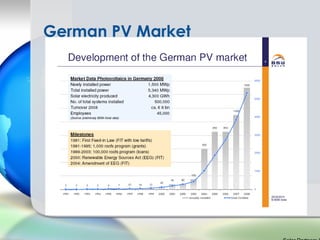
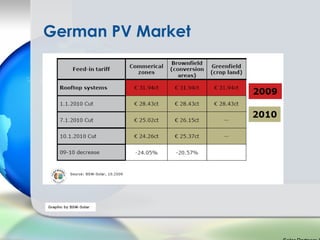
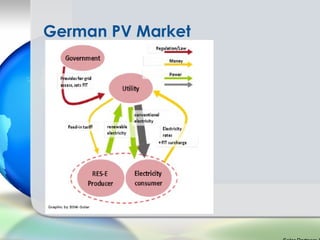
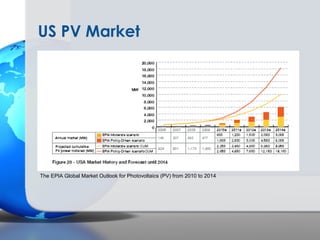
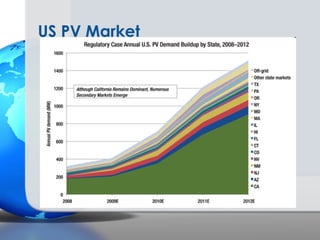
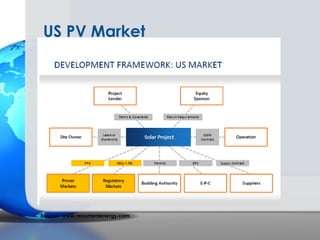
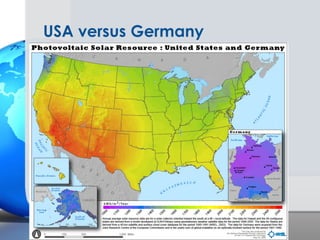
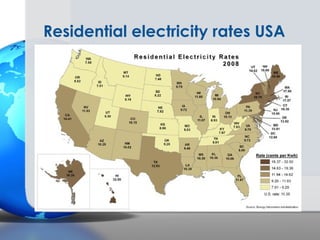
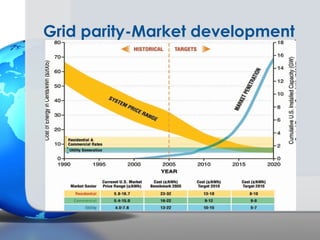
Germany has been a leader in solar PV installation due to its feed-in tariff (FIT) program which guarantees prices for solar electricity. However, FIT programs are very expensive for utilities and customers. The U.S. solar market is growing but faces challenges from inconsistent regulations across different states and grid access issues. As solar panel prices continue to fall and natural resources vary, the U.S. has long-term potential to become the largest market, especially in sunny states like California that are approaching grid parity sooner.