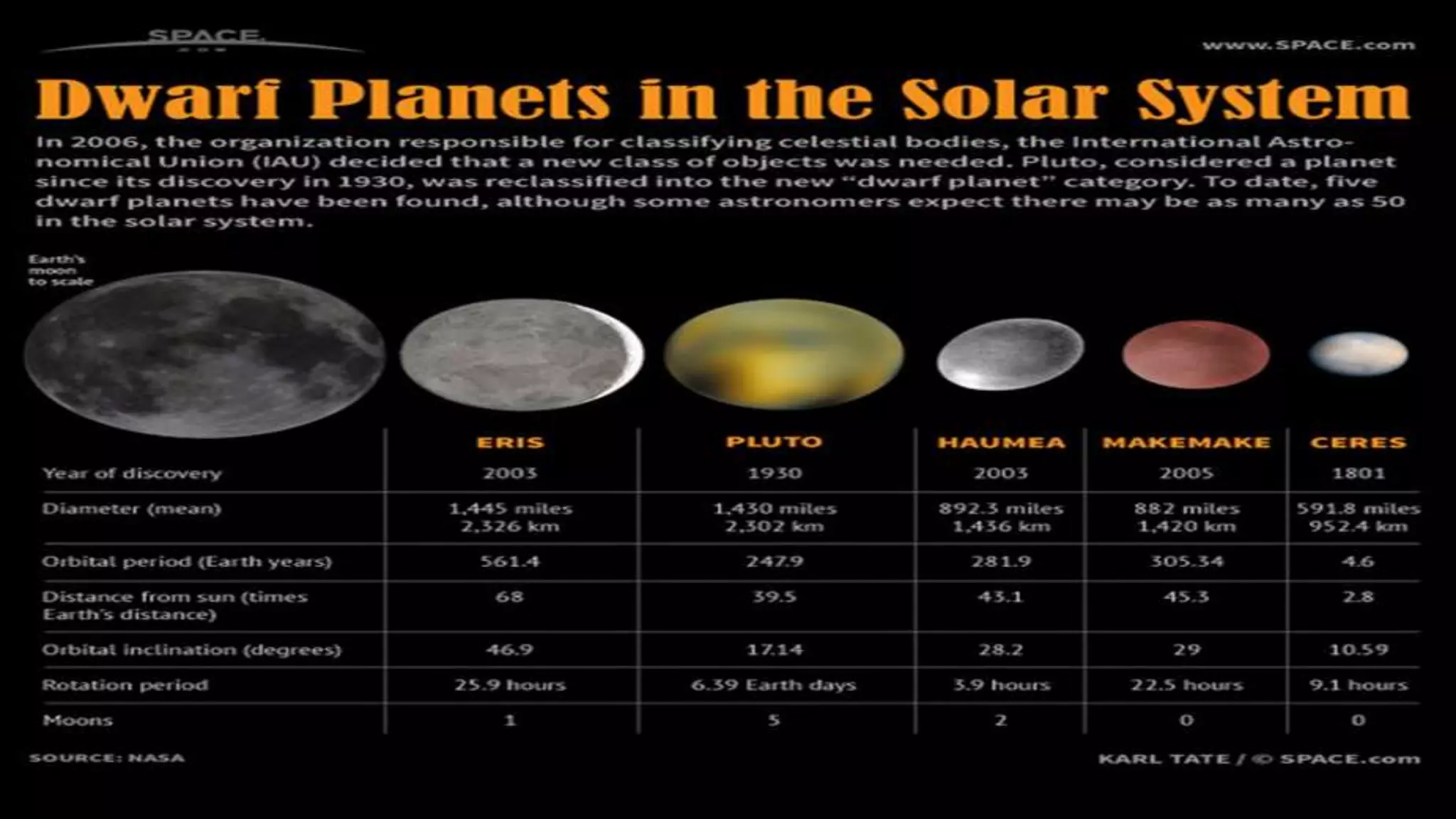
The document discusses the solar system, its formation, and the evolution of Earth, detailing the components such as planets, moons, asteroids, and comets. It explains the solar nebular theory regarding the formation of the solar system and Earth, highlighting significant geological and biological eras in Earth's history. The document also describes various celestial bodies, including natural satellites, dwarf planets, and the conditions necessary for life on Earth.