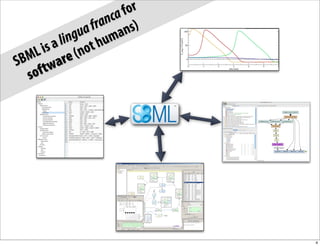
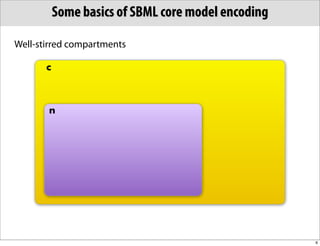
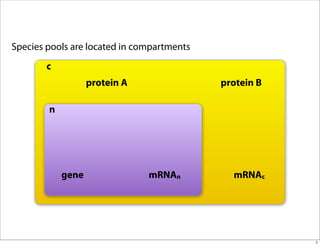
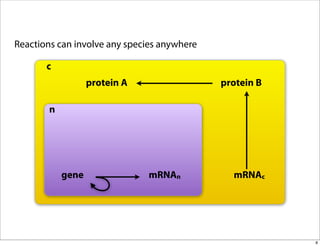
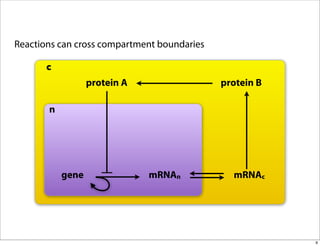
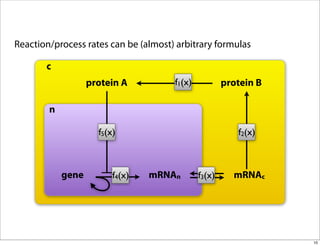
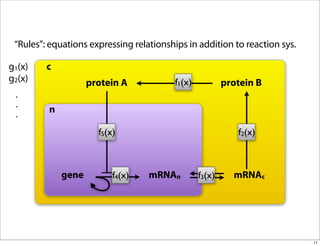
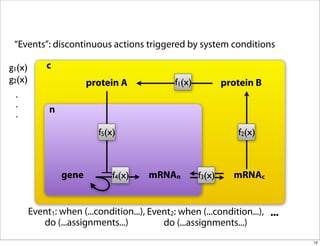
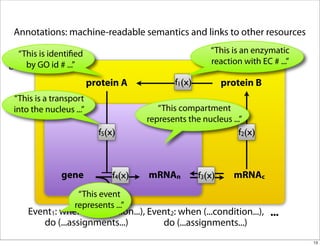
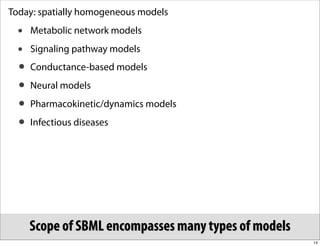
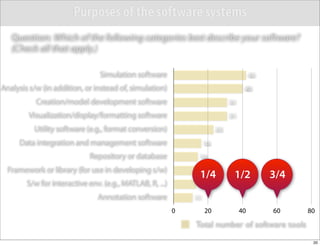
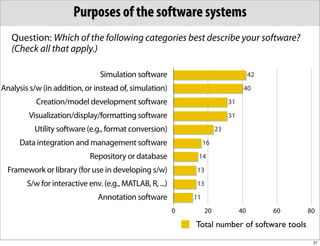
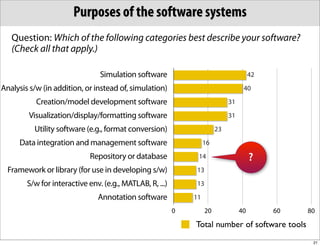
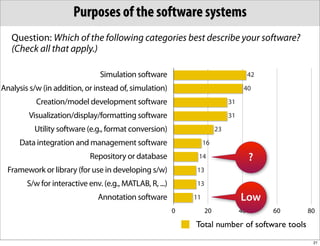
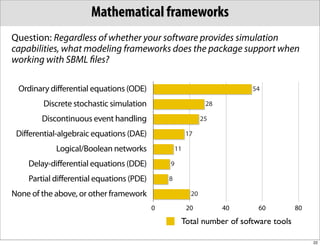
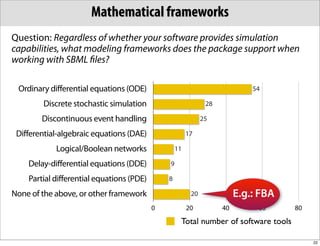
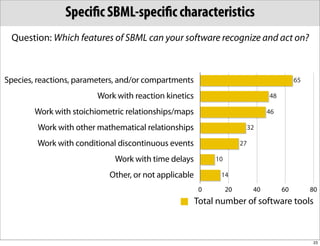
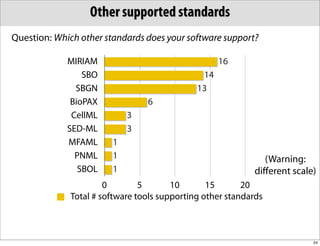
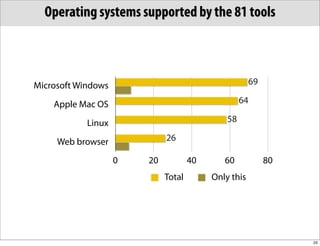
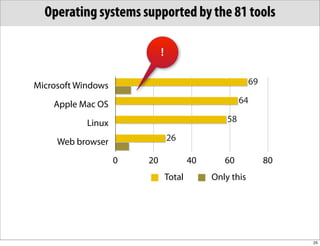
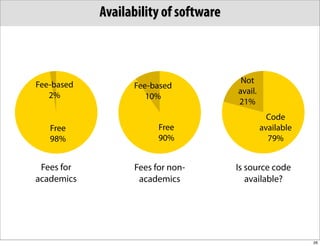
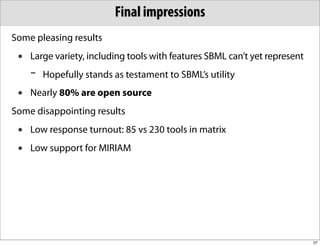
The document discusses the Systems Biology Markup Language (SBML), which is used for representing computational models of biological processes through a simple and flexible encoding system. It covers various aspects of SBML, including its modeling capabilities, software tools, features, and the types of models it supports, as well as the results of a survey on SBML software tools. Additionally, it highlights the diversity and utility of SBML and acknowledges the contributions of various funding organizations.