This document provides an overview of software testing, including definitions, types of testing, and the software testing lifecycle. It defines software testing as a method to assess software functionality. The key points covered are:
- Software testing ensures software does what it's intended to do and remains functional after changes.
- Types of testing include unit, integration, system, and regression testing.
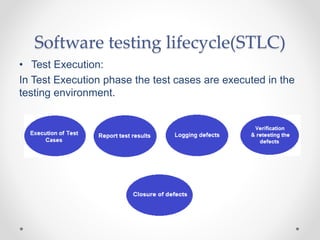
- The software testing lifecycle includes planning, developing test cases, executing tests, and closing test cycles.
- Cloud testing can reduce regression testing time by using virtualized hardware and software services.