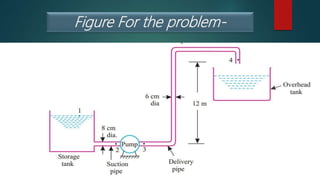
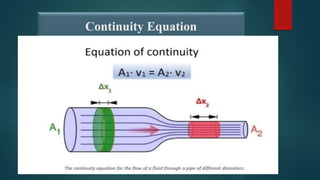
The document presents a fluid dynamics problem involving a pump drawing a solution through pipes with specific parameters. It calculates the pump's power rating and pressure developed using Bernoulli's and continuity equations. Key values include the pump efficiency at 65% and friction losses of 5.5 m.