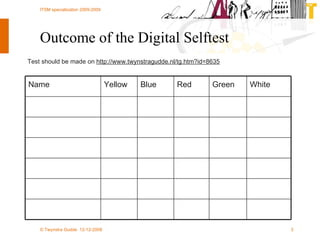
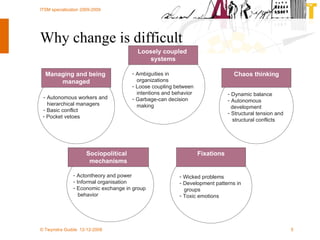
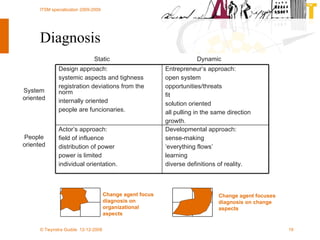
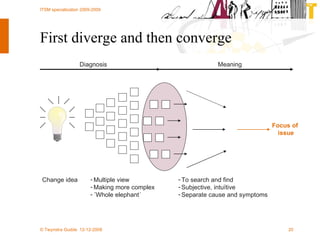
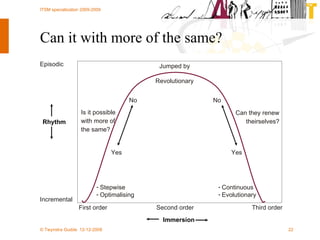
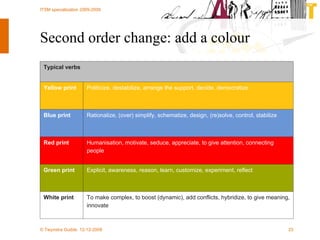
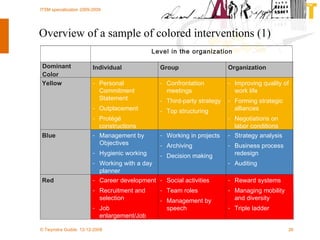
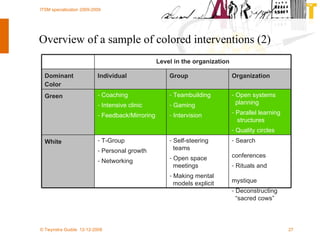
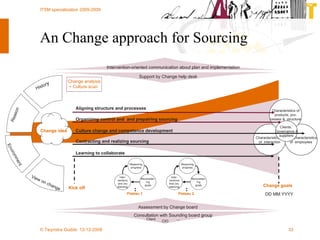
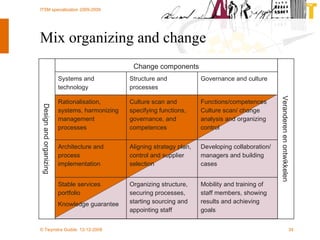
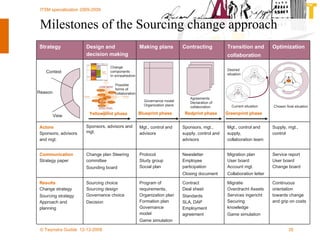
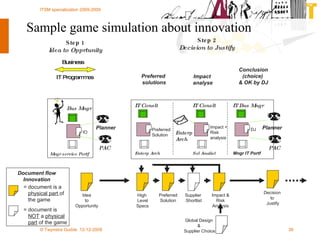
The document discusses various methodologies and frameworks for change management, focusing on five distinct approaches or 'colors' to understand and implement change effectively. It emphasizes the importance of tailoring change strategies to fit organizational needs and the various roles change agents play in this process. Additionally, it outlines a sourcing change approach that integrates technology, people, and organizational aspects for successful transformation.


























![All rights reserved. No part of this presentation may be reproduced or published in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Twynstra Gudde. Frank Willems [email_address] www.twynstragudde.nl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hg-itsm-sourcing-lecture-2-change-management-1230634222473243-2/85/Sourcing-Lecture-2-Change-Management-39-320.jpg)