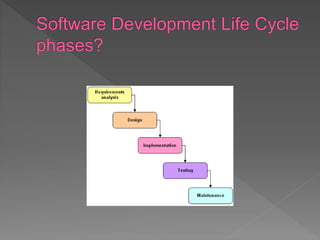
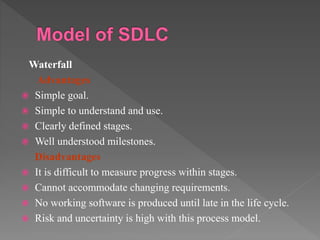
The document provides an overview of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), detailing its purpose, phases, and processes for developing high-quality software that meets customer expectations. It discusses the importance of requirements gathering, system design, coding, testing, and maintenance, and outlines different SDLC models, such as Waterfall and Agile, along with their advantages and disadvantages. The document highlights the need for effective management and adaptability in software development projects.