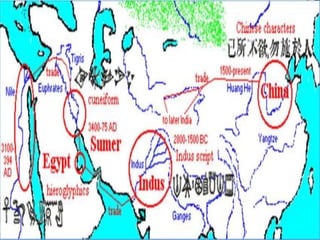
This document outlines the objectives and content of a lesson on the sociocultural and political evolution of human societies. It discusses the major developments from hunting and gathering societies through agricultural, civilizational, industrial, and post-industrial societies. Key points of focus include the transition to farming, the rise of the first civilizations in Mesopotamia and Egypt, the industrial revolution, and the shift to a post-industrial information economy. Students will analyze how technology and social organization changed at different stages of development and illustrate these transformations through a group activity.