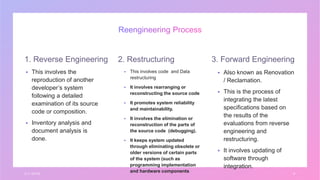
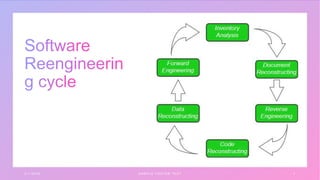
Software reengineering is defined as the process of updating existing software by adding additional features and functionalities to improve maintainability. It involves examining and altering legacy systems to create new versions that improve cost, quality, customer service, and delivery speed. The reengineering process consists of three main stages: reverse engineering to understand the system, restructuring through code and data changes, and forward engineering to integrate new specifications.