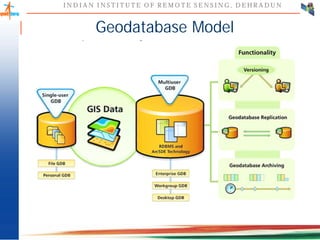
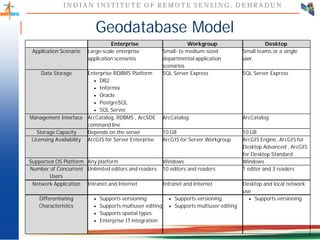
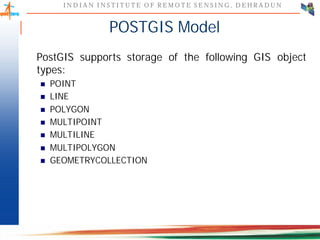
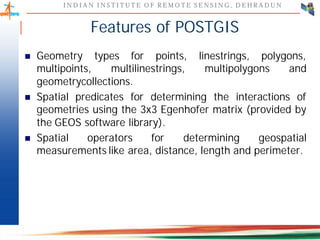
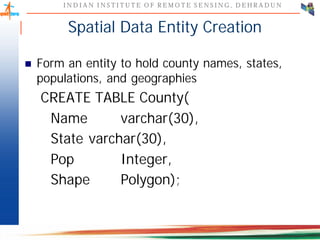
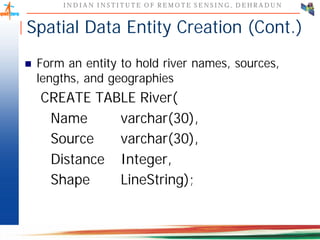
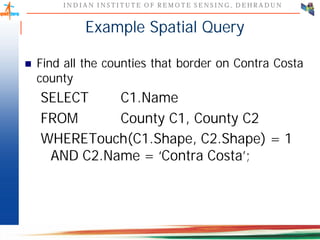
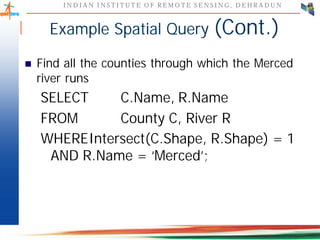
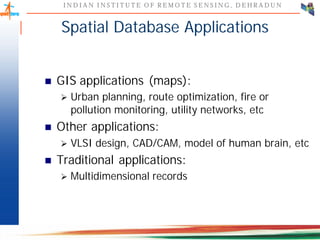
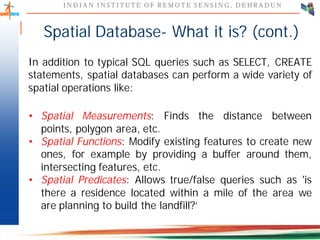
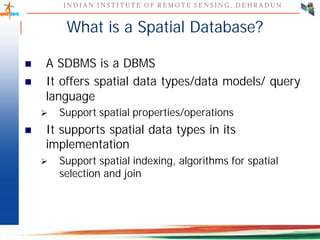
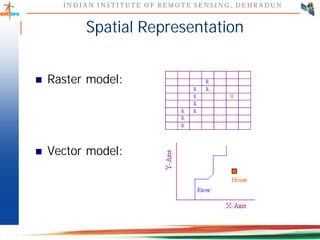
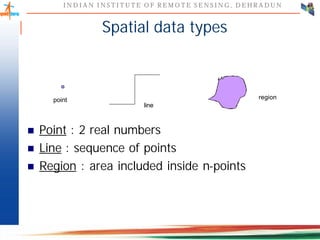
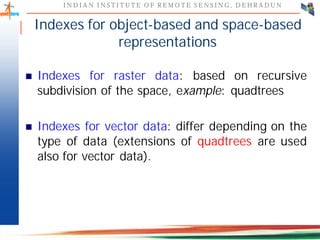
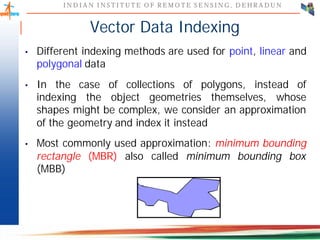
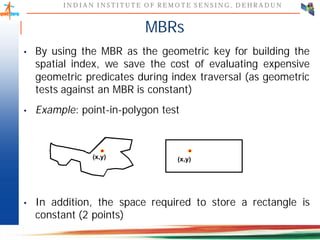
This document discusses spatial databases, which are optimized to store and query spatial data such as points, lines, and polygons. A spatial database adds functionality to a typical database to process spatial data types and perform spatial queries and operations. It describes how spatial databases more efficiently store, retrieve, and analyze spatial data compared to standard databases. Some common uses of spatial databases include geographic information systems, computer-aided design, and medical imaging applications.











![I N D I A N I N S T I T U T E O F R E M O T E S E N S I N G , D E H R A D U N
I N D I A N I N S T I T U T E O F R E M O T E S E N S I N G , D E H R A D U N
Spatial Relations
Spatial Relations
� Topological Relations: containment, overlapping, etc.
[Egenhofer et al. 1991]
A B
B
A
� Metric Relations: distance between objects, etc. [Gold and
Roos 1994]
A
1 Km
A B B
� Direction Relations: north of, south of, etc. [Hernandez et
al. 1990; Frank et al. 1991]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spatialdb-240227092055-c30634c7/85/SPATIAL-DB-IN-DATABASE-MANAGEMENT-SYSTEM-28-320.jpg)