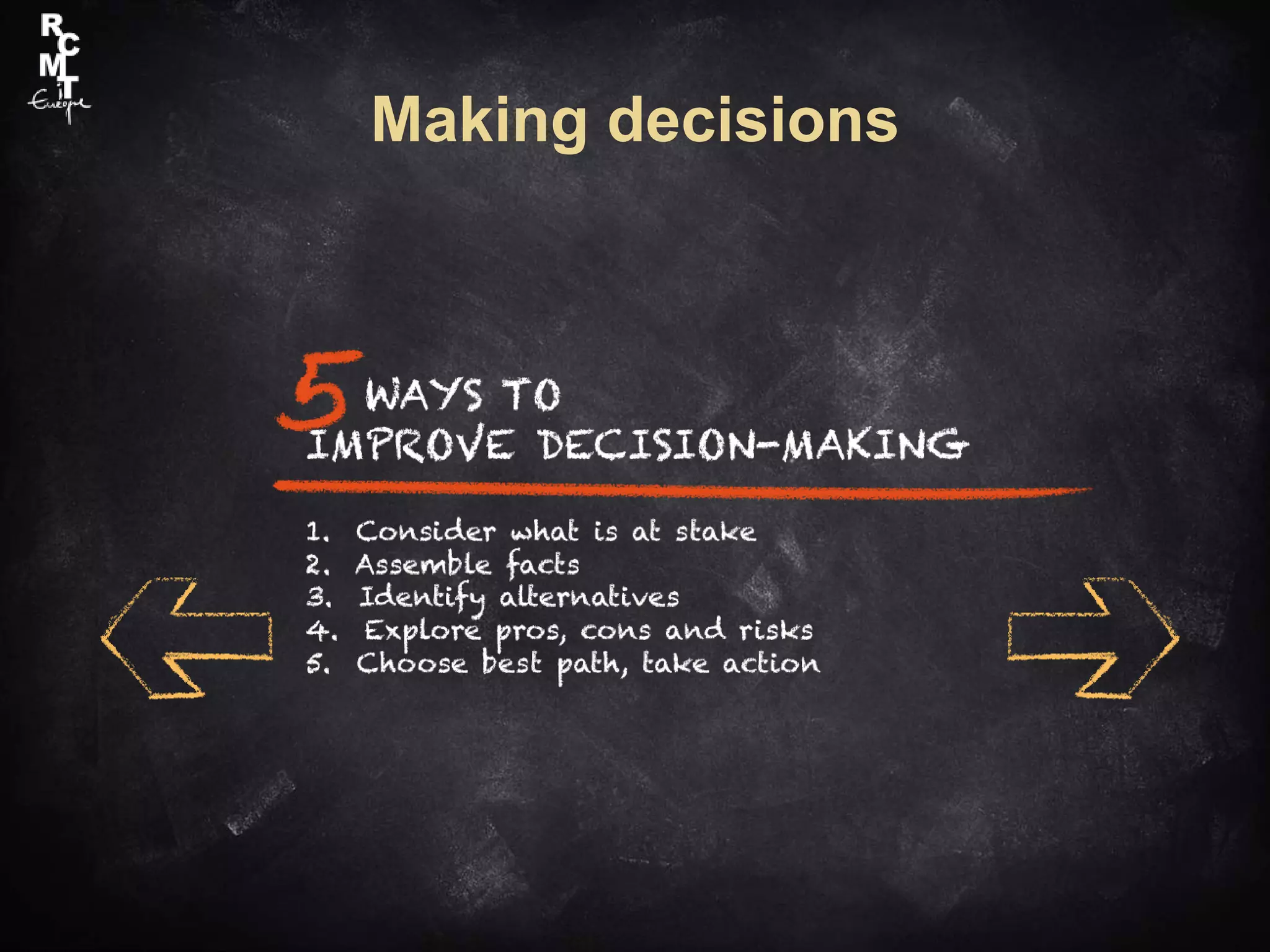
The document discusses the significance of soft skills, which refer to personal attributes that enhance emotional intelligence and interpersonal relations in professional settings. Key soft skills highlighted include communication, teamwork, leadership, creativity, and conflict management, stressing their necessity for securing and maintaining jobs. The document also emphasizes strategies for developing these skills and effective client interaction.