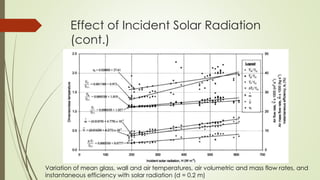
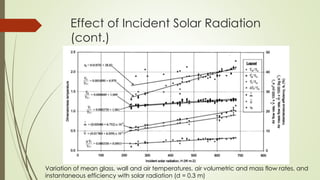
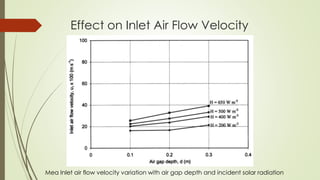
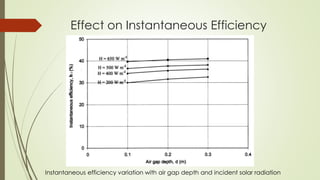
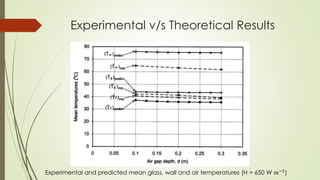
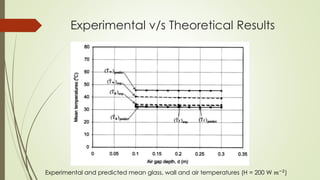
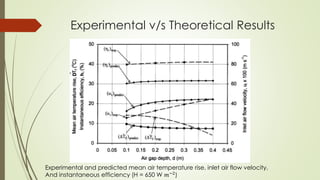
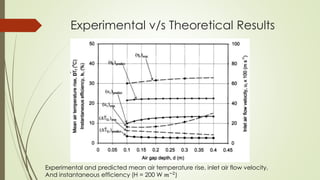
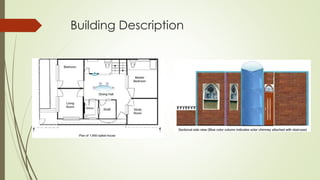
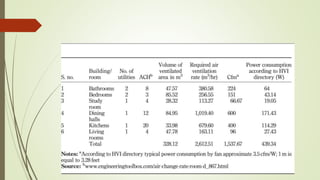
The document analyzes the performance of a solar chimney through experimental testing and theoretical modeling. It describes the working principle, types, advantages and applications of solar chimneys. Experimental results show mean air temperature, wall temperature, and glass temperature increase with increasing solar radiation and air gap depth. Air flow velocity and efficiency also increase under higher solar radiation levels. Theoretical predictions generally agree with experimental measurements, particularly for larger air gap depths. In conclusion, reverse air flow was not observed for gap depths up to 0.3m and experimental/theoretical results showed satisfactory agreement for large gaps.














![References
[1] K.S. Ong*, C. C. Chow, Performance of a Solar Chimney.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solarchimney-150927165530-lva1-app6892/85/Solar-chimney-37-320.jpg)
