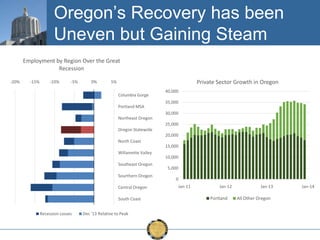
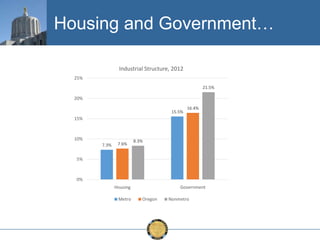
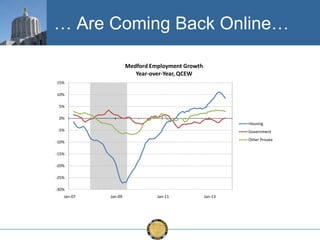
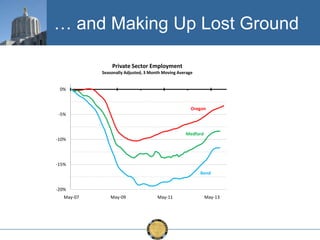
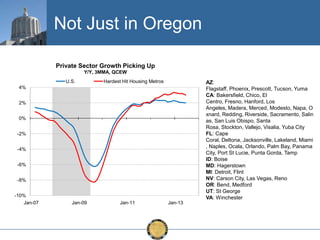
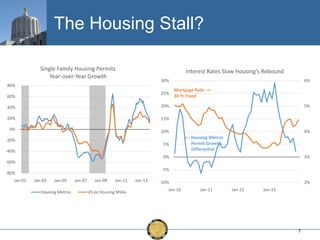
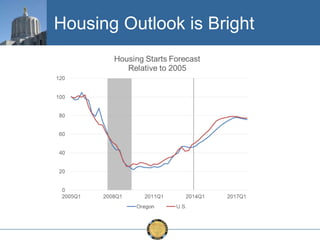
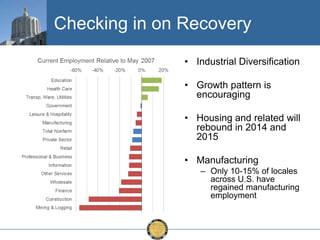
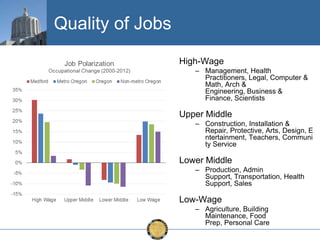
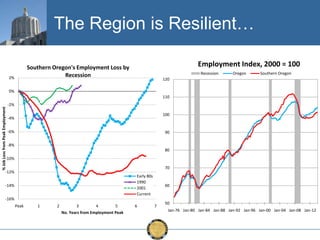
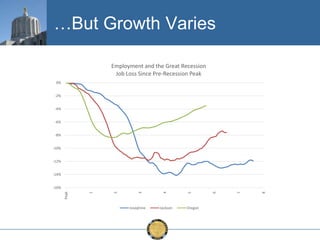
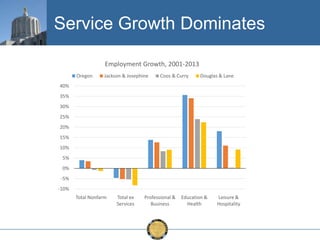
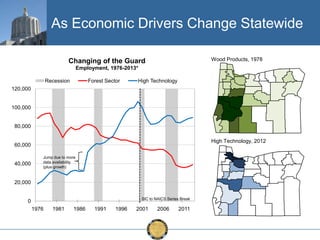
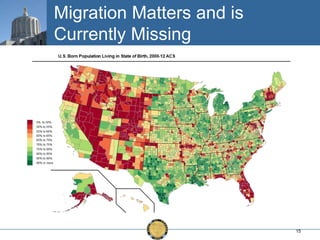
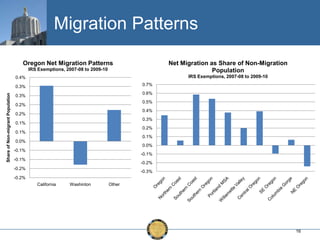
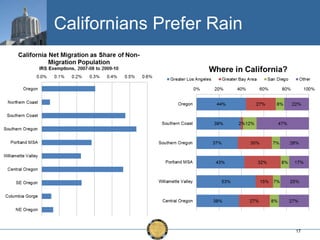
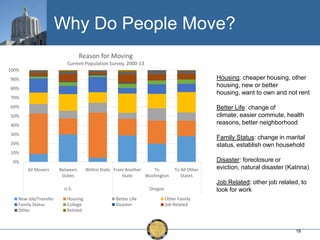
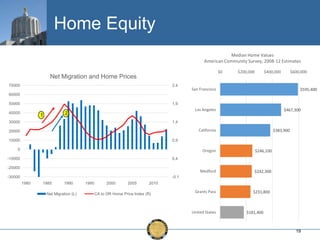
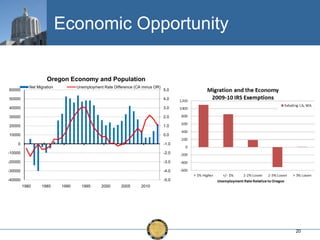
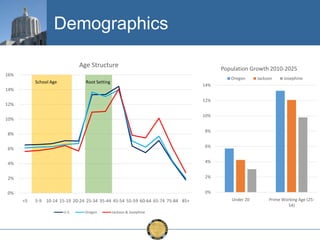
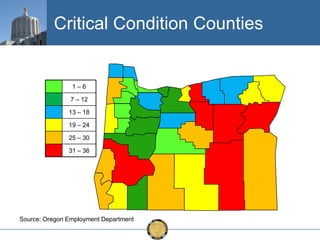
The document discusses the uneven recovery of Oregon's economy since the Great Recession, highlighting variations in employment growth across different regions, particularly Southern Oregon. It emphasizes the resilience of the region and anticipates a rebound in housing and related sectors in the near future, while also addressing challenges such as demographic shifts and public sector limitations. The overall outlook remains positive, with indications of industrial diversification and migration patterns supporting economic growth.