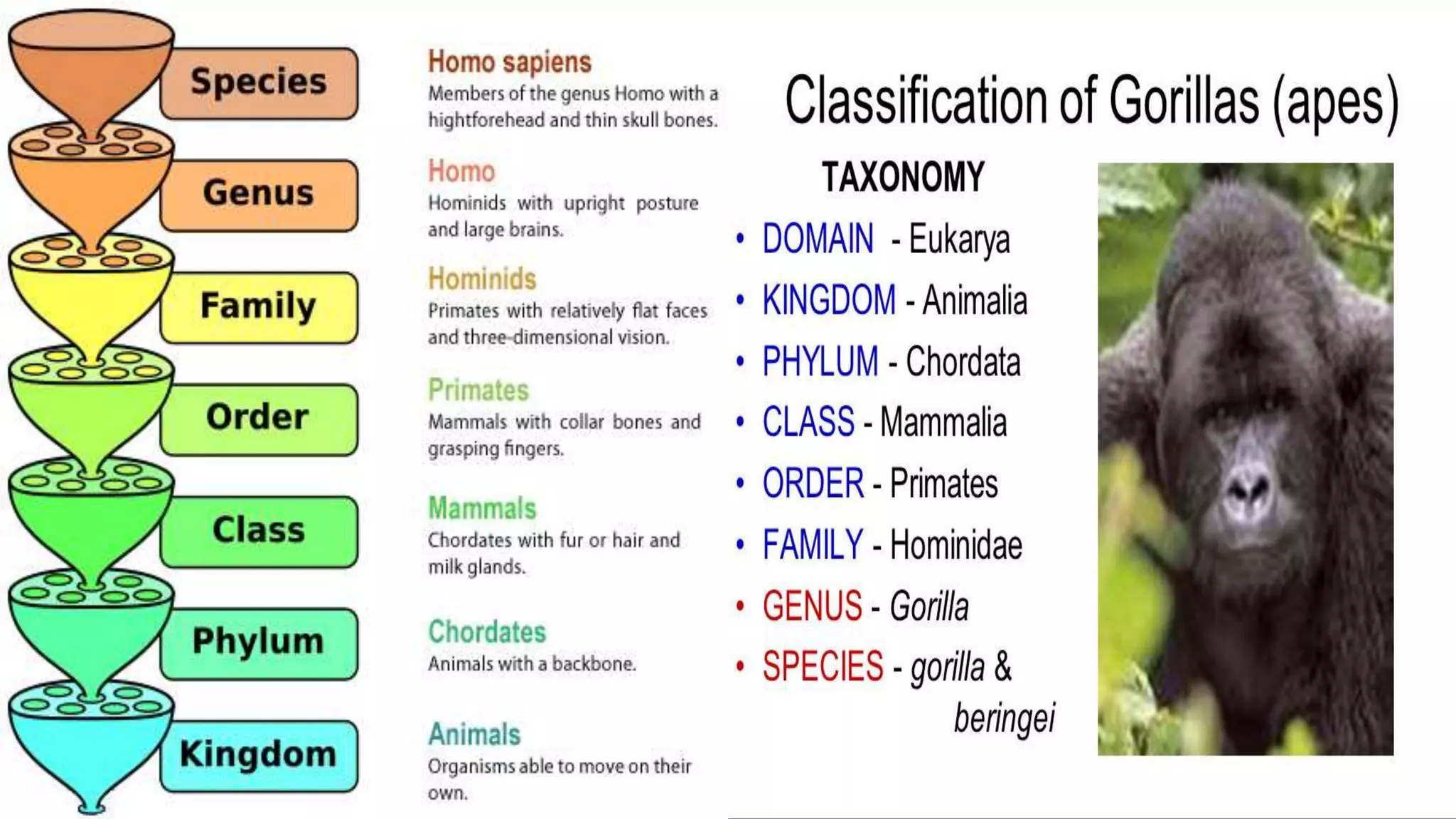
The document discusses species concepts and hierarchical taxonomic classification. It defines species as the basic unit of classification and discusses four species concepts: morphological, biological, taxonomic, and nominalistic. It also explains that taxonomy involves describing, identifying, naming, and classifying organisms and their relationships. Finally, it mentions that Carolus Linnaeus introduced binomial nomenclature and hierarchical classification as a standardized system for taxonomic organization.