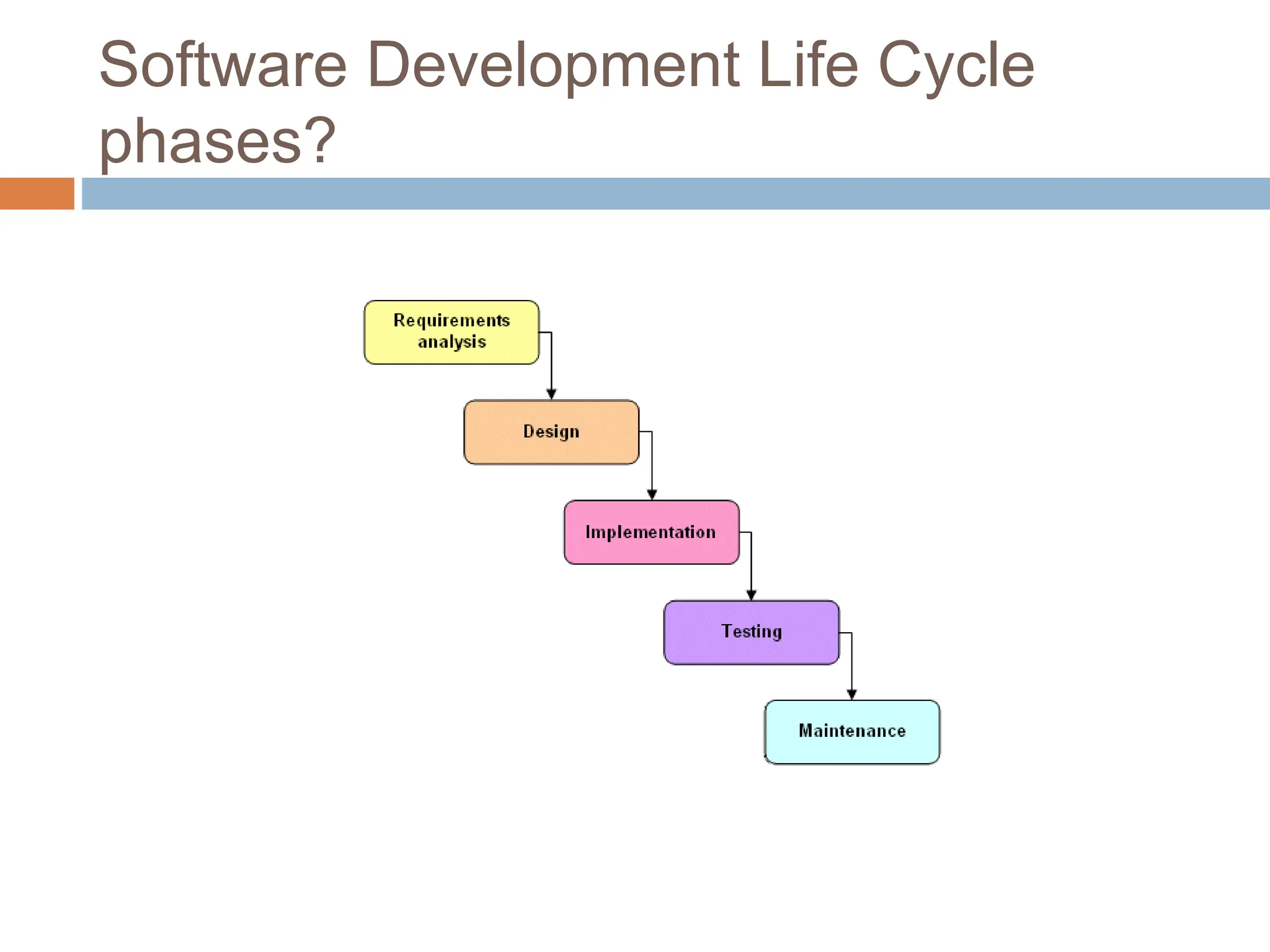
The document discusses the software development life cycle (SDLC), outlining its main phases and models. The SDLC is a framework that defines tasks performed at each stage of software development, from requirements gathering to maintenance. It aims to produce high-quality software that meets requirements. The document outlines several SDLC models - waterfall, incremental, evolutionary, spiral, RAD, and extreme programming - comparing their advantages and disadvantages. It concludes that the SDLC is a process of developing software through analysis, planning, design, implementation, integration, maintenance and testing.