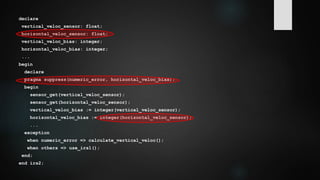
The document discusses several major software project failures and disasters including OS/2, Netscape, Ariane 5, the FBI Virtual Case File system, the 2003 Northeast Blackout, the WoW Corrupted Blood glitch, Knight Capital's $440 million trading loss, and common reasons why software projects fail according to the IEEE. Some key points are that OS/2 lost out to Windows due to marketing and ecosystem factors, Netscape's code rewrite took too long allowing Windows to dominate, type conversion errors destroyed the Ariane 5 rocket, and the FBI system was unusable after $170 million due to poor planning and requirements changes.